
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Before you proceed with the SSO integration, make sure the following conditions have been met:
You must be logged into the Parallels My Account and have access to your organization’s business account, where the license key has been previously registered. See this chapter for more details.
You must understand what email domain(s) your end-users will use for SSO.
You must either have admin access to the DNS host(s) of the corresponding domain(s) to be able to add a verification TXT record(s) or be able to ask your IT service for assistance.
You must either have admin access, which enables you to configure enterprise applications in your IdP Directory, or be able to request support from the IT admin who has the required permissions.
Once the above requirements are met, proceed to the next step.
When you want to distribute pre-configured Windows virtual machines to your users, you may need to manage those machines granularly: enroll them into domains, activate Windows licenses, differentiate PC names, enforce specific policies, enable company-wide licensing tools, etc. All that and more can be achieved with the help of Microsoft's Sysprep utility. To learn more, refer to this article.
Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition can also be deployed to Mac computers using Mac management tools, including, but not limited to:
Jamf Pro
Microsoft Intune
Kandji
Apple Remote Desktop (ARD)
IBM Endpoint Manager
Mosyle
Addigy
Munki
VMware Workspace ONE
This chapter includes detailed instructions on how to deploy Parallels Desktop using Jamf Pro. For instructions on how to use other tools, please see their respective documentation.
To set up a Parallels Desktop update server, you'll need a local Web server. Install a Web server on a computer connected to your network (or use an existing one).
The corporate VM image policy is checked every time a new VM creation process is started by the user in Parallels Desktop on a Mac computer. If the corporate VM image policy is set (a configuration profile with the VM for Intel Mac or VM for M-series Mac payload exists and has been applied to the license key used by this Parallels Desktop installation), the Parallels Desktop Control Center displays a message inviting the user to download the corporate VM image. If the user accepts the invitation, the VM image download begins and the progress indicator is displayed (note that because of the large size of a VM, the download may take some time). If the user declines, he/she is taken to the Installation Assistant where they can create a virtual machine from scratch.
After the VM image download completes, the image is unpacked, and the virtual machine is registered in Parallels Desktop.
Integration between Parallels My Account and corporate Identity Providers (IdP) like Microsoft Entra ID, Okta, Ping Identity, JumpCloud, or Google Workspace enables Single Sign-On (SSO) login to Parallels My Account and automatic provisioning and revocation of Parallels product licenses to end users in your organization. The organization’s business account admins can log into using their company's standard authentication procedure, while the end-users can activate Parallels products on their devices via Single Sign-On.
Even if your organization does not use Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition, you may benefit from the SSO integration with My Account. Such integration provides more control over the users with administrative access to the Parallels product licenses stored in the organization’s business account registered with Parallels.
Warning: Once you have completed the integration process and activated the SSO functionality, only users from the Administrators group in your IdP signing in via SSO will retain access to managing the Parallels business account. All previous administrative privileges based on logins and passwords will become inactive.
Your designated backup login will continue to work.
Once the integration is configured, you can grant access to the organization’s business account to administrators by adding them to the Parallels Business Account Admins group in your Identity Provider’s directory. At the same time, deleting or blocking an administrator account in your Identity Provider automatically deprives them of access to Parallels My Account.
In this section, we provide detailed instructions on how to set up the SSO integration with Microsoft Azure/Entra ID, Okta, and Ping Identity. Even if your corporate identity provider is not on the list, you can still try setting up the integration, provided your service of choice supports SAML 2.0 and SCIM 2.0 protocols.
Once the integration is completed, the administrators will be able to sign into the company's My Account page using the Continue with SSO button at , while Parallels Desktop for Mac users will be able to activate their local copies of the app using the SSO option.
Below is the chart that outlines the setup process. Please note that the is optional.
Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition is a version of Parallels Desktop specifically designed for organizations with a large number of Parallels Desktop installations and virtual machines. Its main goal is to simplify the deployment, monitoring, and management of large, dynamic fleets of virtual machines in organizations with highly diverse needs.
The main feature of Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition that enables granular management is the Parallels Management Portal. Read about it in of the guide.
If your organization is subscribed to Parallels Desktop for Mac Business Edition and then decides to try the Enterprise Edition, you will need to contact your Parallels sales representative to receive a separate, time-limited trial key and add it to your Parallels My Account.
Once the trial ends and you decide to upgrade to Enterprise Edition, the recommended way forward is to contact your Parallels sales representative and convert a Business Edition license to an Enterprise Edition one.
Attention: If your organization's business account holds multiple Business Edition licenses, make sure to communicate clearly which one you want to be upgraded to Enterprise Edition.
In this scenario:
The Enterprise Edition trial license will be suspended;
The added during the trial will become available to the users of the new Enterprise Edition setup;
The policies created during the trial will be saved but not applied to any . You will have to reassign them.
[NOT RECOMMENDED] Technically, your trial Enterprise Edition license can also be converted to a long-term one, keeping your existing Business Edition setup intact, on the following condition:
✅ If your Business Edition license seats have been activated using the per-device/license key method, your trial Enterprise Edition license can be converted to a long-term one, albeit with much effort;
⛔ If your Business Edition license seats have been activated using the per-user/SSO method, your trial Enterprise Edition license cannot be converted to a long-term one, and you'll need to convert one of the existing Business Edition ones.
Creating a completely new setup with new sublicense keys and user groups and migrating your users to it is a daunting task, so we don't recommend this path.
If you have an existing Parallels Desktop for Mac Business Edition setup where end-users activate their copies of Parallels Desktop using Single Sign-On (SSO), you can concurrently trial the same setup on the Enterprise Edition. You will have to take the following steps:
Contact your sales representative using the details provided in Parallels and request a trial license key. If your My Account page does not mention a specific sales representative, use the Request Trial form on ;
Register the received key in My Account;
On the side of your organization's identity provider (IdP), register a new group and include in it trial users;
If your IdP supports group hierarchy, make sure the trial group is a child of the main Parallels enterprise app user group mapped in My Account as part of the (i.e., your mapping should be Parallels app registered with your IdP <- Parallels Desktop users group <- Enterprise Edition trial users group) and add the Enterprise Edition trial users to it;
Warning: For hierarchical setup to work correctly, theSAML token exchanged during the SSO authentication process must include the group identifiers for all the groups a user belongs to. See step (3) in the section of the respective chapter, as seen in Microsoft Azure/Entra ID.
Otherwise, connect the trial group directly to the Parallels enterprise application and make sure to include the trial users in the main Parallels Desktop users group as well (i.e., your mapping should be Parallels Desktop app registered with your IdP <- Parallels Desktop users group AND Parallels Desktop app registered with your IdP <- Enterprise Edition trial group), make sure to include trial users in both user groups;
Make sure the end users with trial accounts have activated their copies via SSO; Note: Activating end-user installations with SSO is not mandatory. Overall, Enterprise Edition supports mixing SSO activations and license key activations as you see fit.
Explore the capabilities.
This section describes how to mass deploy Parallels Desktop Business Edition using Mac management tools.
We recommend that you deploy Parallels Desktop for Mac using your MDM's , provision the activation method and PPPC settings using a , and rely on the to set the required and limitations.
Once your Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise License is registered in your Parallels Business Account, you can proceed to set up and configure your Parallels Management Portal where you can dynamically change user group policies and monitor virtual machines. Access it by clicking the following button:
Learn more about the Parallels Management Portal in of the guide.
When you purchase a Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition license, you must register it with a Parallels Business Account to be able to activate Parallels Desktop for Mac installations.
To create a Parallels Business Account, go to and select the I am a new user option. Once you log into your customer dashboard, follow the procedure described in of our Licensing Guide.
The information about your Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition license and setup will appear in your dashboard, and you can proceed with the deployment process.
Once you have added all the files to the package and in the deploy.cfg file, it's time to turn the resulting folder into a flat package suitable for deployment via your MDM solution of choice.
Do the following:
Inside the Autodeploy Package folder, locate the Scripts folder, right-click on it, and choose Services > New Terminal at Folder. This will open a Terminal window right in the Scripts directory where the build script is located.
Launch the package building script by typing the following command and pressing Enter:
E.g.,
This action creates a .pkg file in the destination folder that is ready for distribution.
By default, you can skip this step and allow the Autodeploy package to simply download the latest version of Parallels Desktop installation image from the Parallels Server.
However, if you wish to include a specific build in the package, open the Parallels Desktop DMG folder and copy the Parallels Desktop installation image file to it (the .dmg file). If you don't have the file, you can download it from .
The package should now look like this:
Please note that the Parallels Desktop installation image file name on the screenshot above is just an example. In your case, the file name will also include the current build number information.
This section explains everything you need to know to start using Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition as quickly as possible.
You can read about each individual step in the respective chapters of this section, but the overall outline is:
Register your license using your . Read more .
Your license must be registered to a Parallels Business Account before it may be used to activate Parallels Desktop. Registration is critical to:
Protect the ownership of your license.
Unlock features that make the lives of IT administrators easier.
Access Premium Support and get visibility into your open tickets;
Download the latest version of the Parallels Desktop ;
Install Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition, following one of the ways outlined in ;
Create and configure a virtual machine golden image, complete with all the required software and settings, and upload it to an accessible location that allows direct file links;
Deploy Parallels Desktop for Mac using one of the methods described in the ;
Make use of the main advantage of Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition, the Parallels Management Portal, as outlined in of the guide.
Should you experience any unexpected difficulties setting up Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition, contact .
If you would like us to improve or add a specific feature to the Parallels Management Portal, you can use our feedback form by clicking on the user icon in the top-right corner and selecting the Provide Feedback option. Just type in your request and hit Send, and our Product Management team will receive your idea via email.
This section describes deploying Parallels Desktop for Mac inside a prepared deployment package. It requires more work and care, so we recommend that you try the first.
Once your organization’s Parallels Desktop setup grows beyond a couple of dozen machines, the need often arises to manage them more granularly while relying less on manual procedures for things like setup, updates, and maintenance.
Thankfully, one of the main features of Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition is the Parallels Management Portal — your one-stop shop for setting up and controlling your entire fleet of Parallels Desktop installations and virtual machines.
This section of the guide deals with all the tasks that can be completed from the Management Portal, such as deployment, management, policy provisioning, and removal of virtual machines.
You can reach the Management Portal by clicking the respective button in your business profile or directly following this .
Note: When working with the Management Portal, make sure to select the Parallels business account with a Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition license registered to it.
Once your Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition trial period or license expires, Parallels will continue to store account settings such as policies and golden images, for 3 months.
When you need to change configuration settings of all virtual machines that are already registered on a Mac computer, you can use the Parallels desktop command-line interface. To do so, you first need to create a script to perform a desired configuration modification. You can then execute the script on a Mac computer using one of the remote Mac management tools described earlier in this chapter.
The following is a script example that disables the auto pausing option for all virtual machines registered on a Mac computer:
The script above uses the prlctl list command to first obtains a list of registered virtual machines and then (inside the loop) sets the --pause-idle option for every VM to "off", which disables pausing of an idle virtual machine.
The complete command-line reference is documented in the .
The Parallels Customer Experience Program is a feedback solution that allows Parallels Desktop to automatically collect usage statistics and system information that will help Parallels to improve the product's quality and support for popular configurations.







To mass deploy Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition, you will need the Parallels Desktop for Mac installation image file (.dmg) and a Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition license key or SSO setup.
You can download the installation image from here.
The Parallel Desktop autodeploy package is used to configure the deployment of Parallels Desktop. Download and prepare it for use as described here.
Please note that if you already have a configured autodeploy package from an earlier version (or build) of Parallels Desktop, don't use it because it may not be compatible with your build of Parallels Desktop. Always download the latest version of the package from the Parallels website using the link above.
If you are deploying one or more virtual machines together with Parallels Desktop, please keep in mind the differences in supported guest operating systems between Mac computers with Apple Silicon and Mac computers powered by Intel processors. For the latest information, see system requirements at https://www.parallels.com/requirements/.
If your organization's Macs run macOS Mojave or macOS Catalina, their users may need to approve kernel extensions before they can launch Parallels Desktop. For more information, please read the following KB article: https://kb.parallels.com/en/128435.
Once you have the Parallels Desktop autodeploy package configured, you can test it on a single Mac before you mass deploy it to other Mac computers in your organization.
To test the package:
Copy it to a Mac on which you want to test it. The Mac should have a configuration similar to other Mac computers on which you'll be deploying Parallels Desktop. Specifically, if your target Mac computers don't have Parallels Desktop and virtual machines installed, the test Mac shouldn't have them installed either. If target Macs have an older version of Parallels Desktop, the test Mac should have it installed too, so you can see what the results will be.
To speed up the execution of the package during testing, consider running it from the command line using /System/Library/CoreServices/Installer.app. When executed this way, the package will not be tested by macOS for digital signature, and the usual package verification procedure will be skipped.
Please note that if you run the package by double-clicking on it, macOS will warn you that the package is not signed and will not install it. If you run the package by right-clicking and choosing Open, the signature check will be skipped but the verification of the package will take a long time if you have one or more virtual machines in it (because of the large size of a typical virtual machine).
When you use the Installer.app to run the package, the installation will commence installing immediately, without any checks or verifications. All of the above only applies when you run the package manually. When you mass deploy it on Mac computers, verification is not performed, and the installation is completely silent.
When the installation is complete, verify that Parallels Desktop is installed, activated, and is functioning properly. If your package is configured to deploy Parallels Desktop in Single Application Mode, try running the application and see that it starts and runs as it should.
Please note that when the package is executed, it writes logs into /var/log/install.log. If you experience issues, examine the logs. If that doesn't help, you can contact Parallels Support for business customers which is available 24/7.
Read on to learn how to mass deploy the package using one of the Mac management tools.
To prepare the autodeploy package, you need to add the following required and optional components to it:
Parallels Desktop installation image (optional).
Parallels Desktop Business Edition license key (required, unless you are using "Activation using corporate account (SSO)").
One or more virtual machines (optional). The user can later install or download a virtual machine via the link in a configuration profile.
One or more Windows application stubs (optional). Stubs are special links to Windows applications installed in a virtual machine that can be added to the Dock in macOS during deployment.
You can also configure deployment options according to your needs by modifying the configuration file included in the autodeploy package.
You will have to take the following steps:
Download the Autodeploy package, which comes in a ZIP format.
Unarchive it.
[OPTIONALLY] Populate the folders with specific installation images and virtual machines.
Set the deployment preferences to your liking by amending the deploy.cfg file.
Transform the resulting folder into an installable package ready for deployment.
The subsequent sections describe how to add the necessary components and how to configure autodeploy package options.
Instead of preparing deployment packages, many modern MDM solutions allow you to deploy known apps via their built-in app catalogs.
This method, however, requires you to accompany the pre-existing Parallels Desktop installation package with a configuration profile containing a specific license key or an instruction to activate the app via Single Sign-On.
Some of the MDM solutions like Jamf Pro already have preconfigured profiles for Parallels Desktop for Mac. In case your preferred MDM solution does not, the next easiest way to achieve that is to use iMazing's Profile Editor app.
A configuration profile with licensing information will persist on target Macs and help you keep your users' copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac activated even through a complete reinstallation (if you include a licensing key in it) or force an SSO sign-in window to pop up at the restart (if you set SSO as the default activation method in the profile). Having a pre-installed licensing profile (preferably protected from removal) will prevent a user of Parallels Desktop for Mac 20.3.0 or newer from activating their copy of Parallels Desktop for Mac with another key.
When preparing a source virtual machine for mass deployment, you may change any of its configuration settings to fit your needs. The following list describes a few common options:
CPU & Memory. Beginning with Parallels Desktop 17, you can configure a virtual machine to select CPU and memory settings automatically depending on the available hardware resources. This option is preselected for all new virtual machines. To ensure it is selected, open the virtual machine configuration, and select Hardware > CPU & Memory. In the right pane, check that the Automatic option is selected.
Shared Folders and Profiles. Parallels Desktop offers great flexibility in bridging the capabilities of macOS and your guest operating system by configuring shared folders and profiles. Think over which files and folders you wish to share between the two operating systems and set them up beforehand.
Enforce USB Device Policies. Specify what types of USB devices can be connected to the virtual machine. See Enforcing USB device policies for complete details. Note: With Parallels Desktop for Mac 26.1 or newer, some virtual machine settings, including USB device policies, can now be controlled centrally using the Management Portal. Read more here.
Installing Applications. You can install all the necessary applications in the virtual machine before deploying it.
For the complete information about Parallels virtual machine configuration, please refer to the Parallels Desktop User's Guide.
This section contains instruction on how to deploy the Parallels Desktop autodeploy package using the following solutions:
Note: In some cases, when deploying the Parallels Desktop autodeploy package on a computer running macOS Catalina or later, you may get an error message saying, "Parallels Desktop Autodeploy.pkg cannot be opened because the developer cannot be verified". To work around this issue, please do the following. Once you have prepared the autodeploy package (but before you deploy it), right-click on the package and select Open from the context menu. In the dialog that opens, click the Open button and wait until macOS completes the file verification. Once the file is verified, use the deployment tool of your choice to deploy the package. See also https://kb.parallels.com/124989
In Parallels Desktop for Mac Business and Enterprise Editions, configuration profiles are sets of parameters that can be applied remotely to a Parallels Desktop installation. Configuration profiles can be used to enable and configure the following functionality in Parallels Desktop for Mac Business Edition:
Provisioning a corporate virtual machine image
Enabling major version upgrades
Attention: In Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition, configuration profiles are being replaced by images provided, and policies managed via the Parallels Management Portal.
At the time of writing, the only scenario in which you may need to apply configuration profiles to an Enterprise Edition setup is when you have more than two virtual machine images (e.g., not just Arm/Intel versions of a Windows machine but also Linux machines, etc.). This will change later as we develop the Management Portal functionality further.
Learn more about managing your Enterprise Edition setup via the Management Portal here.
Configuration profiles are created in an organization's Parallels business account. You must be the administrator of the account to create and manage configuration profiles. License administrators (admins who are allowed to manage specific licenses) cannot manage configuration profiles.
Payloads in a configuration profile contain settings specific to a particular functionality. For example, the VM for Apple Silicon Mac and the VM for Intel Mac payloads allow you to configure virtual machine image provisioning, while the Product Updates payload allows you to manage Parallels Desktop updates. The configuration profile itself is created and configured the same way, regardless of which of its payloads are configured and enabled.
A configuration profile can have one or more payloads configured and enabled. For example, you can configure and enable a particular payload in one profile and a different payload in another profile. This allows you to enable one functionality for one group of users and another functionality for a different group (see below how configuration profiles are applied to Mac computers). You can create as many profiles as necessary.
Configuration profiles are applied to registered Mac computers based on a license or sublicense key that computers are using to run Parallels Desktop. After you create a configuration profile, you need to apply it to one or more license or sublicense keys in your subscription. By doing so, you are essentially applying the profile to Mac computers on which Parallels Desktop was activated using that license key.
The rest of this part of the guide describes how to:
Create a configuration profile
Apply the configuration profile to a license or sublicense key
Configure individual payloads
Starting from Parallels Desktop 18, the Activation using corporate account (sometimes referred as SSO activation) option became available.
This option works best for Medium and Enterprise size organizations that have an identity provider (e.g., Entra ID) and rely on it to automate applications license management routines. With SCIM integration (optional) licenses from contractors and people who left the company and removed from the identity provider directory will be automatically revoked. There is also an option to automatically revoke licenses from people who are not using the product for a long time.
The license key is also not used in this scenario, so there are less chances for it to be misused.
There are three major steps to enable this option:
This option works only if you purchased a special license type. Please check your license certificate for details and contact your sales representative if you have questions. Note: The minimum purchase for this license type is 50 licenses and it is not available as an online purchase from the website.
IT team has to setup integration between your identity provider (Entra, Okta, Ping Identity, or others that support SAML 2.0 and SCIM 2.0) and Parallels My Account, following the instructions in this section of the guide. At this step, you may also want to consider dividing your Parallels Desktop users into user groups. If there is no guide for your identity provider, it is recommended to follow the one for Entra ID.
To provide your employees with the best user experience use the deployment capabilities described in this guide or simply share this link with users: https://parallels.com/directdownload/pd?experience=sso.
This chapter describes features that are specific to Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition.
We expect many Enterprise Edition users to upgrade from our previous flagship version, the Business Edition.
The Enterprise Edition differs in the deployment and management procedures, with a particular emphasis on the new Management Portal, which enables you to apply and quickly change policies to groups of Parallels Desktop users and control and monitor Parallels Desktop virtual machines in your environment.
You can convert your existing Parallels Desktop for Mac Business Edition setup to an Enterprise Edition one by contacting your Parallels sales representative for purchase and further instructions. Make sure to communicate to them whether your setup uses per-device or per-user licensing, as the upgrade procedure differs slightly between these two setup types.
It is important to know that converting your Business Edition license to an Enterprise Edition one will not require you to reactivate your existing installations, move users to new groups, or redeploy your existing setup.
Once you convert your license to Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition, your local Parallels Desktop for Mac installations will retain their assigned security policies until you set up different policies using the Management Portal, following this section of the guide.
Asset tags help identify, control, and track computer assets in an organization. Parallels Desktop for Mac Business Edition provides the ability to set an asset tag in the virtual machine BIOS, which can then be read using the standard tools of the guest operating system. You can set an asset tag using the Parallels Desktop graphical user interface or the prlctl command line utility that comes with Parallels Desktop.
To set an asset tag using the Parallels Desktop GUI:
On the Parallels Desktop menu bar, select Actions > Configure to open the virtual machine configuration dialog.
Select Business.
Use the Asset tag field to specify the desired tag.
To set an asset tag using the prlctl command line utility, use the following syntax:
prlctl set ID|name --asset-id tagwhere ID|name is the virtual machine ID or name, and tag is the asset tag to set.
To obtain the asset tag in Windows, use the WMIC.exe command:
WMIC SystemEnclosure get SMBIOSAssetTagFor the complete syntax of the WMIC utility please see the Microsoft documentation.
Once set, the asset tag never changes. Even if you perform such virtual machine operations as cloning, template manipulation, registering, or any other, the asset tag always stays the same. If you do want to change an existing asset tag for any reason, you can do it manually using of the methods described above.
With Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition, you can set up a local update server on your network from which Mac users can get Parallels Desktop updates. Updates are released periodically to improve the performance and reliability of Parallels Desktop. To reduce Internet traffic when downloading updates, you can set up a local update server, download the available updates to it, and then set up individual Macs on your network to take the updates from it instead of the Internet. Read on to learn about setting a local update server.
Beginning with Parallels Desktop 16 for Mac Business Edition, IT administrators have an option to provision a corporate Parallels Desktop virtual machine image from a link that they specify in Parallels My Account.
Here's a quick overview of how this functionality works:
An administrator first creates a Parallels virtual machine image with the operating system installed. The virtual machine will serve as a corporate VM image to be deployed on users' computers to run Windows applications used in the organization.
The virtual machine is then saved as an archive (ZIP or PVMP, we'll talk about archive formats later) and is placed on a server from which Parallels Desktop users can download it to their computers via HTTP or HTTPS.
The administrator creates a configuration profile in Parallels My Account and specifies the download URL of the virtual machine image (together with other required parameters).
When a Parallels Desktop user initiates the process of creating a new virtual machine, Parallels Desktop checks if a configuration profile with the VM image link exists and is applicable to the Parallels Desktop license key used by this Mac computer. If the profile exists, a dialog is shown to the user, inviting them to download and install the corporate virtual machine image. If the user accepts, the virtual machine is downloaded to the user's computer and is registered in Parallels Desktop.
The subsequent sections describe how to perform the steps above.
If a virtual machine user forgets the password of their guest OS account (e.g. a Windows user password), it can be reset outside the virtual machine using the command line interface.
To use this functionality the following conditions must be met:
Parallels Tools must be installed in the guest OS.
The virtual machine must be running. If it's stopped, start it and wait until you see the guest OS login prompt.
Depending on your requirements, the following option can be selected or cleared in the virtual machine configuration dialog: Security > Require Password to: [ ] Change guest OS password via CLI. If this option is selected, you will be asked to provide the macOS administrator password to change the guest OS password from the command line. If the option is cleared, the administrator password will not be required. By default, the option is cleared.
To reset the password, open Terminal and enter the following command:
prlctl set vm_name --userpasswd username:new_passwordwhere:
vm_name is the virtual machine name. To obtain the list of virtual machines installed on this Mac, type prlctl list.
username is the guest OS user name.
new_password is the new password.
Example:
prlctl set My_Win8_VM --userpasswd JohnDoe:A12345If the Require Password to: Change guest OS password via CLI option is selected in the virtual machine configuration dialog (see above), the command will display the following text and prompt:
Only host administrator can change user password in the guest OS.
Confirm your administrator credentials.
Username:Enter the name of the macOS user with administrative privileges and press the Enter key. Type the user password and press Enter again.
Once the new password is set, you can use it to log in to the guest OS.
Parallels Tools is a collection of utilities and drivers that vastly improve the virtual machine performance and enable some features that are not available otherwise. Parallels Tools are included with every copy of Parallels Desktop and are highly recommended to be installed in every virtual machine right after an operating system is installed in it. Your source virtual machine should have Parallels Tools installed. For instructions on how to install Parallels Tools, please see https://kb.parallels.com/en/115835.
By default, Parallels Desktop Business and Enterprise Edition downloads updates from a special location on the Parallels website dedicated to hosting Parallels Desktop Business and Enterprise Edition updates. Parallels Desktop Standard and Pro editions download their updates from a different location. As an administrator, you have an option to choose the location from which Parallels Desktop Business or Enterprise Edition downloads updates. The reason why you would want to do this is explained below.
When Parallels Desktop updates are released by Parallels, they become immediately available for Parallels Desktop Standard and Pro Editions. Updates for Parallels Desktop Business and Enterprise Edition are released at a slightly later date (from a few days to 1-2 weeks from the initial release). The delay is necessary for additional testing of business features of Parallels Desktop to ensure they meet the highest quality standards. During this period, we even give an updated version of Parallels Desktop to some of our corporate customers,who test and evaluate it in their real-world environments.
We recommend that you use the default configuration and download Parallels Desktop Business/Enterprise Edition updates when they are finalized and available for download. However, if for any reason you don't want to wait, you can configure Parallels Desktop Business or Enterprise Edition to download updates from the Parallels Desktop Pro location. The updates are the same regardless of where you download them from. The only difference is, the updates downloaded from the Parallels Desktop Pro location will have not been fully tested in a business environment.
When you mass-deploy Parallels Desktop, you can set the desired Software Update options in the deployment configuration file. Mass Deployment of Parallels Desktop is described later in this guide. For more information, please read the entire Mass Deployment chapter and specifically the Configuring Deployment Options section. Look for the Software Updates section in the parameter table.
If you need to modify Parallels Desktop software update options on a specific Mac without using the Mass Deployment procedure, you can do this as described below.
To configure Parallels Desktop to download updates from the Parallels Desktop Pro location, execute the following command on a Mac:
defaults write com.parallels.Parallels\ Desktop.plist Application\ preferences.VolumeLicenseUpdatePolicy https://update.parallels.com/desktop/v20/parallels/parallels_sbscr_updates.xmlThe command above writes the specified URL (the parameter in the second part of the command) into the Parallels Desktop plist file. Please note that the "v20" part of the URL indicates the current Parallels Desktop version number. If you are using a later version, substitute this part with the correct number.
To switch back to the default Parallels Desktop Business/Enterprise download location, execute the following command:
defaults write com.parallels.Parallels\ Desktop.plist Application\ preferences.VolumeLicenseUpdatePolicy ParallelsYou can set an expiration date for a virtual machine. This can be a useful option if you are preparing a virtual machine for a contractor (or a third party user) and want to make sure that it works only for the duration of the contract.
To set an expiration date for a virtual machine:
Open Parallels Desktop and select the desired virtual machine.
On the Parallels Desktop menu bar, select Actions > Configure to open the virtual machine configuration dialog.
Select the Security tab.
An expiration date can only be set on an encrypted virtual machine. If your machine is not yet encrypted, click Encryption: Turn On, specify an encryption password, and click OK. Make sure to record the password or you will not be able to start the virtual machine. Wait until the encryption process finishes.
To set an expiration date for the virtual machine, click Expiration Date: Set Date, specify a password and click OK. Make sure to record the password to be able to change the expiration settings later. You should keep this password secret to prevent the prospective user of the virtual machine from changing the expiration date.
On the next screen, specify the following options:
Do not allow this VM start after: specifies the virtual machine expiration date.
Contact info: specifies the system administrator email, phone number, or other contact information. This information will be included in the message that will be displayed to the user when the virtual machine is about to expire. You can include each piece of information on a separate line.
Time Server: specifies the time server URL. The virtual machine expiration time will be checked against this server. The default time server is https://parallels.com.
Date Check Frequency: specifies how often the date and time should be verified against the time server. You can specify it in minutes, hours, or days.
If unable to check date, use VM for: specifies for how long the virtual machine should be kept working if the time server cannot be reached. For the duration of this period, the virtual machine will continue to check the date. If it succeeds before this period is over, the counter is reset, and the virtual machine will continue to work normally.
Click OK when done entering the expiration info.
To modify the current expiration date or password, click Expiration Date: Change Date or Expiration Date: Change Password and enter the new values.
When the expiration date approaches, the virtual machine user will be notified as follows: a message will begin to be displayed seven days before the expiration date. The message will be shown to the user every 24 hours and additionally on every virtual machine startup. Once the date is reached, the virtual machine will be locked, so the user will not be able to start or resume it anymore.
./prepare --dest {Destination_folder}./prepare --dest /Users/{user_name}/Downloadsfor i in $( prlctl list -a --info | grep "ID" | sed 's/.....//;s/.$//' ); do
prlctl set $i --pause-idle off
done
In large organizations with multiple Macs, there may be groups of Parallels Desktop users with very different needs in terms of capabilities and restrictions, from a software engineer who develops for multiple platforms and needs a dozen virtual machines to test every possible scenario to a back-office staff who would benefit the most from Single Application Mode.
The best way to maintain flexible arrangements is by dividing users into groups, each of which would require a sublicense. To create a sublicense, follow these steps:
Warning: If you plan on activating your end users' copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac with license keys on a per-device basis, we strongly recommend against sending out your primary license key to your end-users directly. We recommend employing the Invite Users function which generates unique keys for each invitation email, or creating and sharing additional sublicense keys.
Go to Parallels My Account and select Dashboard in the top-right corner.
In your Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition card, click on the Subscription Details line.
Scroll down to the License Keys card and click Create License Key in its top-right corner.
Click on the key name at the top and change it to reflect the name of the group.
Assign a certain number of Parallels Desktop installations available with this license key, select the key type, and click Save. To learn more about the differences between Dynamic and Reserved keys, see in our Licensing Guide, specifically the section.
If you want your users to activate their copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac using license keys, you could send them invitations to activate, which will contain automatically generated individual activation keys (derived from the respective sublicense keys). To do that, use the Invite Users button on the product card in Parallels My Account.
If your organization uses an identity provider (e.g., Microsoft Azure/Entra ID or Okta), and you want your users to activate their copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac using Single Sign-On, refer to this section of the guide.
Irrespective of their activation method, dividing users into groups will let you benefit from things like custom policies and restrictions.
Single Sign-On (SSO) is one of the options offered for activating Parallels Desktop for Mac. Users who choose this option will see a window that looks like this:
Some users might skip this dialog by clicking Cancel. In this case, you can instruct them on how to re-start the SSO-based activation procedure manually. To start the SSO-based activation:
In the application's menu, choose Parallels Desktop → Account & License... and select the Continue with SSO option.
Note: Users SHOULD NOT enter their corporate login email and password directly on the Sign-In to Parallels Account dialog. They are supposed to log in to their corporate account managed by the Organization’s IdP, not to a Parallels account!
On the Sign-In to Parallels Account dialog, clicking Business Edition (at the bottom of the dialog, on the left) opens the Activate Business Edition dialog.
On the Enter Enterprise Key dialog, clicking Continue with SSO (at the bottom of the dialog, on the left) opens the dialog, which prompts the user to enter the corporate email address. This is where the product activation procedure via Single Sign-On starts!
Users should type their corporate email address in the popup dialog that is opened by clicking Continue with SSO, then click Next.
Attention: If a particular user's account still won't activate using SSO, go back to your Identity Provider's settings and make sure that the user is included in the main user group for Parallels Desktop, as described in the SSO integration setup procedure.
There are three main ways to install Parallels Desktop: fully manually, manually via email invitations, and as part of a mass deployment procedure.
As an organization, you can choose what type of license activation you want to use: a per-device one where you activate each individual installation with a product key, a per-user one that requires signing in with SSO, or a mix of the two which Enterprise Edition also allows.
To learn more, we suggest that you read .
Download the installation image from here;
Use a license key from the My Account admin dashboard to activate.
Note: We strongly recommend to use secondary sublicense keys for this type of installation and not sharing your primary license key with end users.
You can invite users to install Parallels Desktop directly by sending out invitation emails. Do the following:
In your My Account dashboard, go to the Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition card and click on Invite Users;
Choose one of the license keys/subkeys available for the product and click Next;
Fill out the fields in the invitation window:
Choose the language of inviation;
Set the expiration (between 3 days and 1 month);
Add individual email addresses to the group using the Add button, or use the Select File button to add a CSV list instead;
Click Send Invitations.
As a result of this procedure, your users will receive an email that looks like this:
To learn about the mass deployment procedure using MDM solutions, refer to this section of the guide.
Follow the instructions to begin the process of configuring SSO integration in Parallels My Account:
Log into your Parallels account using your email address and password (but not using the Continue with SSO option). We recommend that you use your corporate email address and a password that is different from your main one. Go to the Dashboard page, and make sure that your business account is selected as the current workspace in the top-left corner.
Click the Business Profile item in the business account navigation menu (top-right corner).
Once on the Business Profile page, choose the SSO menu item in the top-right corner to open the IdP Integration configurator page.
When on the IdP Integration configurator page, click Start Configuring to begin setting up the integration between the Parallels My Account service and your identity provider. You will have to complete the configuration in 7 steps. Each step is represented on the page by a separate list item. Uncompleted steps are marked as gray, and the successfully completed ones become green. The configuration process is successfully completed when all seven items on the list are marked green.
Start with Step 1 (Configure Your Organization's Domain(s)), then continue until all seven steps are completed. Click on the title of each step’s section to expand it, and follow the instructions provided. The SSO integration will not start working until all the steps are complete. However, completing all steps at once is not mandatory—you can interrupt the process at any time and continue later. The information entered at the previous steps persists between sessions. Read the sub-chapters in this section for step-by-step setup guides specific to one of the officially supported IdP providers. If your provider is not on the list but supports SAML 2.0 and SCIM 2.0, we recommend referring to the steps described in the Entra ID sub-chapter and applying them according to your IdP's documentation.
When all configuration steps are completed (marked green), the Activate Integration button becomes available at the top of the page. Click the button to activate the integration between Parallels My Account and your Organization’s IdP. You can deactivate the integration anytime by clicking the Deactivate button at the top of the page.
Once the above steps have been completed, proceed to the respective chapter that covers integration with your IdP provider.
Parallels Desktop Control Center is a part of the Parallels Desktop graphical user interface. It's a window from which a Mac user launches virtual machines. By default, the Control Center displays the list of the available virtual machines, as in the following example:
You can customize the Control Center by specifying a URL to your own HTML document, which will be embedded at the top of the Control Center window. The HTML page can contain text, graphics, and links such as your company logo, custom text, a link to a support page, etc. The HTML document format doesn't have any specific requirements.
The URL must be specified during the preparation stage of the Mass Deployment process. Specifically, you need to specify the URL and the HTML page size using the following variables in the mass deployment configuration file (deploy.cfg):
control_center_banner_url
control_center_banner_height
control_center_banner_min_width
For a description of how to specify the values, please see Configuring Deployment Options. The variables are described in the Virtual Machines section.
The following is an example of Parallels Desktop Control Center displaying a custom banner at the top.
You can download a sample HTML document defining the banner using the following URL:
In this section of the Management Portal, you can monitor which user groups (as defined by license keys and their respective groups from your identity provider) are assigned which Golden Images and policies.
This is strictly a monitoring section designed to provide clarity at a glance. The application of policies and assignment of Golden Images happens on the respective pages of the Parallels Management Portal.
Clicking on a specific Golden Image will open the Golden Images section, with that Golden Image open for editing. Clicking on a specific policy will open the Policies section, with that specific policy open for editing.
Please note that all users who have not been assigned to a specific user group will draw their quotas and assignments from the primary license key. To find which license key is your primary or change its name:
Open the Dashboard section of your Parallels My Account customer area.
Find the product card for your Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition license.
Click on the Subscription Details line.
Scroll to the License Keys section.
Locate the license key whose type is marked as Primary.
Windows application stubs are special links to Windows applications installed in a virtual machine that can be added to the Dock in macOS during deployment.
Application stubs are created in macOS when you create a virtual machine and install Parallels Tools in it. To see application stubs for a virtual machine:
In macOS, navigate to /Users/<user-name>/Applications (Parallels)
Expand a desired virtual machine folder. For example, Windows 11 Applications, as shown in the screenshot below:
The icons in the folder are Windows application stubs. If you double-click an icon, the corresponding Windows application will be started in the virtual machine.
You can add one or more application stubs to the autodeploy package to be added to the Dock on a target Mac computer. For example, if your Mac users use a particular application most of the time, it would make sense to add it to the Dock so they can quickly launch it without dealing with the user interfaces of Windows or Parallels Desktop.
Windows application stubs are mandatory when you deploy Parallels Desktop using Single Application Mode. For more information, please see the Single application mode section.
To add one or more application stubs to the autodeploy package, simply copy it to the Windows Application(s) stubs to add to Dock folder of the package.
If you haven't already, use the link below to download the Parallels Desktop Autodeploy Package directly to a Mac computer.
Download the deployment package here.
Attention! Once you have downloaded the ZIP file, it is essential that you remove any quarantine attributes from it, as they may affect all further steps. To do that, execute the following command in the macOS Terminal:
xattr -dr com.apple.quarantine /Users/{username}/Downloads/pd-autodeploy.zip
Make sure the file path matches that of your downloaded package.
If the package has already been unarchived automatically, use the following command:
xattr -dr com.apple.quarantine /Users/{username}/Downloads/Parallels\ Desktop\ mass\ deployment\ paclage
Make sure the file path matches that of your downloaded package.
To verify that the quarantine attribute has been removed, execute the following command (utilizing a package or folder path):
xattr -r /Users/{username}/Downloads/pd-autodeploy.zip | grep com.apple.quarantine
The autodeploy package archive contains a folder named "Parallels Desktop mass deployment package vxxx", where "vxxx" is the autodeploy package version number.
The folder contains the following files:
Changelog.txt — contains a record of changes that were made to the autodeploy package over time.
Deploy.cfg — contains all the parameters that you'll need to check and set, as described here.
Prepare — contains the build script that creates a flat package ready for deployment.
Read on to learn how to add the necessary components to the autodeploy package.
To create a configuration profile for enabling major version upgrades, do the following:
Begin creating a new configuration profile as described in the Creating a configuration profile section.
When you have the new configuration profile dialog open, select the Product Updates payload in the left pane.
In the right pane, select the Enable managing product updates option. This will enable the payload, so when the configuration profile is sent to Mac computers, they will receive it.
To enable major version upgrades, select the Allow upgrade to the major Parallels Desktop version option.
Click Save to save the configuration profile.
The configuration profile now needs to be applied to a license or sublicense key. If you haven't done so already, use the instructions in the Applying a configuration profile to a license key section and apply the profile.
To create a configuration profile for VM image provisioning:
Begin creating a new configuration profile as described in the Creating a Configuration Profile section.
When you have the new configuration profile dialog open, select VM for Intel Mac or VM for M-series Mac payload, depending on the image type that you want to provision.
In the right pane, select the Enable VM image provisioning option and specify the following properties:
Name: Type a name for the VM image as you want it to be named in this profile. This is the name your users will see in Parallels Desktop when they receive an invitation to download it. This field is mandatory.
Description: An optional description. The end user will see this description in Parallels Desktop. For example, if a VPN connection is required to download the image, you may include this information here.
Download URL: The VM Image download URL. Mac users must be able to download the image via HTTP or HTTPS using this URL. This field is mandatory. For additional info, please see Creating and Uploading Virtual Machine Images.
Checksum (SHA-256): The VM image checksum. This field is mandatory. If you used the PVMP format to archive the virtual machine, the checksum was calculated automatically and saved as a VmName.sha256.txt file. If you archived the virtual machine using the ZIP or other supported format, you'll need to calculate the checksum. For the info about the PVMP format and how to calculate the checksum, please see Creating and Uploading Virtual Machine Images.
Click Save to save the configuration profile.
The configuration profile now needs to be applied to a license or sublicense key. If you haven't done so already, use the instructions in the Applying a configuration profile to a license key section and apply the profile.
When configuring USB device settings for a virtual machine, you can enforce what types of USB devices are allowed to be connected. For example, if storage devices (in general) are not allowed, the Mac user will not be able to connect an external hard disk or thumb drive to the virtual machine. This functionality is available in Parallels Desktop Business/Enterprise edition only and is absent in other editions.
To enforce USB device policies, open the virtual machine configuration window and select Hardware > USB & Bluetooth.
In the Allow external devices list:
Clear the types of devices that you don't want Mac users to connect to the virtual machine.
Select the types of devices that should be allowed.
A Parallels Desktop for Mac license key is required to activate Parallels Desktop on target Macs. The key must be specified in the autodeploy package.
You can find the primary key in your Business Account customer area as described in . There, you can also issue secondary keys that we recommend using for activation.
Attention: For security reasons, we strongly advise against using your primary key directly. Any compromised secondary keys can be deleted and replaced with new ones.
To specify the license key:
In the autodeploy package, expand the Parallels Desktop Autodeploy > Scripts > License Key and Configuration folder.
Open the deploy.cfg file in a text editor.
Find the License section (second from the top) and enter your Parallels Desktop Business Edition license key as a value of the license_key variable. The key must be supplied in the following format: "XXXXXX-XXXXXX-XXXXXX-XXXXXX-XXXXXX" (including quotes and dashes).
Save the deploy.cfg file.
Starting from Parallels Desktop 18, '' option became available. This option works only if you have purchased a special license type and set up integration with your identity provider in . Please check your license certificate for details. To enable 'Activation using corporate account' experience, comment the line with the license_key variable.
Note: Parallels Desktop activation requires Internet access. You need to make sure that port 443 is opened on target Mac computers so they can communicate with the Parallels License Server. You can also verify that the Mac computers can reach the Parallels License Server at .
Adding a virtual machine to the autodeploy package is optional. You can mass deploy Parallels Desktop only and install virtual machines on individual Mac computers later. Consider the following possible scenarios:
If you are deploying Parallels Desktop on either Apple Silicon or Intel-based Mac computers (but not both at the same time), you can include a virtual machine in the autodeploy package, so it will be installed on a Mac as part of the deployment process.
The recommended approach is to deploy without any virtual machines in the autodeploy package and instead provision a corporate VM image using a Configuration Profile in Parallels My Account. This method is especially useful when you plan to deploy Parallels Desktop on both Apple Silicon` and Intel-based Mac computers at the same time. For more information, please see and .
Attention: Architectural differences between Intel-based and Apple silicon Macs require different virtual machines for each of them, even if the operating system type and version are the same. If you have both kinds of Macs in your organization and would like to deploy Parallels Desktop with a virtual machine on all of them, you need to create two autodeploy packages (one for Apple silicon and another for Intel-based Macs) and deploy them separately.
There are two ways to include a virtual machine in the autodeploy package: as a downloadable link or as a local file manually added to the package. Regardless of which one you choose, take the following steps first:
Configure the virtual machine as described in the subsections of this chapter.
FULLY STOP the virtual machine by opening Actions in the macOS menu bar and choosing Shut Down. Suspending or pausing it will not suffice.
Reduce the size of the selected virtual machine by doing one of the following:
Open the Parallels Desktop Control Center, right-click on the virtual machine, and select Prepare for Transfer. This will result in a .pvmp file.
Alternatively, open the Parallels Desktop Control Center, right-click on the virtual machine, and select Show in Finder. Right-click on the virtual machine .pvm file and select Compress {vm_name}. This will result in a .zip file.
Known Issue: With Parallels Desktop for Mac version 26.1, deploying a package that includes a .pvmp packed virtual machine file results in that virtual machine failing to register and launch. We recommend using the second method with a .zip file until the bug is resolved.
Several popular MDM solutions have been known to experience issues with deploying large packages. As a way to mitigate this, you can amend the deploy.cfg file to include a link to a file share location with the virtual machine file instead of including it in the package. Take the following steps:
Upload the compressed file to a permitted cloud storage that would be accessible to all target Macs (e.g., OneDrive or Google Share). Make sure the resulting link is direct and open to all the users affected by the deployment. The best way is to choose Share with anyone. Note: A direct https link is a link that explicitly leads to a file, and not a file download page.
Open the deploy.cfg file in a text editor, same as when , scroll to the Virtual Machines section and add the download link there exactly as described, following the instructions carefully.
To add a virtual machine to the autodeploy package directly, simply copy the virtual machine file to the Virtual Machine(s) sub-folder that can be found under Bundle > Virtual machine(s) . More than one virtual machine can be added to the autodeploy package if needed.
Read on to learn about modifications that you can make to the virtual machine configuration before adding it to the autodeploy package.
To invite users to install Parallels Desktop via email:
Log in to your Parallels account at .
On the Dashboard page, locate the Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition product card and click the Invite Users button.
In the dialog that opens, select a license key that you want to use to activate Parallels Desktop on users' computers and click Next.
In the Invite Parallels Desktop Users dialog, specify the following options:
Language of Invitation: Select a language for the instructions in the invitation email.
Invitation Expires in: Use the drop-down list to select when the invitation should expire. After it expires, the temporary activation code included in it will no longer work.
Email address: Type a user's email address and click Add. Repeat for all intended users. You can also specify a CSV file containing email addresses of your users. The CSV file must contain a single column (a valid email address) with multiple rows (one email address on each row). Please note that if the number of users included in this list exceeds the number of available licenses for the specified key, the activation of Parallels Desktop will happen on a first-come, first-served basis.
The Download Invitations button allows you to save the invitation email information to a CSV file. The information includes email addresses that you specified, a temporary activation code (generated individually for each user), and the Parallels Desktop download URL (also generated individually for each user). You can use the information in the downloaded file to create your own invitation email or to answer helpdesk questions, should any arise. Hint: To see how the invitation email looks and to test it, you can send it to yourself first.
Click Send Invitations to send the email to users.
The invitation email that the users receive contains the following information:
Installation instructions and a link from which a user can download the Parallels Desktop installation file.
A temporary activation code. The code will be used automatically when a user installs Parallels Desktop on their computer. If for any reason automatic activation fails, the user can use the code included in the mail to manually activate Parallels Desktop. Please note that this is not the actual license key that you selected when you created the invitation email. This is only a temporary activation code with a limited scope and duration. The real license key is never shown to your Parallels Desktop users.
Note: Each code can only be used once, to activate Parallels Desktop on one computer and should not be shared. To activate on another computer, send another invitation.
Once the users have installed and activated Parallels Desktop on their computers, you will be able to see the list of active installations in your Parallels account.
Once Parallels Desktop is installed on a Mac computer, the user needs to set up a virtual machine to run Windows on their Mac. This can be accomplished using one of the following methods:
A user can create and configure a virtual machine and install Windows in it manually.
An administrator can prepare a virtual machine and put it on a corporate network storage from where users can download it to their computers.
An administrator can set up a Configuration Profile and provision a virtual machine to end users through it. For more information see and . This is the recommended method.
To avoid possible security and privacy issues, a suspended Windows virtual machine can be completely locked from user interaction and viewing.
When this option is enabled and a virtual machine is suspended, the Windows desktop in the virtual machine window (and in the Parallels Desktop Control Center) is replaced with a black background and the Windows session is interrupted. When the virtual machine is resumed, the Windows session is remained locked and the user will have to enter their credentials or authenticate (depending on how Windows is set up) to unlock it and see the Windows desktop.
To enable or disable this option:
Open Parallels Desktop and select the desired virtual machine (e.g. the source virtual machine when preparing it for mass deployment).
On the Parallels Desktop menu bar, select Actions > Configure to open the virtual machine configuration dialog.
Click the Security tab.
Depending on your needs select or clear the Always lock Windows on suspend option.
Close the dialog.
To create a configuration profile:
Log in to your Parallels business account.
In the Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition product card, click Registered Computers.
Click the More item in the main menu (top right) and choose Configuration Profiles, as shown in the screenshot below.
The page listing configuration profiles opens. If you haven't created any profiles yet, the list will be empty.
Click the Create Profile button. A dialog opens where you can configure the profile.
To replace the default profile name (top left), simply erase the default name (New Configuration Profile) and type a new one.
The payloads are listed in the left pane. To configure a payload, select it and then specify the necessary settings in the right pane. Each payload has the "Enable..." option at the top of the right pane. This option enables or disables a payload but doesn't change or discard the payload settings. When a payload is enabled, it is included in the configuration profile when the profile is applied to Mac computers. When a payload is disabled, it is not included, so Mac computers don't receive it. For creating the payload (i.e, a virtual machine image), refer to of the guide.
When done, click Save to save the configuration profile.
At this point we will not configure any of the payloads yet and will go straight to applying the configuration profile to a license or sublicense keys (it is allowed to create a profile with all payloads disabled). Once you learn how to create and apply a configuration profile, we'll talk about how to configure and use each individual payload.
Prior to Parallels Desktop 16, users were not automatically upgraded to the next major Parallels Desktop version. Starting with version 16, this option became available.
In the past, to upgrade Parallels Desktop for Mac Business Edition to a newer version, an IT administrator would need to set up a local update server or use a remote management tool or install the new version manually on a Mac computer. With this new option, administrators have the ability to automate major version upgrades if the organization policy allows it.
Here's a quick overview of how this feature works:
You create a configuration profile in Parallels My Account and configure the Product Updates payload where you enable or disable the "Allow upgrade..." option.
You then apply the configuration profile to a license or sublicense key.
Parallels Desktop periodically checks if a new major version is available. If it is, depending on how updates are configured in Parallels Desktop, the user will see a notification (with an option to upgrade or postpone), or the upgrade will be performed silently. When the upgrade is initiated, the new major version of Parallels Desktop is downloaded to the Mac computer and installed on it. After that, Parallels Desktop restarts, completing the upgrade.
The subsequent topics describe in detail how to configure and use the major version upgrade functionality.
Starting from Parallels Desktop for Mac 20.3.1, the encryption of provisioned virtual machines and Golden Images is governed by the Do not allow running VMs without this company's Parallels license policy (a.k.a. "Lock VM to organization") as described in the chapter. This way, you can ensure that the virtual machines and Golden Images that may contain sensitive corporate data or access will not launch outside your organization's Parallels Desktop environment.
With this change, the respective option in the Security tab of the virtual machines' settings has become inactive, even if the aforementioned policy is not applied. This way, your users won't be able to control their corporate virtual machines' security via the graphical interface or the command line utility.
Attention: The encryption process for a given virtual machine requires roughly double the amount of disk space that the virtual machine occupies. Plan accordingly. Check the status using the respective parameter on the Parallels Management Portal.
Only stopped or suspended virtual machines undergo the encryption process. Therefore, once you apply this policy and the local Parallels Desktop installation receives the respective command from the server, one of the following things will happen:
A new virtual machine created on your company's Parallels Desktop installation will be encrypted based on your organization's Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition license regardless of the way it was created: from a Golden Image, from appliances, or via cloning. This encryption method persists through packing, conversion to a template, or other operations.
A stopped/suspended virtual machine will be encrypted right away.
A running virtual machine will be encrypted as soon as it is stopped or suspended.
A packed virtual machine will be unpacked, encrypted, and packed again.
An archived virtual machine will be unarchived, encrypted, and packed due to the archiving functionality being deprecated.
For a virtual machine encrypted on the user side, Parallels Desktop will wait for the user to perform an operation that requires the encryption password and then change the encryption from the user-side one to the one tied to your organization's Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition license.
As a result of tying your provisioned virtual machines' encryption to the license, users won't be able to launch such virtual machines on Parallels Desktop installations activated with any license other than your company's.
To monitor the update status of Windows installations in Parallels Desktop virtual machines from Jamf, do the following:
Copy from Parallels' GitHub page.
From your Jamf dashboard, go to Settings -> Computer Management -> Extension Attributes and use Ctrl + N to create a new extension attribute. Set the Input type to Script and paste the script into the respective field.
To keep Windows up to date on Parallels Desktop virtual machines, do the following:
Copy from Parallels' GitHub page.
From your Jamf dashboard, go to Settings -> Computer Management -> Scripts and use Ctrl + N to create a new script. Fill out the details on the General tab, then switch to the Script tab and paste the script there.
Switch to the Options tab and add the following labels for clarity:
Parameter 4: Mode (check, list-updates, install, uninstall, check-and-install)
Parameter 5: Unattended ( true | false)
Parameter 6: Auto Reboot ( true | false)
Parameter 7: Verbose ( true | false ) Provides more output
Parameter 8: Force on all VMs ( true | false ) Forces update checks on all VMs regardless of their current state
Click Save.
To apply the script, go to Computers -> Content Management -> Policies and use Ctrl + N to create a new policy. On the General page, under the Trigger section, check all the boxes except for Custom. Set Execution Frequency to Once every day.
Switch to the Scripts page and use the + button to add the previously created script to the policy. Set Priority to After, and assign the following values:
Mode: check-and-install
Unattended: true
Auto Reboot: true
Verbose: true
Force on all VMs: true
Switch to the Scope tab and use it to target all the computers included in this deployment's scope.
Click Save.
From your Jamf dashboard, go to Computers -> Content Management -> Policies and create a policy to monitor and enforce Windows updates across your Parallels Desktop for Mac deployments.
For end-users, activating their copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition is much easier by signing in with their usual set of corporate login credentials. If your organization already runs an identity provider service (e.g., Microsoft Entra ID, Okta, or Ping Identity), you can benefit from the Single Sign-On (SSO) activation method by setting up the integration. This method has the added benefit of automatically disabling the licenses of employees leaving your organization, freeing up their quota.
This chapter represents a migration plan that will not affect your existing per-device (license key) activations while you continue to run them in parallel with the new per-user (SSO) test group.
If your current Parallels Desktop for Mac deployment uses the license key activation method but you would like to switch to SSO, follow these steps:
At this stage, your goal is to set up the integration between Parallels and your identity provider (IdP) and validate that it works for your test group. Once this goal is achieved, you can make the SSO activation method default for all new users of Parallels Desktop for Mac in your organization.
Start the integration process on of Parallels My Account and follow the instructions from .
Warning: Once you have completed the integration process and activated the SSO functionality, only users from the Administrators group in your IdP signing in via SSO will retain access to managing the Parallels business account. All previous administrative privileges based on logins and passwords will become inactive.
Your designated backup login will continue to work.
Throughout this process, your new SSO setup will not affect your existing users of Parallels Desktop for Mac.
Download a copy of Parallels Desktop for Mac on a computer that doesn't have it and attempt to activate it using the SSO method. Make sure to allow Parallels Desktop access to the Downloads folder.
Alternatively, choose an existing non-critical Parallels Desktop seat, deactivate it using the following Terminal command:
prlsrvctl deactivate-license,
restart Parallels Desktop, and try to activate again using SSO. Expand the test to a small group of users.
Once everything is successfully tested, you can either:
Update your company's documentation to instruct all new users to activate via SSO only or
If you have a Mac management tool, deploy a configuration profile to all new Macs that forces the SSO login window to pop up at the app launch until it has been activated.
Once you have successfully completed the previous steps, it's time to expand the SSO activation to your organization's wider Parallels Desktop user base. Start by proactively notifying them of the upcoming switch to per-user (SSO) activation. Your email may also suggest the following steps:
Making sure their copies of Parallels Desktop have been updated to version 20.1.0 or newer;
Opening the Parallels Desktop Control Center and using the Parallels Desktop drop-down menu in the macOS menu bar to open the Account & License... window;
Using the Continue with SSO option in that window (bottom left corner).
However, there will always be users who routinely ignore such emails. If you have a Mac management tool at your disposal, you could force selected users to re-activate with SSO by following these steps:
Update all Parallels Desktop for Mac seats to version 20.1.0 or newer;
Execute the following commands:
prlsrvctl deactivate-license
sudo -u $(stat -f%Su /dev/console) defaults write "com.parallels.Parallels Desktop" ActivationExperience -string "sso"
sudo -u $(stat -f%Su /dev/console) defaults write "com.parallels.Parallels Desktop" "isSSOExperienceForced" -bool FALSE
You can monitor per-user (SSO) activations using the following path in Parallels My Account: click on the Business Profile link in the top-right corner. On that page, click on the Users (N) link, also in the top-right corner. From the first drop-down menu, select the Users: With product licenses option. The resulting list will contain all the Parallels Desktop users who have activated their copies using SSO.
Continue to monitor the user count on this page for the next few weeks to ensure progress.
As administrator of a large Parallels Desktop for Mac deployment, you may need to restrict your users' ability to perform certain common actions, such as creating a completely new virtual machine that would be outside of your control and not configured to your company's standards, or remove your standard-issue provisioned virtual machine.
One of the advantages of Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition is the ability to set up, monitor, or change all such policies on all of your organization's workstations in a centralized manner via the Parallels Management Portal. Refer to the section for more information.
Your users won't be able to access the Settings -> Security panel on their managed machines where that panel looks like this:
Parallels Desktop Enterprise, Business, and Pro editions include developer tools which are aimed at software developers using Parallels Desktop as part of their development and testing setup. The tools are accessed by clicking the Develop menu on the virtual machine menu bar and then choosing one of the available options (e.g. Start SSH Session, Start Debugging Session, and others).
If users in your organization are not using these tools, you can hide the Develop menu altogether. The reason you would want to do this, some of these features (if used accidentally) may start a debugging session or engage in some other development-specific activities that may temporarily disrupt normal Parallels Desktop operation.
This option is a part of a virtual machine configuration and can be set using the Parallels graphical user interface as follows:
Open the virtual machine configuration dialog (click the gear icon or choose Actions > Configure).
In the dialog, click Options (at the top) and then click More Options in the left pane.
In the right pane, select or clear the Show developer tools option. This will show or hide the Develop menu on the virtual machine menu bar (you don't have to restart a virtual machine if it's running).
To modify this setting from the command line, execute the following command in Terminal:
where ID/Name is the GUID or name of a target virtual machine.
When mass deploying Parallels Desktop on Mac computers in your organization, you can configure the autodeploy package to apply these settings to all included virtual machines automatically. For details, see .
When users run Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition, they can get support at any time by clicking the Help > Support Center menu. By default, this will open one of the following:
If you are a large organization with your own Help Desk, the menu will open a message box saying the user should contact the system administrator for assistance.
If you are a small organization without a Help Desk or if you are using a trial version of Parallels Desktop, the menu will open the Parallels Desktop support web page.
You can change the default behavior described above and make the Help > Support Center menu open a custom URL, such as your corporate Help Desk page or any other web page you desire.
The customization can be done during mass deployment of Parallels Desktop by modifying the corresponding deployment configuration parameter. Please see for the complete info (see the description of the Help and Support section of the configuration file).
You can also make the customization manually on an individual Mac as follows:
Log in to the Mac.
In the Finder, navigate to the /Users/<User_Name>/Library/Preferences directory and locate the com.parallels.Parallels Desktop.plist file.
Open the file using the Property List Editor application, which is included with Xcode.
Find the SupportRequestUrl property in the file. If the property doesn't exist, add it to the file specifying its data type as String.
To specify the action that should be performed by the Help > Support Center menu, set the value of the SupportRequestUrl property:
To display the default text message, clear the property value.
To open a URL, specify the full URL of the desired web page or resource.













The next step is to configure individual Macs to take their updates from the local update server. This can be done automatically during the mass deployment of Parallels Desktop by modifying the appropriate deployment configuration option. Please see Configuring Deployment Options for the complete info (see the description of the Software Updates section of the configuration file).
If you have an existing Parallels Desktop installation that was not configured for automatic updates during deployment, then read on to learn how to do it manually.
To configure Parallels Desktop automatic updates, you need to modify the Parallels Desktop property list file on a Mac as follows:
Find the com.parallels.Parallels Desktop.plist file located in the Library/Preferences subfolder in the user's home folder. This is the Parallels Desktop property list file that contains the user-specific information.
Open the file using the Property List Editor application (included with Xcode).
Set the update policy by modifying the Application preferences.VolumeLicenseUpdatePolicy property. If the property doesn't exist, add it to the file specifying its data type as String. Set the property value using one of the following options (see also the Notes subsection below):
"Parallels" — when this value is set, the updates will be downloaded from the Parallels update server via the Internet. The value is case-sensitive.
Complete URL of the parallels_updates.xml file residing on your local update server. For example, "https://10.0.0.1/pdfm/v8/en_us/parallels/parallels_updates.xml". When the URL is specified, the updates will be obtained from the local update server.
"None" — automatic updates are disabled. The value is case-sensitive.
Specify how often Parallels Desktop should check for updates. This is done by modifying the Application preferences.Check for updates property. If the property doesn't exist, add it to the file specifying its data type as Number. Specify the property value using one of the following options:
0 — Never
1 — Once a day
2 — Once a week
3 — Once a month
Set the automatic download option. Find the Application preferences.Download updates automatically property. If it doesn't exist, add it to the file specifying its data type as Boolean. Set the property value using one of the following options:
True — Download updates automatically. Specify this value when using a local update server.
False — Notify the user about the updates but don't download them automatically. This option is useful only when updates are downloaded from the Parallels update server, and the user has full control over the update functionality.
Save the file and close the Property List Editor application.
On initial Parallels Desktop activation using a Business Edition key, the Parallels Desktop update properties will be absent from the com.parallels.Parallels Desktop.plist file. In such a case, a Mac user will be able to configure Parallels Desktop automatic updates using the Parallels Desktop graphical user interface.
When the update-related properties are added to the com.parallels.Parallels Desktop.plist file, the automatic updates will be performed according to the specified values. In addition, the value of the Application preferences.VolumeLicenseUpdatePolicy property will affect the Parallels Desktop update-related elements in the Parallels Desktop graphical user interface as follows:
If the property contains a URL of the local update server or "None", the Parallels Desktop update-related controls will be disabled (grayed out) in the Parallels Desktop graphical user interface. The displayed settings will have no effect on how the Parallels Desktop updates are carried out. Therefore, the user will not be able to configure automatic updates or check for updates manually.
If the property doesn't exist, has no value, or contains "Parallels" as a value, the Parallels Desktop update controls will be enabled in the user interface giving the user the ability to configure automatic updates and check for updates manually.
prlctl set ID|Name --show-dev-tools on|off



The steps that you, as the system administrator, need to take to migrate your Parallels Desktop for Mac Business Edition setup to Enterprise Edition depend on the type of activation in your existing Business Edition setup:
Per-device, when you activate a copy of Parallels Desktop on each individual Mac using a license or sublicense key that you have created in Parallels My Account or
Per-user, when each user activates their copy of Parallels Desktop by signing in with their corporate credentials using the standard SSO procedure via your organization's identity provider.
If your existing Parallels Desktop setup is activated on a per-device basis using license keys, you will have to take the following steps:
Contact your sales representative using Parallels My Account and purchase an upgrade;
Ask them to convert your existing Business Edition license to an Enterprise Edition one (the recommended path). If your organization has multiple Business Edition licenses, tell your sales representative which one to convert.
Make sure the product type on the license card in My Account has changed from Business to Enterprise;
[OPTIONAL] Configure Golden Images using the Parallels Management Portal;
[OPTIONAL] Set up or verify the existing sublicenses and configure or reassign policies accordingly;
[OPTIONAL] If your organization uses an identity provider (e.g., Microsoft Azure/Entra ID, Okta, or Ping), consider setting up a Single Sign-On (SSO) activation method and switching at least some of your users to it, as Enterprise Edition allows you to maintain a mix of license key and SSO activations across the same setup.
Make sure that all Parallels Desktop for Mac users in your organization have upgraded to at least version 20.1.0 or newer to enable communication with the Management Portal;
Verify that all your end-user installations remain activated;
Check the monitoring tab in the Management Portal and see it populated with virtual machines on your network.
As a result of this:
The Business Edition product card of your choice on your My Account page will change to an Enterprise Edition product card, while the Enterprise Edition trial license will be suspended;
You will not have to reactivate your end-users' copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac unless you have decided to split them into groups using sublicense keys (step 5 above);
Your Golden Images from the trial license will be saved and offered to the users on your new Enterprise Edition license.
This is not a recommended scenario. However, if you choose it, you will need to follow these steps:
Contact your sales representative using Parallels My Account and purchase an extension;
Explicitly tell them that you wish to convert your trial Enterprise Edition license to a permanent one. Your Business Edition users will remain activated with their Business Edition license;
[OPTIONAL] Create sublicenses for the groups of your Enterprise Edition users to benefit from granular policy management or if you wish to manage ;
[OPTIONAL] Configure Golden Images using the Parallels Management Portal;
[OPTIONAL] Configure or reassign policies to groups according to your preferences;
Make sure that all Parallels Desktop for Mac users in your organization have upgraded to at least version 20.1.0 or newer to enable communication with the Management Portal;
Migrate/reactivate users to the new Enterprise Edition ;
Verify that all seats have been activated;
Check the monitoring tab in the Management Portal and see it populated with virtual machines on your network.
As a result of this:
The Enterprise Edition trial license product card on your My Account page will be replaced with the permanent license card;
You will not have to manually migrate all the users to the new setup and activate their licenses (Step 7 above);
Your Golden Images from the trial license will be saved and offered to the users on your new Enterprise Edition license.
If your existing Parallels Desktop setup is activated on a per-user basis (SSO activation), you will have to take the following steps:
Contact your sales representative using Parallels My Account and purchase an upgrade;
Make sure that all Parallels Desktop for Mac users in your organization have upgraded to at least version 20.1.0 or newer to ensure communication with the Management Portal;
Make sure the product type on the license card in My Account has changed from Business to Enterprise;
[OPTIONAL] Configure Golden Images using the Parallels Management Portal;
[OPTIONAL] Your SSO setup used with the Business Edition license did not involve multiple user groups. If you would like to benefit from the flexibility it provides, follow the instructions in this chapter;
Warning: If your IdP is Microsoft Azure/Entra ID, pay particular attention to steps (3) and (4) in theMapping existing groups... section to avoid potential issues with re-activation, license quota allocation, and policy application.
Verify that all your end-user installations remain activated;
Check the monitoring tab in the Management Portal and see it populated with virtual machines on your network. The end-user copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac refer to the server to verify their licenses every seven days. If you would like your users to reactivate their copies sooner, you could use your device management solution to run this command remotely:
prlsrvctl deactivate-licenseAs a result of this:
The Business Edition product card of your choice on your My Account page will change to an Enterprise Edition product card, while the Enterprise Edition trial license will be suspended;
Your end-users' copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac will eventually get in touch with the server and update their licensing information (Step 7 above);
Your Golden Images from the trial license will be saved and offered to the users on your new Enterprise Edition license.
If your previous Parallels Desktop for Mac Business Edition setup had enabled, you will have to configure the respective policies using the Parallels Management Portal. See this chapter for more information.
Your new setup will continue to respect any policies (like a specific local update server or policy or default virtual machine image) delivered via configuration profiles. However, this functionality will be removed in the future. For all new setups, we strongly recommend making the best use of the Parallels Management Portal's functionality.
For virtual machine images, the Management Portal currently supports providing one for Intel Macs and one for Apple Silicon Macs. In the future, as we remove support for configuration profiles, we will introduce support for providing multiple virtual machine images for each architecture, and you will be able to target specific user groups with each one.
Blocking major Parallels Desktop version upgrades can currently be achieved via the Policies section of the Parallels Management Portal.
As mentioned before, we recommend you to deploy the licensing/PPPC profile first, and follow it up with the Parallels Desktop for Mac app from your MDM's app catalog.
This chapter uses Jamf Pro for demonstration purposes. If you use a different device management solution, check their respective guide on distributing profiles and using built-in app catalogs.
For the purposes of activating Parallels Desktop for Mac, Jamf Pro offers a pre-configured profile for Mac computers where you can the preferred activation method to a license key or SSO, and add your preferred PPPC settings. Follow these steps:
From the main Dashboard, go to Computers > Content Management > Configuration Profiles and click the + New button.
On the Options tab, fill out the required parameters on the General page, such as Name, Description, Level, and Distribution Method.
Use the left-side scroll menu or its dedicated search bar to get to the Applications & Custom Settings section, expand it, and click on the External Applications option.
Click the + Add button, choose Jamf Repository under Source, and com.parallels.desktop.managedprefs under Application Domain. Use the other drop-down menus to choose the version and variant.
Use the Activation Experience drop-down menu to choose SSO or License Key. In the latter case, insert the license key into the respective field.
Use the left-side scroll menu or its search bar to locate the Privacy Preferences Policy Control section, and click Configure.
Under App Access, set the Identifier to com.parallels.desktop.console, Identifyer Type to Bundle ID, and leave the Validate the Static Code Requirement box unchecked. In the Code Requirement field, paste the following value, making sure to copy it carefully:
identifier "com.parallels.desktop.console" and anchor apple generic and certificate 1[field.1.2.840.113635.100.6.2.6] /* exists */ and certificate leaf[field.1.2.840.113635.100.6.1.13] / exists */ and certificate leaf[subject.OU] = "4C6364ACXT"
If you want to verify the value of this parameter independently, launch macOS Terminal on a Mac with a copy of Parallels Desktop installed and execute the following command:
codesign -display -r - /Applications/Parallels\ Desktop.app
Under App or Service, use the + Add button to, at the very minimum, allow the app to access the Desktop (SystemPolicyDesktopFolder), Documents (SystemPolicyDocumentsFolder), and Downloads (SystemPolicyDownloadsFolder) folders. You may also want to enable Accessibility and ScreenCapture for other Parallels Desktop functionality, such as error reporting.
At the very top of the Configuration Profiles page, switch to the Scope tab and select the target computers or user groups.
In the bottom-right corner, click Save.
If you prefer to distribute your pre-made configuration profile using Jamf Pro, from the main Dashboard, go to Computers > Content Management > Configuration Profiles and click the Upload button in the top-right corner, selecting the .mobileconfig file with the configuration profile made in the previous chapter.
This will open the profile for editing, where you will be able to switch to the Scope tab and select the target machines or specific user groups.
Refer to your MDM solution's guide for syncing user groups with your identity profider.
To deploy Parallels Desktop for Mac using Jamf Pro's built-in app catalog, from the main Dashboard, go to Computers > Content Management > Mac Apps and click the + New button in the top-right corner. Select Jamf App Catalog as source and choose Parallels Desktop 20.1 or newer for deployment.
Attention: Parallels Management Portal requires the local installations of Parallels Desktop to be version 20.1 or newer to establish and maintain connection.
During the setup, you can choose a group of computers that the app will be deployed to. You can set up groups under Computers > Groups.
In macOS, you may control various aspects of the operating system and particular apps' behavior by installing or remotely deploying the so-called configuration profiles: files that contain specific instructions written in specified syntax. Such files have a .mobileconfig extension. They can be created or edited manually or in special software and distributed along with the app using your preferred device management solution.
Some of the MDM solutions like Jamf Pro already have preconfigured profiles for Parallels Desktop for Mac. In case your preferred MDM solution does not, this chapter describes how to create one in iMazing Profile Editor.
Follow these steps to create a profile that will control the Parallels Desktop activation method and (optionally) set the privacy preferences for it in advance so that your users won't have to click Allow on multiple system access requests when they first launch the app:
Download and install iMazing Profile Editor from their website or Mac App Store.
Launch the app.
While in the General domain, set the following values at your discretion:
Payload Display Name: what your profile will be named.
Payload Organization: put your company's name here.
Payload Description: what your profile controls.
Prevent users from removing this profile: we recommend that you activate this option.
Payload Scope: whether the profile should apply to the whole Mac, no matter what user signs in, or just the particular user.
Target Device Type: Mac.
Scroll down the left-side bar until you find the item called Parallels Desktop for Mac. Select it and click the + Add Configuration Payload button. This will add the Parallels Desktop activation method payload to your profile.
Under Activation Experience, select SSO for the sign-in experience of per-user licensing or License Key for per-device licensing. In the latter case, providing the license key to activate Parallels Desktop is mandatory.
Optionally, scroll down the left-side bar to find the payload called Privacy Preferences Policy Control, add it to the configuration profile, and set it up as you see fit, following these guidelines from Apple. At the very minimum, we recommend that you enable Parallels Desktop's access to Desktop, Documents, and Downloads folders.
Note: For the purposes of PPPC settings, Parallels Desktop for Mac and any of its virtual machines share the same bundle ID, which is com.parallels.desktop.console. The Identifier Type should be set to Bundle ID, Authorization to Allow, and Allowed to 1.
Use File -> Save As to save the newly created profile for further distribution. You may choose to sign the profile; if so, make sure the certificate with which you sign is also present on all target Macs.
Configuration profiles are applied to registered Mac computers based on a license or sublicense key that they are using to run Parallels Desktop. By applying a configuration profile to a license or sublicense key, you are essentially applying it to Mac computers that use (or will use in the future) that key.
To apply a configuration profile to a license or sublicense key:
In Parallels My Account, click Dashboard in the top menu and then click Active subscriptions inside the Parallels Desktop for Mac Business Edition product card.
Click a subscription to open a page containing the subscription information.
In the License Keys list, choose a license or sublicense key and click the "gear" icon at the end of the row. This opens a dialog containing the license key information and settings. In the dialog, select the Configuration Profile tab.
Initially, the tab page will say that "Configuration profile is not set" and the drop-down menu next to it will contain the "Default" profile. This is because you haven't applied a custom configuration profile to this license key yet. Info: Default is a built-in profile that Parallels Desktop is using internally. It doesn't contain any payloads that you can configure when you create a custom profile. If you don't have any custom profiles assigned to a license key, the "Default" profile is used.
Expand the drop-down menu and select the configuration profile that you created earlier.
Click Save.
Once a configuration profile is applied to a license key, the following will happen on Mac computers that use this key:
The next time Parallels Desktop communicates with Parallels cloud, it will receive the configuration profile and will save the data that it contains locally.
When an action is performed (by the user or by a scheduled event) that has to do with one of the configuration profile payloads, the data is read from the local storage and is used accordingly depending on the payload and its settings. This is described in more detail in topics that describe individual payloads.
This concludes the description of how to create a configuration profile and how to apply it to a license or sublicense key. The subsequent sections describe how to configure individual payloads and how to use the corresponding functionality when managing Parallels Desktop installations in your organization.
Regardless of how you choose to deploy Parallels Desktop to your end users, you will need to provide them with virtual machines to run. Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition accepts virtual machine images in a packed .pvmp format. To create such an image:
Using your own Parallels Desktop setup, create a Parallels virtual machine, install the operating system in it, pre-install the software that your users may need, and otherwise configure the virtual machine according to your requirements. Note that if your organization has both Apple silicon and Intel Macs, you need to create a separate virtual machine for each processor architecture. For the list of supported operating systems, please visit https://www.parallels.com/requirements/. Note: Boot Camp-based virtual machines, archived virtual machines, and linked clones cannot be used for deployment.
If your virtual machine is running Windows, you may need to use Sysprep to strip it of installation-specific information such as the SID (Security Identifier), GUID (Globally Unique Identifier), and other identifiers before deploying it. Follow the directions from this KB article.
Make sure the virtual machine is shut down.
If your virtual machine has snapshots, it is recommended that you remove them. This will significantly reduce the virtual machine size. Moreover, these snapshots may be unusable on another computer because of hardware differences.
When the virtual machine is ready, it needs to be packed as a .pvmp file before you make it available for download to your users. To pack it:
Open the Parallels Desktop Control Center;
Right-click on the virtual machine that you want to transfer and select Prepare for Transfer. Parallels Desktop will start packing the virtual machine. This process may take some time, depending on the virtual machine size;
Once the .pvmp package is created, you can right-click it and choose to show where it is stored in the Finder;
An SHA-256 checksum for the virtual machine package is calculated automatically and saved as a .txt file in the same folder. You will need it later during the deployment process. You can also calculate the checksum by executing the shasum command.
Once you have a virtual machine saved as a .pvmp archive, upload it to a server from which Parallels Desktop users can download it to their Mac computers via HTTPS. The requirements are:
The link has to be direct, explicitly leading to the image file and not a file download page. E.g., if you are using Microsoft Sharepoint, take these steps:
Create and copy a shareable link to a file following the normal "Copy link" procedure.
Before using the link for deployment, paste it into a text editor, and replace the text after the ? with download=1.
You have to ensure that no authentication is required to download the image file.
Optionally, you may use a URL shortener.
You may use an internal file sharing resource accessible with VPN enabled.
Once your link is ready, we suggest you check it with a curl command from the Terminal, e.g.:
curl {full URL starting with https://} -o {/Users/<username>/Downloads/image.pvmp}Enrolling Parallels virtual machines in Azure Active Directory with Microsoft Intune enables managing and securing your virtual machine environment. To achieve that goal, you will have to create a provisioning package and deliver it to your end users. To learn more about provisioning packages for Windows, follow this link.
Warning: You will only be able to successfully enroll the machines deployed from an Autodeploy Package that includes a Windows virtual machine prepared for deployment, and with the vm_reset_hwid parameter in the deploy.cfg file set to "yes". For more information on configuring the Autodeploy Package, please refer to the respective section of this guide.
Be advised that setting this parameter to "yes" may affect active software licenses on the deploying machines; however, without this step, your Azure infrastructure will not be able to detect all the VMs as separate entities.
Follow these steps:
1. Install Windows Configuration Designer from Microsoft Store or download it directly from the Microsoft website.
2. Once installed, launch it and create a new project following the Provision desktop devices template.
3. Once the project is created, you will see the following page:
At this point, you need to choose a name convention. Once done, click Next and switch to the Set up network tab. There, you need to switch off the setup network toggle and click Next, proceeding to the Account Management page.
4. The following step is important: You need to select the Enroll in Azure AD option and obtain a bulk token.
Here, you need to sign in with your Microsoft Azure credentials. Once you’ve successfully signed in, you’ll see the message confirming the successful receipt of the token.
5. Click Next. Feel free to skip the remaining steps by clicking Next on each one of them.
6. Finally, you need to double-check your configuration summary and ensure everything is correct.
Click Create and memorize the path to the package file.
From this point, you have three possible ways to proceed:
Share the package with users who will need to launch it to enroll their virtual machines in Azure;
Install the package manually on every machine;
Add the package to the installation process as part of the SetupComplete.cmd script, as described in section 5 of this KB article.
Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition allows you to protect the configuration of a virtual machine with a custom password.
When a password is set, even a local Mac administrator will be required to enter it in order to modify virtual machine settings.
To set a password in the Parallels Desktop graphical user interface:
Open Parallels Desktop and select a virtual machine.
On the Parallels Desktop menu bar, select Actions > Configure to open the virtual machine configuration dialog.
Select Security.
Click the Custom password: Turn On... button.
Enter a password, then enter it again to verify and click OK.
To change or remove the password:
To change the password, click the Change Password button and follow the instructions on the screen.
To remove the password, click Custom password: Turn Off and follow the instructions on the screen.
If the password is set and the user tries to view or modify the virtual machine configuration, they will be required to enter this custom password.
In addition to the graphical user interface, you can use the prlctl command-line utility to set a custom password for editing the virtual machine configuration.
To set the password, type the following command in Terminal:
prlctl set "vm_name" --custom-pwdwhere vm_name is the virtual machine name in quotes. You'll be asked to enter a password and then confirm it.
To change or remove the password, type the same command as above:
prlctl set "vm_name" --custom-pwdYou'll be asked to enter the current password and then a new password.
To view the current protection status for a virtual machine, type the following command:
prlctl list "vm_name" -iIn the output, search for the Security section and look at the Custom password protection property. It will be either set to "on" or "off".
If you are mass deploying Parallels Desktop and one or more virtual machines, you can simply set the custom password in the source virtual machine. When a virtual machine is deployed on Mac computers, the password will be retained.
Single Application Mode is a special Parallels Desktop deployment option that allows you to largely obscure Parallels Desktop and Windows on a Mac, making Windows applications appear native to macOS. This mode is designed for system administrators who want Mac users in their organization to run one or more Windows applications while minimizing their interaction with Windows or Parallels Desktop.
Attention: Combining Single Application Mode with Single Sign-On (SSO) requires Parallels Desktop for Mac version 26.1 or newer, and the respective version of the deployment package.
To make Parallels Desktop run in Single Application Mode, you need to deploy it on Mac computers via the autodeploy package. This includes preparing the autodeploy package in a special way and then either deploying it on Mac computers using Mac management tools or running it manually on a Mac.
For more information about how to use the autodeploy package and how to deploy Parallels Desktop in Single Application Mode, please see the following pages:
This section of the Management Portal is where you go to designate the virtual machines that will be deployed across your organization. You can deploy multiple golden images. Each golden image may contain up to two separate virtual machine images, one for Apple silicon Macs and one for Intel Macs.
If you are configuring your Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition setup for the first time, the Golden Images section in your Parallels Management Portal will look like this:
Use the Create Golden Image button and follow the instructions .
Each golden image can be assigned to one or several . Starting from the September 2025 update, Golden Images are assigned to user groups as part of .
Each Golden Image card contains the list of policies in which this image is provisioned and the number of virtual machines provisioned with it:
Note: At the moment, each group of users may only have one golden image assigned to it (for up to two processor architectures).
Fill out the following fields when adding a golden image record:
Name. Give the virtual machine a descriptive, easy-to-read name, e.g., {company_name} Windows 11 Pro for Arm. This name will be shown to your users;
[OPTIONAL] Description. Feel free to add a more detailed description that helps to understand the specific purpose or setup of each image, e.g., This image is for the accountants to run Excel for Windows. This description will be shown to your users;
Enable for {architecture}. You may provide golden images for one specific processor type or both. Note: You may choose not to add one of the images if your organization only uses Macs with one processor architecture;
Download URL for {architechture}. Upload your virtual machine .pvmp file to a server location that supports direct links and is accessible to all the machines where you plan on deploying it, and share the file. Optionally, you may use a URL shortener. Apple silicon Macs and Intel Macs will require two separate image files. Make sure the files are accessible without authentication. Before proceeding, .
Note: A local network file share may be a suitable solution, provided the remote machines can connect via VPN;
Checksum (SHA-256). When packaging a virtual machine (right-click on it in the Control Center and choose Prepare for Transfer), the resulting .pvmp file is accompanied by a .txt file containing a SHA-256 checksum for it. Copy and paste the contents of that file in this field.
Note: If you have the .pvmp virtual machine file but not the .txt file with its checksum, you can quickly find it by following these steps:
Right-click on the .pvmp file while holding down the Option key and choose Copy {file_name} as Pathname;
Open Terminal;
Type in shasum -a 256 {file_desination}, pasting the copied pathname from Step 1, and hit Enter.
The output will look similar to the following:
63a90c3c38cc8c358221da339068fc1292b10bf7c00ed8449787b0e6019d706b /Users/parallels/Parallels/Windows11Pro.pvmp.
Once you are done filling out the required fields, click Save to activate the golden image.
To change the settings for a golden image, click Edit on the golden image's card, and change the settings as described above.
Mind that changing the link will not update the virtual machines already provisioned from that Golden Image, and both old and subsequently provisioned new VMs will count as provisioned from that image.
To remove a golden image, select the one you want to delete, click Edit on the golden image's card, click Delete Golden Image in the bottom left corner of the card, and confirm the deletion.
Warning: Deleting a golden image is irreversible. If you have deleted a golden image by mistake, you will have to create it again. If the groups that were assigned that image, were also , the users in those groups wouldn't be able to install new virtual machines until assigned another golden image.
If you attempt to delete a Golden Image that has virtual machines provisioned from it, you will get a warning message prompting you to remove those virtual machines first. Without removing them, you won't be able to delete the Golden Image as otherwise, you would lose administrative control over them. If you don't want users to install new virtual machines based on the image, it is easier to remove the image from the policy or policies where it's provisioned.











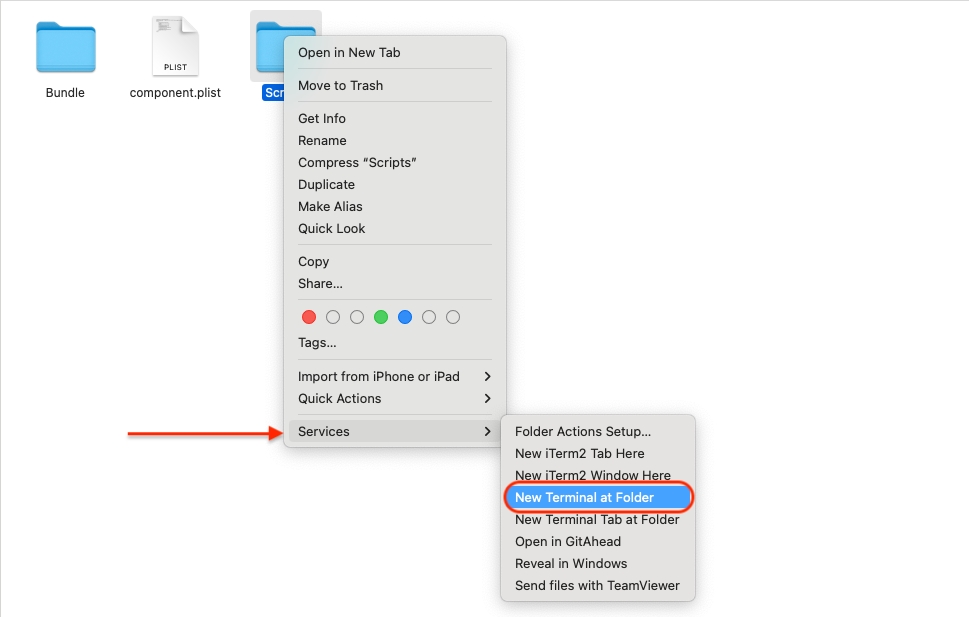
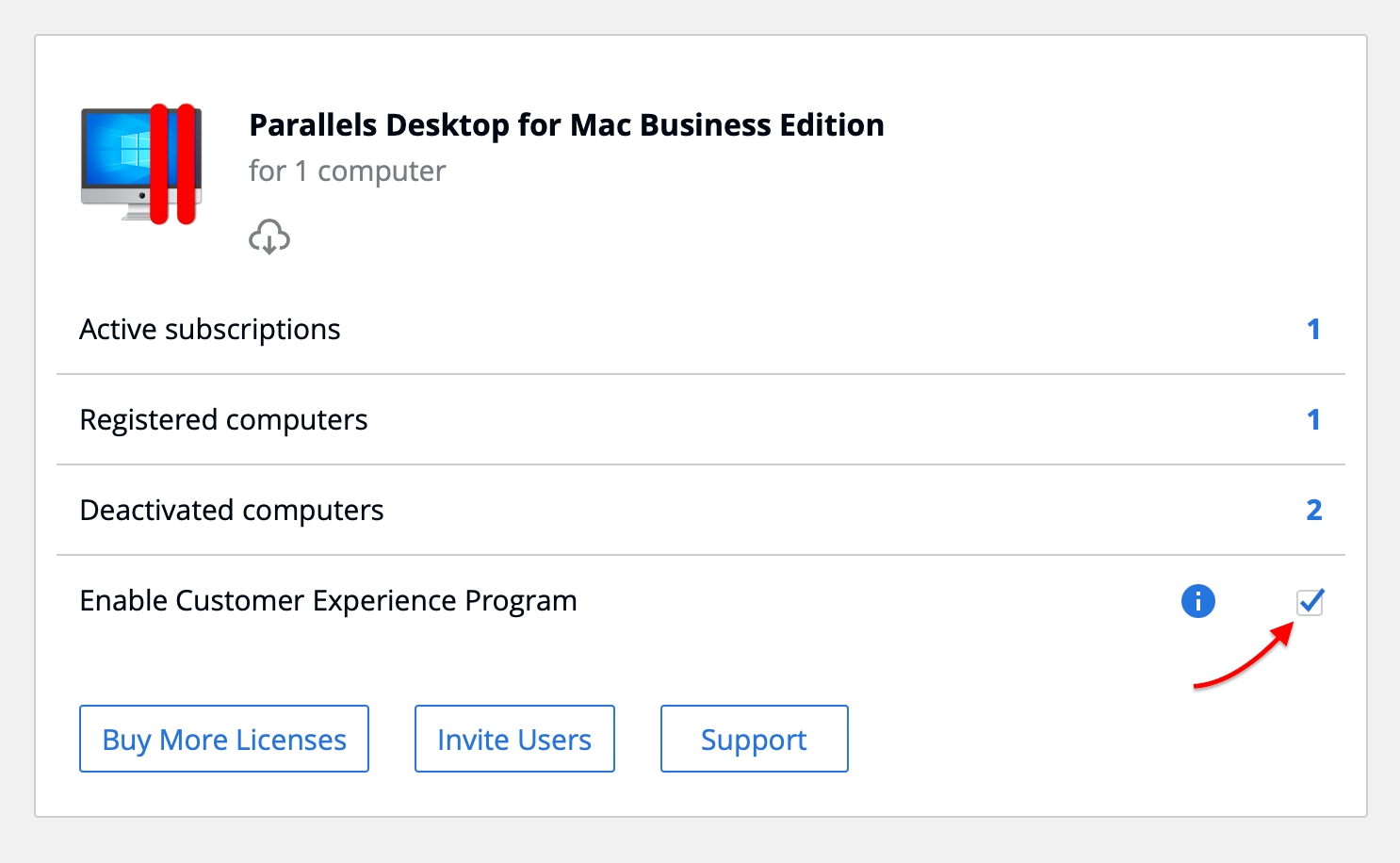
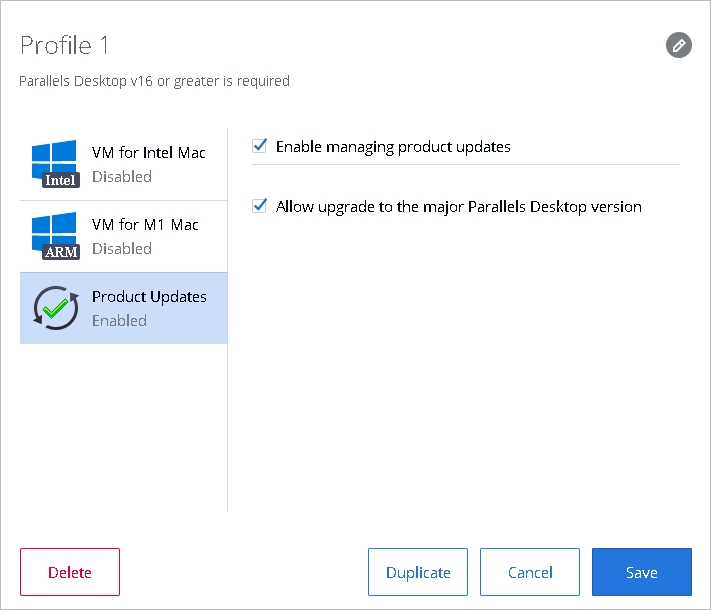

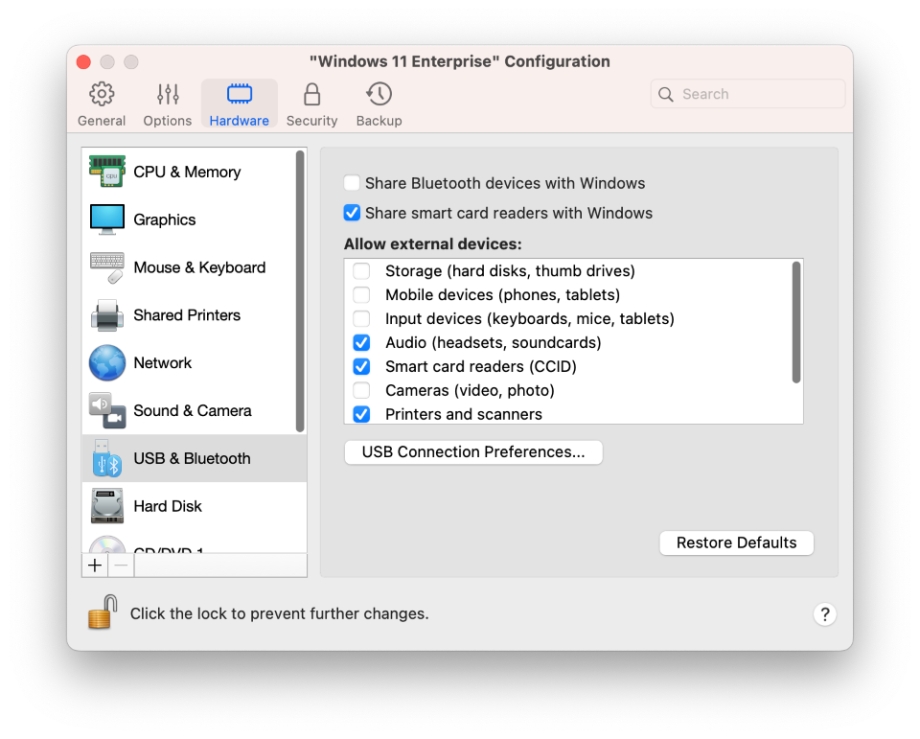



Jamf Pro includes the Software Distribution functionality that you can use to deploy the Parallels Desktop package to Mac computers in your organization. To deploy the package, you need:
Jamf Pro server installed or deployed in Jamf Cloud and configured.
Target Mac computers enrolled in Jamf Pro.
A distribution point (cloud or file share) configured and be accessible from the target Mac computers.
A distribution point is a server that hosts files and packages for distribution to computers. By default, the cloud distribution server is JCDS, where the recommended size limit for any single file/package is 20GB. If your Parallels Desktop deployment package includes a virtual machine and exceeds 20GB, you could consider switching your cloud distribution to Amazon S3, which allows 30GB files. You can change your cloud distribution point in Settings -> Server -> Cloud distribution point.
However, if your existing Jamf cloud distribution setup is already used for deploying other files and packages, and you would like to distribute a large Parallels Desktop deployment package which includes a pre-configured virtual machine, you could use a dedicated file share distribution point. To do so:
Go to Settings -> Server -> File share distribution points and user Ctrl+N to create a new one.
On the General tab page:
Type a name for the distribution point.
Specify the IP address or the host name of the distribution point server.
Leave the Use as principal distribution point option unchecked.
Leave the Failover distribution point as None.
Click the File Sharing tab and specify the following:
Protocol: Select AFP or SMB depending on which protocol is used on your server for file sharing.
Share name: Specify the share name. For example, if your server name is MYSERVER and your full share name is \\MYSERVER\JAMF-SHARE, specify JAMF-SHARE in this field.
Port: In most cases the default value is what a given protocol normally uses. If you know that your server uses a different port number, specify it here.
Read/Write Account: Specify credentials of an account that has read/write access to the share.
Read-Only Account: Specify credentials of an account that has read-only access to the share.
Click Save to save the settings and add the distribution point to your Jamf Pro setup.
If the size of your Parallels Desktop deployment package is within the limits of your preferred cloud distribution point, you can upload it for distribution:
Go to Settings -> Computer management -> Packages and use Ctrl+N to add a new package.
Fill out the Display name, Info, and Notes fields.
Use the Filename section to choose the Parallels Desktop deployment package file for uploading.
Click Save and wait for the package to upload. Monitor the Packages page for any error messages.
For a streamlined user experience, make sure to configure and deploy to the same target computers a configuration profile that will pre-determine the PPPC (Privacy Preferences Policy Control) access permissions for the Parallels Desktop app. This way, your users won't see any notifications about access to Desktop, Documents, or Downloads folders, etc.
From your Jamf dashboard, go to Computers -> Content Management -> Configuration Profiles and use Ctrl + N to create a new profile.
Fill out the mandatory fields in the General tab, such as Name, Description, and Distribution Method, as you see fit. Make sure to set the Level parameter to Computer Level.
Scroll down the left-side bar to reach the Privacy Preferences Policy Control tab and click on it.
Under App Access, set the Identifier to com.parallels.desktop.console, Identifier Type to Bundle ID, and leave the Validate the Static Code Requirement box unchecked. In the Code Requirement field, paste the following value, making sure to copy it carefully:
identifier "com.parallels.desktop.console" and anchor apple generic and certificate 1[field.1.2.840.113635.100.6.2.6] /* exists */ and certificate leaf[field.1.2.840.113635.100.6.1.13] /* exists */ and certificate leaf[subject.OU] = "4C6364ACXT"
If you want to verify the value of this parameter independently, launch macOS Terminal on a Mac with a copy of Parallels Desktop installed and execute the following command:
codesign -display -r - /Applications/Parallels\ Desktop.app
Under App or Service, use the + Add button to, at the very minimum, allow the app to access the Desktop (SystemPolicyDesktopFolder), Documents (SystemPolicyDocumentsFolder), and Downloads (SystemPolicyDownloadsFolder) folders. You may also want to enable Accessibility and ScreenCapture for other Parallels Desktop functionality, such as error reporting.
At the very top of the Configuration Profiles page, switch to the Scope tab and select the target computers or user groups.
In the bottom-right corner, click Save.
We suggest ensuring this profile is successfully deployed to all target computers before deploying the installation package.
Follow these steps:
From your Jamf dashboard, go to Settings -> Computer management -> Packages and use Ctrl + N to add the previously created deployment package to the system.
To deploy the added package, go to Computers -> Content Management -> Policies and use Ctrl + N to create a new package deployment policy. In the General tab, make sure to set Execution Frequency to One per computer, and in the Packages section, choose the recently added deployment package. Choose the target computers in the Scope tab.
Once the policy is retrieved by a Mac, it will install and activate Parallels Desktop on that Mac. Once completed, the user can begin working with Parallels Desktop.
If you are testing your policy, you can wait for it to trigger, or you can run it manually using the Self Service app. The app is installed when a Mac is enrolled in Jamf Pro and can be opened from the Applications folder in macOS. If there are errors executing the policy, you can review them in the app. Please also note that when testing a policy, don't try to run it on the same Mac that you use as a distribution point because an attempt to mount a share on the same Mac that hosts it will fail.
is a special Parallels Desktop deployment option that allows you to largely obscure Parallels Desktop and Windows on a Mac, making Windows applications appear native to macOS. This mode is designed for system administrators who want Mac users in their organization to run one or more Windows applications while minimizing their interaction with Windows or Parallels Desktop.
When Parallels Desktop is deployed using Single Application Mode:
A Mac user will not see the Parallels Desktop icon, user interface, or the virtual machine window while interacting with Windows applications.
A Windows application icon is added to the Dock and registered in macOS for opening the associated file types. When the user clicks on the icon, the application will run on a Mac desktop like a native macOS application.
A user's macOS workflows will remain largely unaffected by the background presence of Parallels Desktop and Windows.
Warning: Single Application Mode is incompatible with the Activation using corporate account (SSO) option.
To deploy Parallels Desktop using Single Application Mode, do the following:
Add a virtual machine to the autodeploy package. For instructions, see Adding a Virtual Machine. Please take note of the following:
You can add only ONE virtual machine when using Single Application Mode.
The virtual machine must be completely shut down before adding it to the autodeploy package. DO NOT simply close it, as this will be detected as a crash by Windows, and a Mac user will have to deal with it at startup.
Add a Windows application stub to the autodeploy package that will be used to run a desired Windows application on a Mac. If you want to deploy more than one Windows application, add a corresponding stub for each one. For details, please see Adding Windows Application stubs.
To enable Single Application Mode, set the enable_single_application_mode="yes" parameter in the deploy.cfg file, as described in Configuring deployment options. The parameter is included in the User Experience section of the deploy.cfg file.
Deploy Parallels Desktop to Mac computers as described in Deploying Parallels Desktop and Virtual Machines on Macs.
For Windows to be completely hidden on a Mac, you need to make some changes manually because they cannot be automated. The following list describes these changes:
Enable auto logon in Windows. Make sure that Windows in the virtual machine doesn't ask the user to log on. If this is not done, a Mac user will see the Windows logon screen when Windows starts or reboots.
Configure file associations in Windows. This is necessary so that Windows doesn't open another Windows application when the user tries to open a file from the primary application. For example, let's say you deployed Outlook for Windows. A Mac user may try to open a text file attachment in Outlook. Normally, the file will open in Notepad in Windows, which may confuse the user. To prevent this, you can associate text files with TextEdit (a macOS application) in a virtual machine. The ability to associate file extensions with macOS applications is a standard Parallels Desktop feature available in Windows in a virtual machine. In addition, we recommend that you have as few applications installed in Windows as possible in order not to create additional file associations.
Use the Productivity profile. When creating a virtual machine for Single Application Mode, choose the Productivity profile in the virtual machine Installation Assistant. If you are using an existing virtual machine, change its profile by going to Configuration > General > Configure for, clicking Change, and then selecting Productivity.
Remove Sound & Camera devices from the VM configuration. This will eliminate the chance of macOS prompting the user to provide Windows with access to the respective hardware. To do that, go to Configure > Hardware > Sound & Camera and click the "-" button in the bottom left corner.
Note: There's a known issue when users may see Windows screens when Windows is installing updates. There is also a known issue of macOS prompting users to allow Windows apps access to user folders at the first launch. Consider starting the application once after deployment and resolving all requests manually.
If you are deploying Parallels Desktop on macOS High Sierra, macOS Catalina, or macOS Mojave, you need to make sure in advance that Parallels Desktop kernel extensions are either approved or don't require user consent on each Mac. This is particularly important when using the Single Application Mode because if the extensions are not approved, Mac users will see warning messages about them when they try to run a Windows application for the first time. For more information, please see https://kb.parallels.com/en/128435.
This section allows you to monitor all the Parallels virtual machines in use with your organization and delete them in case of need. The list shows not only the corporate machines installed from the Golden Images but also other virtual machines running on your users' Parallels Desktop installations.
You can use the drop-down menu in the top-left corner to select which of the following parameters you want to monitor:
User name. This parameter is derived from the user account name on that Mac;
Computer name;
VM device name. As designated during the virtual machine’s image preparation process;
VM device ID. As generated during the virtual machine's registration with Parallels Desktop;
VM state. This parameter has the following possible values: Running, Stopped, Suspended, Unknown;
VM status. This parameter will help you sort between active virtual machines, the ones whose Parallels Desktop setup had been deactivated, and the ones that have failed to delete;
VM OS, VM Edition, VM OS build. This sorts your organization’s virtual machines by the operating systems, including editions and build numbers;
VM serial number. This serial number is generated by Parallels Desktop for Mac. For Windows and Linux virtual machines, the format is "Parallels-6A F9 99 70 E2 6E 4F AB A4 CD 91 8C E4 29 A4 7D" while for macOS virtual machines, the format is "XNTJH2MFPN". This parameter resets to a new random value when a virtual machine image registers on an end-user's Mac;
VM Source. This parameter helps you identify which virtual machines were set up using your company's Golden Images;
VM encryption. This parameter reflects the encryption status of a specific virtual machine. The possible values are "Not encrypted", "Encrypted with a custom password", or "Encrypted (license based)". The latter value reflects the use of the Do not allow running virtual machines without this company's Parallels license policy as described in the Policies chapter;
Last command. This parameter reflects the last command sent to the Parallels Desktop installation. The possible values are "None"; or "Pending delete", "Pending lock", "Pending redownload", "Pending restart", etc. for the commands that have been sent but not yet executed; or "Failed to delete", "Failed to lock", etc., for the commands that failed to execute;
Last used date (UTC). This shows when the particular virtual machine was last launched. This parameter may help you quickly find unused virtual machines;
Last reported date (UTC). This parameter shows the date and time a specific virtual machine’s presence was reported to the server;
Parallels Desktop Version. This shows the major version number of the Parallels Desktop installation used to run a specific virtual machine. This may help you identify installations that have failed to upgrade to a newer, better version of Parallels Desktop;
Parallels Desktop State. This shows the activation state of the Parallels Desktop installation used to run a specific virtual machine. The possible values are "Activated (SSO)", "Activated (License Key)", and "Deactivated". If you are, e.g., trying to migrate your user base from one activation type to another, this parameter may help you identify the users that require your attention;
Parallels Tools Version. Using this parameter, you can, for example, identify the machines in your organization that either do not have Parallels Tools installed or use an outdated version;
Mac serial number;
CPU. In this column, you can sort your virtual machines by their operating systems’ target architecture: Intel or Arm (Apple silicon);
Uncheck the parameters you won’t need for your monitoring requirements.
Use the drop-down menu in the bottom-right corner to adjust the number of virtual machines shown per page from 10 to 40.
Use horizontal scrolling to adjust column widths and ensure all selected columns are displayed.
Use the search bar in the top right corner to find virtual machines by their known parameters, or use the individual filters in each column to search by that column’s parameter. Clicking on the funnel symbol in the header of each column will help you filter virtual machines by a specific parameter.
This may, for example, help you quickly identify the machines that require your immediate attention when an urgent upgrade is required to plug a known severe vulnerability.
Once you have located a specific virtual machine, you can delete it by right-clicking on it and selecting Delete Virtual Machine or using the context menu on the right marked with three dots. Read the dialog carefully and confirm by clicking Delete.
If you delete the only virtual machine that was running on a particular Parallels Desktop installation, its user will be offered to download a new virtual machine from the Golden Image supplied by your organization.
Sometimes, information on a specific virtual machine may be incomplete or entirely missing from the Parallels Management Portal's virtual machine monitoring panel described earlier in this chapter. This section provides a list of possible explanations for each case so that you may follow it to eliminate potential causes.
The VM is no longer active or has been removed.
The Parallels Desktop for Mac application did not manage to report/communicate with the Parallels backend after the VM was created.
The Parallels Desktop for Mac application is on an older version that does not support reporting these specific details. Use the Parallels Desktop Version parameter to verify.
The Parallels Desktop for Mac application has been updated but hasn’t reported to the portal yet. Use the Last reported date (UTC) parameter to verify.
A virtual machine OS version info may be missing when that virtual machine hasn't been launched, or Parallels Tools weren't installed for it.
Parallels Tools is not installed.
Parallels Tools is installed but outdated and requires an update. Use the Parallels Tools Version parameter to verify.
When creating a new policy or editing an existing one, you may use the opportunity to establish remote administrative control over the settings for individual virtual machines in your corporate setup. This may help you prevent information leaks or minimize potential security vulnerabilities. This chapter lists the virtual machine settings that are available for remote control.
The following settings are currently available:
Attention: While all the listed settings are available for virtual machines running Windows, not all of them are supported for virtual machines running Linux, or macOS (on Intel or Apple silicon Macs). The supported guest operating systems are clearly marked across each individual setting. Consult the following table for applicability of particular settings.
VM startup and shutdown
This drop-down menu controls how the virtual machine starts.
Manual. This option leaves the decision to launch or shut down the virtual machine to the user.
Ready in background. With this option, the virtual machine starts automatically with your Mac and remains ready in the background. This way, clicking on a Windows app icon in macOS instantly launches it without having to wait for the virtual machine to boot up.
Network source Note: If this setting is controlled remotely, the users won't be able to change other Network settings like Network Conditioner either. Adding another network adapter to the virtual machine's hardware configuration won't help: its settings will also be set as prescribed in the policy and won't be available for changing.
This drop-down menu controls the network settings for the Parallels virtual machines covered by a specific policy. The options are:
Disconnect. This option fully disconnects the virtual machine from any networks.
Shared Network (recommended). This option enables the Network Address Translation (NAT) feature for the virtual machine. In this case, your virtual machine shares whatever network connection is currently used by your Mac.
Host-Only. This option allows the virtual machine to connect to your Mac and other Parallels virtual machines on it but make it invisible outside the Mac. If this option is selected, the virtual machine cannot connect to the Internet.
Bridged Network (Default adapter). This options allows the virtual machine to access the local network and Internet through the default network adapter of your Mac. The virtual machine is treated as a stand-alone computer on the network and should be configured as such. Note: When set locally, this option allows you to select which Mac network adapter to use. However, when controlled remotely via a policy, the only option is to use the default adapter.
Isolate VM from Mac Note: Some of the settings in this section are not available on all supported platforms.
This section contains several ways to isolate the virtual machine from macOS, so that they no longer share folders, profiles, and applications. Connected external devices are no longer automatically accessible by the guest OS, the virtual machine and Mac no longer synchronize volume, and you can no longer copy or move objects between the virtual machine and macOS. Isolating your virtual machine from macOS may provide a higher level of security by not allowing compromised items from one OS to come into contact with the other. The section contains several specific settings for a more granular setup:
Disable sharing Mac folders with VM. This will prevent the virtual machine from accessing folders in the host Mac's macOS.
Disable sharing VM folders with Mac (Windows only). This will prevent the virtual machine from accessing folders in the virtual machine.
Disable sharing VM apps with Mac (Windows only). This will prevent opening Windows applications from the host Mac's macOS Finder.
Disable sharing Mac apps with VM (Windows only). This will prevent opening the host Mac's macOS applications from within the virtual machine.
Control clipboard synchronization (not supported for macOS virtual machines on Apple silicon Macs). This setting controls the contents of copy-and-paste clipboard between the Mac's macOS and the virtual machine.
Disconnect. Use this setting to completely isolate the clipboards of the Mac's macOS and the virtual machine.
Bidirectional. Fully syncronized clipboard, allowing users to freely copy and paste between the two systems.
Guest OS to Mac only
Mac to Guest OS only
Disable sharing smart card readers with VM (not available for macOS virtual machines on Apple silicon Macs)
Activating this option will isolate the smart card readers connected to the Macs from the Parallels virtual machines that run on them.
Do not allow external devices
Activating this option will bar your users from connecting external (i.e., USB) devices to the Parallels virtual machines running on their Macs. Note: When activated locally, this option enables you to granularly blacklist specific types of USB devices that you want to prevent, e.g., storage devices, mobile phones, or cameras. The Management Portal policy doesn't allow blacklisting specific types of USB devices yet. .
Always lock VM on suspend (not available for macOS virtual machines)
This option enforces the locking of virtual machine operating systems when they are suspended. Once the virtual machine is resumed, you’ll have to log into its operating system to unlock it.
Do not allow changing VM configuration (not available for macOS virtual machines on Apple silicon Macs)
Activating this option would prevent users from changing any virtual machine settings that are not listed here. For a complete list of virtual machine settings available in Parallels Desktop, read . Note: The linked chapter primarily describes settings available for Windows virtual machines. Available settings for Linux and macOS machines may differ.
Show Developer Tools (not available for macOS virtual machines on Apple silicon Macs)
This option unlocks an additional Parallels Desktop macOS bar menu that allows users to start SSH and debugging sessions with their virtual machines, generate core dumps, edit Windows registry, and . Developer tools are also available via .
Disable automatic updates of Parallels Tools
Parallels Tools are a suite of behind-the-scenes tools that allow seamless interaction between your Mac's macOS and a guest operating system. They normally update automatically, but this setting enables you to prevent that. To learn more about Parallels Tools, follow .







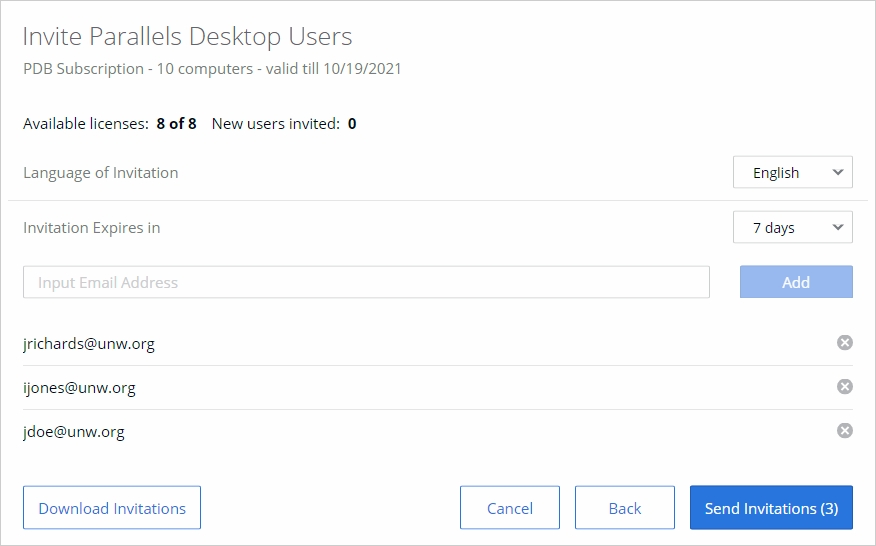









On this page, you can assign policies for pre-existing user groups that you can set up in Parallels My Account. Each user group is a sublicense of your main Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition license with a unique key. Read this chapter to learn more.
Attention: If you want, you may assign a new policy to the users activated with the primary license key. However, for security reasons, we strongly advise against using your primary key directly. Any compromised secondary (sublicense) keys can be deleted and replaced with new ones.
To create user groups and populate them with users, please refer to this page. If you plan on using Single Sign-On for license activation, refer additionally to this page.
To create a new policy, click on the Add button in the top left corner of the page. This will launch the multi-page policy creation process where you will have to provide the following information:
Name. Use a unique descriptive name in case the number of policies increases in the future.
Description.
Policy applies to. This setting allows you to add and remove the groups (as defined by secondary license keys) that the policy applies to. Note: At any given time, each group may only have ONE policy applied to it, so you won't be able to add groups that already have other policies that apply to them. If you don't divide your Parallels users into groups, or have users assigned to the primary license key, you may assign a policy to the primary license key. To add a group, use the drop-down menu as indicated in the image above. To remove one already added, click on the (X) symbol next to the one already listed. Note: You may choose to apply a specific policy to the users whose copies of Parallels Desktop are activated with the primary license key. These settings will not affect any users who are on secondary license keys or have been included in one of the SSO user groups.
Click Next.
Throughout the policy creation process, you may use the Next and Previous buttons to move between the various steps and check settings.
Each policy includes a dedicated Golden Image that you may want to tailor to that group's specific needs.
Attention: Starting from version 20250909 of the Parallels Management Portal, the Policies page is the sole place for assigning Golden Images to specific groups, while the Golden Images page remains the place where you create and/or customize them. Previous Golden Image assignments will be automatically combined with existing policies or turned into new ones.
Use the drop-down menu to select the preferred Golden Image and click Next.
At this step, you need to select specific limitations that will apply to this group of users. Presently, policies only define what users from your organization can do with their Parallels Desktop setups and not their virtual machines. The available controls are:
Limit users to provisioned VMs only. This policy prevents users from setting up new virtual machines from sources other than your organization’s Golden Images, as well as importing or cloning pre-existing ones. You may want to enact this policy to prevent members of your organization from setting up virtual machines for their own extracurricular activities.
Limit the number of provisioned VMs per user to one. This setting prevents users from installing any more virtual machines from the approved sources (i.e., your organization’s Golden Images). Note: If you select this option alone, without the previous option, users will still be able to add new virtual machines using third-party sources, such as the default images available through Parallels Desktop.
Do not allow removing provisioned VMs.
Do not allow upgrading to the next major Parallels Desktop version. This setting will still allow users to update their Parallels Desktop installations to a minor version (e.g., 26.0.1 to 26.1) but will prevent them from upgrading to a major version (e.g., from 20.x to 26.x) when it becomes available. Enabling this setting will allow you to first ensure that a major new version suits your needs before proceeding with a fleet-wide upgrade. Note: This setting will have no effect if your organization is running a local update server or your update policies are managed via an MDM solution.
Do not allow editing Parallels Desktop preferences. This setting prevents users from changing the preferences for their Parallels Desktop setups. With this policy applied, users attempting to open Parallels Desktop preferences by clicking Parallels Desktop > Preferences in the Mac menu bar will encounter a message telling them the action is blocked and referring them to the IT department. To learn more about the settings that can be changed in the Parallels Desktop Preferences panel, read of the Parallels Desktop's user guide.
Do not allow running VMs without this company's Parallels license. This setting prevents users from transferring and launching their virtual machines (as well as Golden Images) to Parallels Desktop installations that don't have your organization's Enterprise license. Read more on virtual machine encryption here. Note: The initial application of this setting to existing Parallels Desktop installations already running provisioned virtual machines will trigger a re-encryption procedure that will temporarily render those virtual machines unavailable for use. The users will receive a clear message when attempting to launch such virtual machines. Encrypting virtual machines using a command-line interface will become unavailable.
Select the required settings and click Next.
This step allows you to control virtual machine settings remotely as part of the policy. Enable it by toggling the switch for the provisioned virtual machine image that you have selected previously (it will be marked as Current GI), and introduce the required settings.
If your policy allows users to create/add virtual machines from sources other than the provisioned Golden Image, you may also want to toggle the switch for VMs from other sources and introduce different or similar settings for those.
For the detailed description of available settings, refer to this sub-chapter.
Once you have filled out all the settings, click Add to enable the policy. You won't be able to create it unless all mandatory fields are filled.
The newly created/amended policy will apply to the target installations when the local Parallels Desktop for Mac installation checks for them. It is designed to happen on the following triggers:
The launch of the app.
Activation or reactivation.
Creating a new virtual machine.
A change of state of a virtual machine, including:
Start.
Suspend.
Resume.
Shutdown.
Change of virtual machine parameters (see more here).
Change of the Mac's network status, e.g., getting online.
If none of the above occurred, once a day per schedule.
The default view of the main Policies screen shows you the list of all the policies under your management, citing their names as provided during the setup process, their descriptions, and the list of groups they apply to. Right-clicking on a policy from the list allows you to edit or delete it.
If a policy is marked as "not applied", it either means that no groups were selected during the creation, or the group(s) it initially applied to was (were) deleted.
Warning: Deleting a policy is non-reversible. Please make sure you are deleting the right one.
By default, the integration process between Parallels My Account and your identity provider, described in , implies that all users of Parallels Desktop for Mac in your company will end up in one user group.
However, as explained in , it may be beneficial to spread your end users across multiple groups, depending on their departments or functions within the company. This will enable administrators to provision tailored or set their own restrictions for each individual group of users, as described in of the Parallels Management Portal section of this guide.
Attention: All the users that need to activate Parallels products using SSO still have to also be included in the main user group created as part of the .
The goal of this chapter is to explain the intricacies of the grouping process and prevent potential activation or policy application issues. As a result of these procedures, you will end up with distinctive groups of Parallels Desktop users tied to specific sublicense keys, to which you can apply specific policies and restrictions and provision different golden images.
Warning: Under no circustances should you attempt to configure a multi-group setup without first establishing a working, well-tested configuration with just one user group as described in the and having a working plan how to revert to that.
You may choose to divide your company's Parallels Desktop users into entirely new groups or use the groups that already exist in your IdP setup. However, we strongly recommend you to plan before acting:
Create an organizational chart with all planned subdivisions.
List the concrete differences in their access requirements that may warrant individual virtual machine images and the application of specific policies. Check the list of available policies .
Itemize the number of Parallels Desktop licenses that each group may need. Consider, which users need guaranteed access, and which groups will suffice on "first come, first served" principle. Compare the sum total of required licenses with the overall number of license seats in your Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition setup. Create the respective in Parallels My Account to see if the numbers add up.
For the purposes of this guide, the most important term on your IdP's side is a unique group identifier, which, depending on your IdP, can also be known as UUID, Object ID, or group name. Another important term is a SAML token: a file which contains information about a user and is sent by IdP to the service provider (in this case, Parallels) during the SSO authentication process. The individual meaningful pieces of information in SAML tokens are called claims.
What binds these three terms together is that certain claims in SAML tokens contain group identifiers, allowing Parallels service to see what groups the authenticated user is included in on the IdP side.
Some IdPs allow administrators to create hierarchical user group structures to better reflect the organizational structure of the company, e.g., a "Product" group that would include subgroups like "Engineers", "Designers", "QA", etc. In this case, a member of the "Engineers" subgroup would have at least two group identifiers in their SSO claim: one for the "Product" group, and one for the "Engineers" subgroup.
With the above information in mind, your overall process to divide the Parallels Desktop for Mac users in your organization into individually managed groups should include the following steps:
Evaluate which existing groups of users may need which specific policies and restrictions. Read carefully.
Plan the user allocation. Consider how many users from each affected group may need to activate and use Parallels Desktop for Mac, which will require guaranteed service (reserved sublicense keys), and which will be better off on a first-come, first-served basis (dynamic sublicense keys). Read more about the difference .
Ensure the correct settings of the Parallels Desktop application on your IdP side so that the SAML token exchanged during the SSO authentication process includes the group identifiers for all the groups a user belongs to. In Microsoft Azure/Entra ID, follow this path Home → Entra ID (formerly AD) → Enterprise applications → Select Application → Single sign-on → 2. Attributes & Claims -> Edit and make sure the Group Claims setting is set to All Groups and not Groups assigned to the application.
Once you make this change, the Parallels service will receive information about all user groups a given user is a member of on a SSO sign-on attempt, and will deduct the seat from a specific license key accordingly. Note: In the case of Okta, you have to map pre-existing groups to the application directly.
[IMPORTANT] Ensure that your Microsoft Azure/Entra ID setup identifies users correctly:
Go to MS Azure Home > Entra ID (formerly AD) > Enterprise applications.
Select the Parallels enterprise application in the list, click on it to open the application’s home page, and choose Provisioning in the Manage section on the left-hand side panel.
Open the Attribute mapping tab and click on Provision Microsoft Entra ID Users. There, under the Attribute Mappings section, locate the externalId parameter, click Edit, change the Source attribute parameter from mailNickname to objectId, and click OK. Click Save in the top left corner.
Note: Without this step, there may be a mixup in product license provisioning between users with similar names.
To benefit from tailored policies and license key quotas, create sublicense keys as directed in . To map a user group on the IdP side with a specific sublicense key, take this group's group identifier and add it to the selected key in Parallels My Account. In the case of Microsoft Azure/Entra ID, the group identifiers can be found by following this path: Home -> Microsoft Entra ID (former AD) -> Enterprise Applications -> Select Application -> Users and groups -> Select Group -> Object ID. To paste the value in Parallels My Account, linking the group to a specific sub-license key, open Parallels My Account and follow this path: Find the Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition product card -> Click on the Subscription Details line -> scroll down to the License Keys section. Click the cogwheel symbol to open that sublicense key's card and switch to the User Groups tab. Click Add Group and paste the group's name and UUID (Object ID) in the respective fields. Note that in the case of Okta, the user group UUIDs are the same as the group names, as described in the respective .
Note: You can assign more than one user group to a specific license key. When dividing your users into groups and subgroups and assigning those groups to sublicense keys, your priority should be to ensure that no single user is simultaneously a member of two groups (directly or via a hierarchical structure) that are assigned to two different keys. Such a setup may lead to their license seat being assigned from the wrong sublicense.
Once you have added all the groups you want, click Save.
Now, your users can activate their copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac using their groups' assigned quotas, and you can apply group policies as you see fit.
The chart below will help you troubleshoot your multi-group setup, showing the possible reasons why an SSO process may fail.










Follow the steps below one by one to integrate Parallels My Account with Google Workspace.
A domain is a part of the email addresses (after the @ symbol) used by the end users in your organization. When end users try to log in to Parallels My Account using SSO, they are prompted to enter their work email address. Parallels My Account checks the domain part of the email address and recognizes that the user belongs to your organization. Click on the title of Step 1 to expand it, and read the instructions carefully.
Add one or more domains your organization uses.
Each domain must be unique and can only be registered to one business account that your organization has registered with Parallels.
Make sure to add only the domains your organization can control.
The Parallels My Account service verifies the domain ownership by checking a specific TXT record that must be added to the DNS host of the corresponding domain. Make sure that all domains added to the list are verified before proceeding with the next steps.
Depending on the software and/or provider, a TXT record may take up to 72 hours to propagate. You can check whether it's been configured using the following command:
$ dig TXT {yourdomain}.{com}Registering the Parallels enterprise application (required for integrating with the Parallels My Account service) in the IdP Directory allows you to configure the SSO-related parameters and correctly provision the integration between your IdP and the Parallels My Account service.
With Google Workspace, it is simpler to first create the necessary user groups for the app. At least two groups are required: one for users with business account privileges in Parallels My Account (enabling them to manage issuing license seat quotas etc.) and at least one for the users who need to activate Parallels Desktop for Mac on their computers.
To create a group in Google Workspace, do the following:
Launch your Google Admin console and use the left-hand side panel to expand the Directory section and choose Groups.
Click on Create group to launch the procedure of creating a group.
Fill out the required details, make sure to activate the Security label, and click Next.
On the next page, select the security settings as you see fit and click Create Group to finish the process.
Choose Add members at the next step and populate the group. Note: Remember that anyone who needs to activate Parallels Desktop for Mac with their Google Workspace login must be included in the main Parallels Desktop users group, even if they are already included in the group for business account administrators.
Remember to repeat the process to create at least two groups, one for users with business account privileges in Parallels My Account (enabling them to manage issuing license seat quotas, etc.) and at least one for the users who need to activate Parallels Desktop for Mac on their computers.
The below process describes setting up a new Enterprise Application for Google Workspace:
Launch your Google Admin console and use the left-hand side panel to expand the Apps section and choose Web and mobile apps.
Open the Add app drop-down menu and choose the Add custom SAML app option.
Fill out the name and description for the Parallels app.
In the next step, copy the presented values from Google Workspace to Step (4) Configure SAML Integration section of the Parallels My Account SSO setup page the following way:
SSO URL (Google Workspace) -> Identity Provider SSO URL (Parallels My Account)
Entity ID (Google Workspace) -> Identity Provider Entity ID (Parallels My Account)
Certificate (Google Workspace) -> Public Certificate (Parallels My Account).
At the next step, Service Provider Details, use the values from the Step (4) Configure SAML Integration section of the Parallels My Account SSO setup page to copy the following parameters:
Assertion Consumer Service URL (Parallels My Account) -> ACS URL (Google Workspace)
Service Provider Entity ID (Parallels My Account) -> Entity ID (Google Workspace)
Set the remaining parameters to the following values:
Leave the Start URL field blank.
Under the Name ID section, set the Name ID format to EMAIL, and Name ID to Basic Information > Primary email.
The next step, Attribute mapping, is very important, and you should pay close attention to setting all the parameters correctly, keeping the spelling and capitalization exactly as presented. Use the Add Mapping button to map the following value pairs:
Basic Information > First name (Google Directory attribute) -> displayName (App attribute).
Basic Information > Primary email (Google Directory attribute) -> name (App attribute).
Employee Details > Employee ID (Google Directory attribute) -> objectidentifier (App attribute).
Under the Group membership section, choose the groups of Parallels My Account administrators and Parallels Desktop users created previously and map them to the app attribute groups.
Click Finish to complete the setup process.
Switch back to the SSO setup page in Parallels My Account and mark Step (2) Register the Parallels Enterprise App and Step (4) Configure SAML Integration as complete.
Proceed to the next step.
Having created the user groups in the previous step, you should add the groups' names and IDs to the respective fields Step (3) Configure User Groups Mapping of the integration configurator page in Parallels My Account.
Take the following steps.
Launch your Google Admin console and use the left-hand side panel to expand the Directory section and choose Groups.
Copy the group's name to a notepad app for both the Administrators and the Users group.
Switch to the Parallels My Account integration page, expand Step (3) Configure User Groups Mapping, and use the click to edit links to copy the respective group's name into BOTH FIELDS, UUID and Display Name, for administrators, and click Save.
Take care to use the correct values for each group.
Mark Step (3) Configure User Groups Mapping as complete.
Once the required groups have been created in the IdP Directory and associated with the Parallels app, move on to the next step.
The SAML 2.0 is supposed to be configured for the Parallels enterprise application registered with Google Workspace at the time of the Parallels enterprise application registration (refer to chapter (2) Register Parallels enterprise app and configure SAML settings earlier in this document for more details).
Make sure to check the Step 4 section on the integration configurator page at Parallels My Account. All fields must be filled in, and the Configuration in the IdP Directory is done option must be enabled.
If everything is set, proceed to the next step.
SCIM 2.0 integration between Parallels My Account and your Organization’s IdP allows you to keep user identity information in Parallels My Account in constant sync with the updates made to user identities in the IdP Directory.
Warning: At this point, Parallels does not support SCIM integration for Google Workspace.
Due to the lack of SCIM integration, the administrator will have to manually add and remove users in Parallels My Account, as well as on the Google Workspace side.
To revoke a license on the Parallels My Account side, follow these steps:
Open the Virtual Machines page of the Parallels Management Portal and identify the machine using the following three parameters: User name, Computer name, and Parallels Desktop state. The latter will help you spot the machines activated using SSO.
Write down the computer name of the Mac where you need to revoke the license.
Open the Parallels My Account main page, select the Enterprise product card, and click on the Registered Computers link.
Select the target Mac using the checkbox on the left, and use the Actions menu in the top right corner to deactivate the license.
On the Parallels My Account SSO setup page, expand Step (5) Configure SCIM Integration and make sure the Enable SCIM Support checkbox is unticked.
Continue to the next step.
For users to be able to make use of the application to sign or activate with Parallels, they have to be created and added to the groups tied to the Enterprise Application.
If you need to add more users to the groups created in step (2), open your Google Admin console and use the left-hand side panel to expand the Directory section and choose Groups. Point your mouse at a specific group and use the Add members button to populate it with users as required.
Once it is done, or if you plan to add users later, switch back to the Parallels My Account SSO setup page, expand Step (6) Add Users to Application Groups, and mark the Configuration in the IdP Directory is complete checkbox at the bottom of the section.
The backup login can be used to access your organization’s business account registered with Parallels, bypassing Single Sign-On in the event of an SSO malfunction. By default, the backup login is set to the email address of the currently logged-in user. If you want to define a different backup login, add more users first on the Users page of the Business Profile section in Parallels My Account. The new user must log into the business account at least once before they can be designated as a backup login.
Warning: Once you have completed the integration process and activated the SSO functionality, only users from the Administrators group in your IdP signing in via SSO will retain access to managing the Parallels business account. All previous administrative privileges based on logins and passwords will become inactive.
Your designated backup login will continue to work.
Follow the steps below one by one to integrate Parallels My Account with JumpCloud.
A domain is a part of the email addresses (after the @ symbol) used by the end users in your organization. When end users try to log in to Parallels My Account using SSO, they are prompted to enter their work email address. Parallels My Account checks the domain part of the email address and recognizes that the user belongs to your organization. Click on the title of Step 1 to expand it and read the instructions carefully.
Add one or more domains your organization uses.
Each domain must be unique and can only be registered to one business account that your organization has registered with Parallels.
Make sure to add only the domains your organization can control.
The Parallels My Account service verifies the domain ownership by checking a specific TXT record that must be added to the DNS host of the corresponding domain. Make sure that all domains added to the list are verified before proceeding with the next steps.
Depending on the software and/or provider, a TXT record may take up to 72 hours to propagate. You can check whether it's been configured using the following command:
$ dig TXT {yourdomain}.{com}Registering the Parallels enterprise application (required for integrating with the Parallels My Account service) in the IdP Directory allows you to configure the SSO-related parameters and correctly provision the integration between your IdP and the Parallels My Account service.
The below process describes setting up a new Enterprise Application for JumpCloud:
Log into the JumpCloud administrative console. On the left-hand side panel, find the User Authentication section and select SSO Applications". Click the + Add New Application button on the new page.
At the Select Application step, choose the Custom Application option in the bottom right corner and click Next at the next screen.
At the Select the features you would like to enable step, choose Manage Single Sign-On (SSO) and Export users to this app (Identity Management) options. For the SSO functionality, choose the Configure SSO with SAML option. Click Next.
At the Enter general info step, fill out the parameters as you see fit and click Save Application in the bottom right corner. Make sure to devise a unique login URL under Advanced Settings. Note: We recommend you uncheck the box Show this application in User Portal. Clicking on the application icon from JumpCloud's user portal triggers IdP-initiated SSO, which is currently not supported.
Click Configure Application in the bottom right corner to continue setting up the Parallels application's integration with JumpCloud.
Select your application from JumpCloud's list of Configured Applications, and make sure you are switched to the SSO tab.
In the IdP Entity ID field, type in a unique name, e.g., "JumpCloudParallels".
Go to the SSO setup page of Parallels My Account, expand Step (4) Configure SAML Integration, and copy the URL parameters into the respective fields of the SSO tab on the JumpCloud side:
From Service Provider Settings/Service Provider Entity ID (Parallels) to SP Entity ID (JumpCloud);
From Service Provider Settings/Assertion Consumer Service URL (Parallels) to ACS URLs/Default URL (JumpCloud).
Note: Alternatively, you may use the Download the metadata file link on the Parallels side and the Upload Metadata button on the JumpCloud side to populate the fields automatically.
IMPORTANT! Under the Sign* section of the JumpCloud SSO settings tab, make sure to select the Assertion and Response option.
IMPORTANT! Under the Login URL section of the JumpCloud SSO settings tab, make sure to tick the Declare Redirect Endpoint box for this address to be included in the IdP metadata file.
Scroll down to the Attributes section and use the add attribute button to add the following attributes exactly as shown in the image below:
Under the GROUP ATTRIBUTES section, check the box titled include group attribute and set the parameter to groups, and click Activate SSO if it is not active yet.
Switch back to the Parallels My Account, expand Step (2) Register the Parallels Enterprise App, and check the Configuration in the IdP Directory is complete box.
While you have the SSO tab of your Parallels application open on the JumpCloud side, you can also finish configuring the SAML integration. Follow these steps:
On the JumpCloud side, in the same SSO tab of your Parallels app card, scroll to the very top and click the Export Metadata button. This will download an XML file to your computer.\
On the Parallels My Account side, go back to the SSO setup procedure, expand Step (4) Configure SAML Integration, locate the Identity Provider Settings section and use the Upload the metadata file link to upload the XML file that you have just downloaded from JumpCloud.
Note: If the upload fails for some reason, open the file in a text editor and copy the contents as directed: the value entityID into the Identity Provider Entity ID field, the URL from the location value into the Identity Provider SSO URL field, and the public key from the <ds:X509Certificate></ds:X509Certificate> tag into the Public Certificate field.
Click Save to update the configuration and check the Configuration in the IdP Directory is complete box.
Proceed to the next step.
You must create user groups associated with the Parallels Desktop application in your IdP Directory. Later, you will add users to those groups to let Parallels My Account know which users should have business account admin privileges in the Parallels ecosystem. At least one user group is required to add users with admin access to your organization’s business account registered with Parallels, and one more is required for the users of Parallels Desktop for Mac. Once the group is created, you should add the group's name and ID in Step 3 of the integration configurator page in Parallels My Account.
Start with creating the group in the IdP Directory. To do so, switch to your IdP management portal and follow the standard procedure of creating a user group and associating it with the Parallels enterprise application, as provided by your Organization’s IdP. The description below illustrates the registration procedure for JumpCloud. It is assumed that you have appropriate permissions to manage user groups in JumpCloud. To create a user group for the Parallels enterprise application in JumpCloud:
In the JumpCloud admin console, find the User Management section on the left-hand side panel and click on User Groups.
Click on the + button to create a new group.
In the new group panel, give it a name (e.g., Parallels Desktop Administrators), and optionally, add a description and click Save Group in the bottom right corner.
At least two groups are required: one for the administrators with access to license management in Parallels My Account and one for the app users who need to activate their Parallels Desktop licenses.
Note: If any of the administrators also need to activate Parallels Desktop, you also need to add them to the user group.
Wait for the newly created group to appear on the group list and click on it to configure.
On the Details tab, scroll down to the Custom Attributes section, click the + Add Custom Attribute button, and select the type String.
In the Attribute Name field, put the name of the group attribute as specified in Step 11 of the (2) Register Parallels Enterprise App and Configure SAML Settings section above, in this case, groups.
For Attribute Value, see the address in your browser's address bar and identify the unique group ID in it, i.e., for https://console.jumpcloud.com/#/groups/user/67c0bea6ecc3120001efa8da/details, the value will be 67c0bea6ecc3120001efa8da. Write down the identifier value for later use.
Click Save Group and repeat for all the groups.
In JumpCloud, go back to the SSO Applications section, open the Parallels app, switch to the User Groups tab, check the boxes for both admin and user groups, and click Save.
Switch to the Parallels My Account integration page, expand Step (3) Configure User Groups Mapping, and use the click to edit links to fill out the group name and UUID (the value from Step 7 earlier) fields for administrators and users, as specified on the JumpCloud side, and click Save.
Take care to use the correct names and UUIDs for each group.
Once the required groups have been created in the IdP Directory and associated with the Parallels app, move on to the next step.
The SAML 2.0 is supposed to be configured for the Parallels enterprise application registered with JumpCloud at the time of the Parallels enterprise application registration (refer the chapter (2) Register Parallels enterprise app and configure SAML settings earlier in this document for more details).
Make sure to check the Step 4 section on the integration configurator page at Parallels My Account. All fields must be filled in, and the Configuration in the IdP Directory is done option must be enabled.
If everything is set, proceed to the next step.
SCIM 2.0 integration between Parallels My Account and your Organization’s IdP allows you to keep user identity information in Parallels My Account in constant sync with the updates made to user identities in the IdP Directory. JumpCloud supports the SCIM 2.0 protocol, which is used for this purpose.
To set up SCIM integration with JumpCloud, do the following:
In JumpCloud, select SSO Applications from the left-hand side panel and click on the Parallels app created earlier.
In the app panel, switch to the Identity Management tab.
Select API Type: SCIM API, leave the Use mTLS authentication box unchecked, SCIM Version: SCIM 2.0, switch to the My Account IdP integration page, and expand Step (5) Configure SCIM Integration.
Copy the value of the SCIM Base URL parameter to the Base URL field on the JumpCloud side and the value of Bearer Token to the Token Key field, respectively.
On the JumpCloud side, type a user's email address that is already included in one of the groups during the group mapping configuration and click Test Connection.
Once the connection tests successfully, click Activate, switch to the Parallels My Account IdP integration page, and check the Configuration in the IdP Directory is complete box in Step (5) Configure SCIM Integration.
Continue to the next step.
For users to be able to make use of the application to sign or activate with Parallels, they have to be created and added to the groups tied to the Enterprise Application.
To add users to the groups created in step (3), go to JumpCloud, select User Groups from the left-hand side panel, click on the required group, switch to the Users tab, and populate it with users as required.
Once it is done, or if you plan to add users later, switch back to the My Account SSO setup page, expand Step 6, "Add Users to Application Groups", and mark the Configuration in the IdP Directory is complete checkbox at the bottom of the section.
The backup login can be used to access your organization’s business account registered with Parallels, bypassing Single Sign-On in the event of an SSO malfunction. By default, the backup login is set to the email address of the currently logged-in user. If you want to define a different backup login, add more users first on the Users page of the Business Profile section in Parallels My Account. The new user must log into the business account at least once before they can be designated as a backup login.
Warning: Once you have completed the integration process and activated the SSO functionality, only users from the Administrators group in your IdP signing in via SSO will retain access to managing the Parallels business account. All previous administrative privileges based on logins and passwords will become inactive.
Your designated backup login will continue to work.
Follow the steps below one by one to integrate Parallels My Account with Microsoft Entra ID.
A domain is a part of the email addresses (after the @ symbol) used by the end users in your organization. When end users try to log in to Parallels My Account using SSO, they are prompted to enter their work email address. Parallels My Account checks the domain part of the email address and recognizes that the user belongs to your organization. Click on the title of Step 1 to expand it and read the instructions carefully.
Add one or more domains your organization uses.
Each domain must be unique and can only be registered to one business account that your organization has registered with Parallels.
Make sure to add only the domains your organization can control.
The Parallels My Account service verifies the domain ownership by checking a specific TXT record that must be added to the DNS host of the corresponding domain. Make sure that all domains added to the list are verified before proceeding with the next steps.
Depending on the software and/or provider, a TXT record may take up to 72 hours to propagate. You can check whether it's been configured using the following command:
Registering the Parallels enterprise application (required for integrating with the Parallels My Account service) in the IdP Directory allows you to configure the SSO-related parameters and correctly provision the integration between your IdP and the Parallels My Account service. The description below illustrates the registration procedure for Microsoft Entra ID. It is assumed that you have the permissions required to register and configure enterprise applications with Entra ID. To register a Parallels enterprise application with Microsoft Entra ID:
Log into the Microsoft Entra ID portal using an account that has the privileges required to register and configure enterprise applications for your organization.
On the , choose Microsoft Entra ID from the services gallery to open the landing page.
Choose Enterprise applications in the Manage section on the left-hand side panel to open the page with the list of the enterprise applications registered with your organization.
Click New application above the list of registered applications to open the Browse Entra ID Gallery page which allows you to add a new app.
Click Create your own application to start the procedure of registering a new custom enterprise app. The popup panel Create your own application opens on the right.
Type the name of the application (the actual name remains at your discretion), choose the Integrate any other application you don't find in the gallery (Non-gallery) option, click Create and wait while the new enterprise application is being created. You will end up on the landing page of your new Parallels enterprise application.
Once the Parallels enterprise application registration in the IdP Directory is completed, switch back to the integration at Parallels My Account, expand the section of Step 2, and select the Configuration in the IdP Directory is done option at the bottom of the section. Then proceed to the next step.
You must create user groups associated with the Parallels Desktop application in your IdP Directory. Later, you will add users to those groups to let Parallels My Account know which users should have business account admin privileges in the Parallels ecosystem. At least one user group is required for adding users with admin access to your organization’s business account registered with Parallels. Once the group is created, you should add the group's name and ID in Step 3 of the integration configurator page in Parallels My Account.
Start with creating the group in the IdP Directory. To do so, switch to your IdP management portal and follow the standard procedure of creating a user group and associating it with the Parallels enterprise application, as provided by your Organization’s IdP. The description below illustrates the registration procedure for Microsoft Entra ID. It is assumed that you have appropriate permissions that allow you to manage user groups in Entra ID. To create a user group for the Parallels enterprise application in Microsoft Entra ID:
Log into the Microsoft Entra ID portal using the account which has privileges for managing user groups and configuring enterprise applications. 9
On the , choose Microsoft Entra ID in the services gallery to open the Entra ID landing page.
Choose Groups in the Manage section on the left-hand side panel to open the page with the list of the user groups registered in your tenant.
Click New group above the list of registered groups to open the page for creating a new group.
When on the page for creating a new group, specify:
Group type: Security,
Name and description of the group at your discretion,
Membership type: Assigned.
Click Create and wait while the group is being created.
Once the group is created, it appears on the list of groups automatically. Select the group from the list (click on it) to open the page with the group’s properties.
Repeat steps 3, 4, 5, and 6 once again. Your goal is to set up two groups, one for the admins of your organization’s Parallels business account and another for the users of Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition, who will be granted permission to activate their copies via SSO. If your admins also need to be able to use Parallels Desktop for Mac, add them to both groups. Note: Please make sure that the respective group names on the IdP side and the Parallels My Account side match precisely. This will help you avoid potential problems, as some IdPs use group names in their identification and authorization processes.
Copy the names of the specified groups and the Object ID (assigned automatically) to Parallels My Account. To do so, switch back to the Parallels My Account integration , expand the Step 3 section, click on Click to edit on the respective group, paste the group name and ID into the corresponding input fields, and click Save. Repeat twice for the Parallels Business Account Admins and Parallels Desktop Users groups.
Switch back to the Microsoft Azure portal and associate both groups with the Parallels app. To do so:
Choose MS Azure Home > Entra ID > Enterprise applications;
Select the Parallels application from the list and click on it to open its home page;
Select Users and groups on the side panel on the left;
Click Add user/group;
In Add Assignment, click on None Selected under Users and Groups to launch group selection;
Select the groups created in Step 4, and click Select;
Finally, click Assign.
Make sure to link both groups, the administrators and the users.
While on the Parallels application’s home page in MS Azure Home, select Properties in the left-hand side panel, scroll down to the Assignment Required setting, and make sure it’s enabled.
On the same page, make sure that the Visible to users option is disabled.
Click Save at the top of the page.
Once the required groups have been created in the IdP Directory and associated with the Parallels app, switch back to the Parallels My Account . If everything is set, move on to the next step.
SAML 2.0 integration between Parallels My Account and your organization’s IdP allows your organization's users to activate their copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition using Single Sign-On (SSO) while your admins can use it to log into the business account registered with Parallels using their main corporate login credentials.
To complete this step, you must copy certain parameters from your Parallels My Account to the settings section of the Parallels application registered in the IdP Directory and then copy certain data provided in the IdP Directory to the Parallels My Account admin panel.
The following description illustrates the procedure for Entra ID. It is assumed that you have appropriate permissions that allow you to configure enterprise applications in Entra ID. If your organization uses a different IdP service, follow the instructions provided in the admin guide specific to your IdP of choice.
Expand the Step 4 section on the in Parallels My Account. Note that there are two groups of parameters in the section. The first group has two values, Service Provider Entity ID and Assertion Consumer Service URL, which must be copied from Parallels My Account to the IdP Directory. The second group includes three parameters – Identity Provider Entity ID, Identity Provider SSO URL, and Public Certificate. The values for these parameters must be copied from your IdP Directory to Parallels My Account.
There are two ways to copy the parameters between Parallels My Account and the IdP Directory: via metadata files (assuming your IdP software supports transferring those parameters via external files) or manually.
Begin with copying the first group of parameters — Service Provider Entity ID and Assertion Consumer Service URL (both values are pre-set automatically and cannot be changed) from Parallels My Account to the IdP Directory.
Click Download a metadata file link in the subtitle of the group to save these parameters to the external metadata file. To transfer the values of the parameters from the metadata file to the IdP Directory, follow these steps:
Log into the Microsoft Azure portal using the account which has privileges for configuring enterprise applications.
Choose MS Azure Home > Entra ID > Enterprise applications, select the Parallels enterprise application from the list, click on it to open the application’s home page, and choose Single sign-on in the Manage section on the left-hand side panel to open the page for configuring the Single Sign-On method for the enterprise application.
When on the Single Sign-On configuration page, choose SAML as the Single Sign-On method. The page for configuring a Single Sign-on with SAML will open.
Switch to your IdP integration page in My Account, scroll down to, and expand Step 4 ("Configure SAML integration"). Under Service Provider Settings, click the Download a metadata file link to download the metadata.xml file.
Return to the Set up Single Sign-on with SAML page and click Upload metadata file at the top of the page to open the popup dialog that allows you to select the file. Select the file you have previously downloaded from Parallels My Account, then click Add to load the data from the selected file. The popup panel opens with the properties of the basic SAML configuration loaded from the metadata file.
Check that the following parameters are set: Identifier (Entity ID), Reply URL (Assertion Consumer Service URL), and the values of the parameters match those in the respective Parallels My Account section. Click Save.
On the left pane, choose Single sign-on. Select Attributes and Claims, then Edit, then click Add a group claim.
In Group Claims, select All Groups and click Save.
To close the configuration, click Close at the top of the panel on the right. Then, return to the SAML-Based Sign-On page.
On the SAML-Based Sign-On page, under the SAML Certificates section, locate Federation Metadata XML and click Download.
Switch to your IdP integration page in My Account, scroll down to and expand Step 4 ("Configure SAML integration"). Under Identity Provider Settings, click on the Upload a metadata file link and select the downloaded XML file.
Select the Configuration in the IdP Directory is done option at the bottom of the section and click Save to finish the configuration. Proceed to the next step.
Alternatively, you can set up the basic SAML configuration manually. To do so, perform steps 1-3 as described above in the section. When on the Set up Single Sign-on with SAML page, click Edit in the section (1) Basic SAML Configuration. A popup panel will open with the properties of the basic SAML configuration (the values won’t be set). Copy the value of the Service Provider Entity ID from Parallels My Account to the Identifier (Entity ID) box in the IdP Directory. Copy the value of Assertion Consumer Service URL from Parallels My Account to the Reply URL (Assertion Consumer Service URL) box in the IdP Directory. Click Save at the top of the panel to save the configuration. Close the Basic SAML Configuration panel.
Proceed to configure Attributes & Claims by adding the “user.groups” claim on the xn page in Entra ID as described above (refer to step 6 above in the section).
Next, copy the three parameters from MS Azure’s Set up Single Sign-on with SAML settings to My Account. On the Single Sign-on page, scroll to 4. Set up Application Name and copy the value of the Login URL to the Identity Provider SSO URL field in My Account. Next, copy the value of Entra ID Identifier to the Identity Provider Entity ID field in My Account. And finally, under the SAML Certificates section, click to download the Certificate (Base64) file and copy the file’s contents to the Public Certificate field in My Account.
Finally, select the Configuration in the IdP Directory is done option at the bottom of the section and click Save in Parallels My Account to confirm that you have finished the configuration procedure in the IdP Directory. Proceed to the next step.
SCIM 2.0 integration between Parallels My Account and your Organization’s IdP allows you to keep user identity information in Parallels My Account in constant sync with the updates made to user identities in the IdP Directory.
It is assumed that your IdP software supports SCIM. For this reason, the SCIM Support option in the Step 5 section on the integration configurator page in the Parallels My Account is enabled by default. If your IdP does not support SCIM, disable the option and move on to the next step.
The following description is based on the assumption that SCIM is supported.
To configure provisioning via SCIM, you must copy two parameters: SCIM Base URL and Bearer Token (both values are pre-set automatically and cannot be changed) from the Step 5 section of the in Parallels My Account to the IdP Directory.
The description below illustrates the procedure for Microsoft Entra ID. It is assumed that you have appropriate permissions that allow you to configure enterprise applications in Entra ID. If your organization uses a different IdP service, follow the instructions provided in the admin guide specific to your IdP of choice. To configure SCIM settings at the IdP management portal:
Log into the Microsoft Azure portal using the account that has privileges for configuring enterprise applications.
Choose MS Azure Home > Entra ID > Enterprise applications. Select the Parallels enterprise application in the list, click on it to open the application’s home page, and choose Provisioning in the Manage section on the left-hand side panel to open the page for configuring the provisioning settings of the enterprise application.
On the Provisioning page, click Get Started. It opens the page where you can configure the provisioning settings.
When on the configuration page, set Provisioning Mode to "Automatic", then expand the Admin Credentials section and set the Tenant URL to SCIM Base URL (retrieve the value from Parallels My Account), Secret Token to Bearer Token (retrieve the value from Parallels My Account).
Click Save to save the changes.
[IMPORTANT] While in the Manage section of the Provisioning page, open the Attribute mapping tab and click on Provision Microsoft Entra ID Users. There, under the Attribute Mappings section, locate the externalId parameter, click Edit, change the Source attribute parameter from mailNickname to objectId, and click OK. Click Save in the top left corner. Note that without this step, there may be a mixup in product license provisioning between users with similar names.
Return to Overview (Preview) in the left side panel and click Start provisioning in the top-left corner.
Once the provisioning settings in the IdP Directory have been saved, switch back to Parallels My Account and select the Configuration in the IdP Directory is done option at the bottom of the section to confirm that you have finished the configuration procedure in the IdP Directory. Then, continue to the next step.
Add users and administrators to their respective groups created in Step 3 (described above) to permit them to activate their copies of Parallels Desktop (users) and log into Parallels My Account (administrators) using their corporate login credentials. To do so, switch to the IdP management portal and follow the conventional procedure (as provided by the IdP software) for adding users to the groups. Once it is done, or if you plan to add users later, select the Configuration in the IdP Directory is done option at the bottom of the section.
The backup login can be used to access your organization’s business account registered with Parallels bypassing Single Sign-On in the event of an SSO malfunction. By default, the backup login is set to the email address of the currently logged-in user. If you want to define a different backup login, add more users first on the Users page of the in Parallels My Account. The new user must log into the business account at least once before they can be designated as a backup login.
Warning: Once you have completed the integration process and activated the SSO functionality, only users from the Administrators group in your IdP signing in via SSO will retain access to managing the Parallels business account. All previous administrative privileges based on logins and passwords will become inactive.
Your designated backup login will continue to work.
$ dig TXT {yourdomain}.{com}

























Create a file named parallels_updates.xml on the Web server where it can be accessed via HTTP. The file is an XML document that should contain specifications for a particular Parallels Desktop update available on your local updated server.
To create your own document, use the following sample XML document and the XML document specification that follows it as a reference.
Parallels Desktop
1
12
0
12494
262214
Sumer
0
Build 13291 is available!
Update description goes here</UpdateDescription>
URL to the update file goes here</FilePath>
219515
0
2017-06-17 01:23:00
0
en_US
parallels
mac
desktop.13.0.12927.482436.en_US.parallels.mac
desktop.13.0.12473.274921.en_US.parallels.mac
desktop.13.0.12262.823647.en_US.parallels.mac
ParallelsUpdates
Root element.
Product
Container for Parallels Desktop information.
ProductName
string
Use "Parallels Desktop".
UpdateEnabled
int
Specifies whether the automatic updates are enabled. To enable updates, specify 1.
Version
Container for Parallels Desktop version information.
Major
int
Major version number (e.g. 13)
Minor
int
Minor version number. Specify 0.
SubMinor
Build number. This element may be empty.
SubSubMinor
Revision number. This element may be empty.
StringRepresentation
Product codename. This element may be empty.
Update
Container for the information about the Parallels Desktop update.
Attributes:
uuid — String. A globally unique ID identifying the product.
The uuid attribute is very important and must contain the correct information for the update to work. The attribute value consists of the following parameters (substrings) separated by periods (see the provided XML example):
desktop — specify "desktop"
major — major version number (e.g. 13)
minor — minor version number (0)
build — build number
revision — revision number
locale — locale ("en_US", "de_DE", etc)
vendor — vendor ("parallels")
platform — platform ("mac")
UpdateType
int
Update type. Specify 0.
UpdateName
string
The user-defined update name.
UpdateDescription
string
The update description.
FilePath
string
A URL to the update file on your local update server. The actual update files can be obtained from Parallels.
FileSize
int
The update file size, in megabytes.
Status
int
Specify 0.
DateTime
string
Date and time when the updated was published. Use the following format:
yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss
Chargeable
int
Specify 0.
LocaleName
string
Locale name ("en_US", "it_IT", etc).
DistributorName
The update distributor name. Specify "parallels".
OsType
Operating system type. Specify "mac".
Ancestry
Container for the list of updates that directly preceded this update.
Ancestor
string
An individual Parallels Desktop update information.
This element may appear more than once in the same document, one for each update.
The value is combined using the following parameters (substrings) separated by periods (see the provided XML example):
desktop — specify "desktop".
major — Parallels Desktop major version number.
minor — minor version number.
build — build number.
revision — revision number.
locale — locale (e.g. "en_US")
vendor — vendor ("parallels").
platform -— platform ("mac").
The autodeploy package contains a special script, which is automatically executed on a target Mac after the package is transferred to it. When executed, the script reads the configuration parameter values from the deploy.cfg file, which you can modify according to your needs.
To modify the parameters, expand the License Key and Configuration folder in the autodeploy package and open the deploy.cfg file in a text editor. The configuration parameters are organized in sections, which are described below.
The License section is used to specify the Parallels Desktop Enterprise Edition license key. It contains only one parameter, license_key, which should be left commented for but needs to be uncommented and specified with a working 30-character license key for the license key activation experience. Read for more information.
Attention: In Parallels Desktop for Mac, the activation method defined by a pre-installed configuration profile always takes priority over the one specified in the deployment package. Therefore, if you deploy a package to a machine that already has a configuration profile installed, the activation will happen as defined in the configuration profile.
This section contains the parameters that specify how and where the virtual machines get deployed once a local copy of Parallels Desktop for Mac is installed and activated.
The User Experience section contains parameters that control various aspects of user interaction with Parallels Desktop, including from the user and present a Windows app almost like a native Mac app.
The Help and Support section is used to specify the action for the Help > Support Center menu item in the Parallels Desktop graphical user interface.
The Technical Data Reports section is used to specify whether Parallels Desktop issue reports should contain screenshots of the macOS and virtual machine desktops. You can exclude screenshots for security reasons.
Over the course of the Parallels Desktop product evolution, some previously available settings have been deprecated (e.g., customer experience program participation), and others (e.g., security and software updates) have been redesigned to be managed centrally from the .
Destination options and file name conflict resolution strategies
The (Optional) Deploy virtual machines section of the configuration guides describes strategies that define virtual machine deployment options:
Option 1: Parallels Desktop only. This option installs and activates a copy of Parallels Desktop without provisioning a virtual machine, which in turn happens via the Management Portal.
Option 2: Specifying a VM download link in the package without including a VM image itself in the package. This option requires you to upload an image to a shared network location.
You will need to create separate packages and virtual machines for each architecture if you have both Intel and Apple silicon Macs.
If you choose to upload virtual machines to a file share destination and deploy them using a publicly available link, you should set their names and destinations by providing an uncommented string with the link and the new name and destination, e.g.
"https://storage.company.com/VM.zip"="~/Parallels/Windows.zip"
or
"https://example-my.sharepoint.com/exmpleurl1?e=XXXX&download=1"="~/Parallels/CorporateVM.tar.gz"
Option 3: Including a VM in the deployment package (requires separate images for Apple silicon and Intel x86 processor architectures) by placing them in the package's Bundle/Virtual Machine (s) folder, taking into account the possible total package size limitations of your company's device management solution.
By default, the package will place the virtual machines as defined by the vm_register_mode and vm_destination_folder variables (see below).
For custom deployment paths, use the variable/value pair as described below, making sure to retain the original virtual machine file name, including the .pvm or .pvmp extensions. For .pvmp source file extension (packed virtual machines), the destination extension should also be .pvmp.
If the vm_register_mode is set to shared, the specified path must be relative to /Users/Shared/Parallels.
The section also contains advice on file conflict resolution strategy in case the target Mac already contains Parallels virtual machines: replace (default), which permanently deletes the existing VM; copy, which renames the new VM and registers it under the new name; and skip, which leaves the existing VM in place.
Examples:
"Shared VM.pvm"="./Shared VM.pvm"
"Private VM.pvm"="/Parallels/Private VM.pvm"
"Packed Shared VM.pvmp"="./Shared VM2.pvmp"
"Packed Private VM.pvmp"="/Parallels/Private VM2.pvmp"
"Shared VM.pvm"=copy("./Shared VM.pvm")
"Private VM.pvm"=skip("/Parallels/Private VM.pvm")
"Packed Shared VM.pvmp"=replace("./Shared VM2.pvmp")
unknown_vms_policy
This parameter specifies what is to be done with the existing virtual machines that are not part of the deployment package. The default value is keep, and the alternative is remove, which permanently deletes any existing virtual machines that are not used by other users of the target Mac.
vm_reset_hwid
Specifies whether the virtual machine's SMBIOS ID (hardware ID) will be regenerated. Each Parallels virtual machine is assigned a universally unique SMBIOS ID when created. For your enterprise management software (e.g., Microsoft Intune) to properly account for unique Windows and software activations, unique SMBIOS IDs are required. However, specific scenarios like software development and testing may require keeping SMBIOS IDs unchanged.
Set the value of the vm_reset_hwid variable as follows:
"yes" [RECOMMENDED]— Regenerate the ID.
"no" — Keep the original SMBIOS ID.
vm_register_mode
Specifies the registration mode for the deployed virtual machines. The accepted values are:
"Private" — The virtual machines will be registered for the active user only. The virtual machines will be placed in the /Users/<username>/Parallels folder.
"Shared" — The virtual machines will be registered for all users of a Mac. The virtual machines will be placed in the /Users/Shared/Parallels folder.
The default destination folder for virtual machines can be modified using the vm_destination_folder variable (see below).
vm_destination_folder (Optional)
Allows you to change the default destination folder for virtual machines. The default folder is determined by the value of the vm_register_mode variable (see above). The vm_destination_folder variable allows you to change the default folder while retaining the selected virtual machine's registration mode parameter value.
Note: Deploying shared VM(s) is allowed only to the "/Users/Shared/Parallels" and its subdirectories, so the vm_destination_folder value for the Shared VM case must be a relative path.
vm_deploy_mode
Specifies whether the virtual machine(s) will be copied or moved from the autodeploy package to their destination folder on a Mac (see the explanation below).
Accepted values:
"Copy" — Copy the virtual machine(s).
"Move" — Move the virtual machine(s).
If your autodeploy package contains one or more virtual machines, they need to be copied or moved to their destination folder on a Mac during deployment (see vm_register_mode and vm_destination_folder variables). Moving a virtual machine file is almost instantaneous, while copying it will take a considerable time due to the large size of a typical virtual machine. The option you specify here depends on the following:
If the deployment tool that you are using copies the entire autodeploy package to a Mac computer before running it, you can use the fast "Move" option. Jamf Pro and Apple Remote Desktop copy packages to a Mac before running them so you can use the "Move" option when using these tools. Note that the package and the destination folder must be located on the same mount point on a Mac for the "Move" operation to be fast; otherwise, it'll be essentially a copy-and-delete operation, hence slow.
If you are running the autodeploy package from a network share mounted on a Mac (e.g., manually) or a read-only destination, then you should use "Copy" because moving a virtual machine from a remote location will be as slow as copying it. Additionally, moving the virtual machine from the package will remove it, rendering the package incomplete (you want it to stay intact if you want to install it on other Macs).
Note: Starting from macOS 10.13, the "Copy" mode supports the APFS clone file feature. This means that if the target FS is APFS, the feature is used to reduce the time and disk space when deploying a VM.
Note: When testing the autodeploy package on a local Mac, it is better to use "Copy" to avoid removing a virtual machine from the package.
control_center_banner_url
This and the two variables below are grouped together and allow you to customize Parallels Desktop Control Center by displaying a custom HTML banner at the top of its window. For additional information, see Using custom graphics and links in the Control Center.
The URL of a custom HTML page is to be displayed as a banner in the Parallels Desktop Control Center window. To disable the banner, comment out the variable or specify an empty string as a value.
control_center_banner_height
The banner height, in pixels. The recommended value is 350.
To use the current value (if you are updating Parallels Desktop on a Mac), comment out the variable.
control_center_banner_min_width
The banner's minimum width measured in pixels. When resizing the Control Center window, its minimum width will be limited accordingly. The recommended value is 350.
To use the current value (if you are updating Parallels Desktop on a Mac), comment out the variable. To disable the minimum width limitation, comment out the variable or specify 0 (zero) as a value.
enable_single_application_mode(Windows VMs only)
Specifies whether to enable Single Application Mode. For more information, please see Single Application mode.
Possible values:
"yes" — enable Single Application Mode.
If the parameter is commented out, Parallels Desktop will be deployed using the "standard" mode.
When using the Single Application Mode, it is recommended to prepare the Windows guest operating system to have auto login enabled.
NOTE: You cannot redeploy Parallels Desktop with this option set to "no" or commented out to disable Single Application Mode. For that, you need to completely remove Parallels Desktop from your users' Mac computers, and only then can you redeploy Parallels Desktop with this option commented out.
sso_login_dialog_header and sso_login_dialog_description
This section allows you to modify the Single Sign On (SSO) dialog's header and text. This way, you can show your users a more customized dialog that, e.g., mentions your company's name or tells them to use a specific domain name if they have several corporate email addresses. If you are deploying over an existing installation that already has these values set to your preference, keep them commented out. If uncommented and left empty, the default dialog will be shown.
vm_set_hv_mode_apple_forcibly_since_macos_11_0(Deprecated, x86-only)
This parameter overrides hypervisor choice on Intel Macs and is important for scenarios where nested virtualization is expected to be required: Hyper-V, WSL2, or Docker inside Windows virtual machines.
For virtual machines on Intel Macs that need nested virtualization, set the parameter to "no".
To forcibly change the hypervisor type to 'Apple', use the following setting:
vm_set_hv_mode_apple_forcibly_since_macos_11_0="yes"
show_developers_menu
Specifies whether to show or hide developer tools in the Parallels Desktop GUI. For more information, please see Hiding Developer Tools in the Parallels Desktop GUI.
Possible values:
"no" — hide developer tools.
"yes" — show developer tools.
Please note that this setting will be applied to every virtual machine included in the autodeploy package. You can also configure each virtual machine to hide (or show) developer tools before deployment, but with this option, you can apply the setting automatically during deployment. Note: In Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition, this setting, along with many others, can be centrally controlled from the Management Portal using policies.
support_url
Specifies a URL of a page that will be displayed when a user selects the Help > Support Center menu option in the Parallels Desktop graphical user interface. To display the default message, specify an empty string (this is the default behavior). To display your own Web page (help desk, wiki, etc.), specify its URL.
See also Customizing the Support Center options.
lic_admin_url
Specifies a URL that will be included in error message dialogs related to licensing operations. The URL should point to a web page or a resource that the user can visit to get help with the problem.
The error message appears when there's a problem activating, renewing, or deactivating a Parallels Desktop license. If you specify a URL using this variable, it will be included in the message dialog in the form "For details click <URL>". If you don't specify a URL (comment out the variable or specify an empty string), the default "Contact your system administrator" message will be displayed.
report_allow_screenshots
"yes" — Include screenshots of the macOS and virtual machine desktops in Parallels Desktop problem reports.
"no" — Do not include the screenshots.
hide_license_request_params
This parameter allows you to hide hostnames in activation and heartbeat requests. The possible values are on and off.
Follow the steps below one by one to integrate Parallels My Account with Okta.
A domain is a part of the email addresses (after the @ symbol) used by the end users in your organization. When end users try to log in to Parallels My Account using SSO, they are prompted to enter their work email address. Parallels My Account checks the domain part of the email address and recognizes that the user belongs to your organization. Click on the title of Step 1 to expand it and read the instructions carefully.
Add one or more domains your organization uses.
Each domain must be unique and can only be registered to one business account that your organization has registered with Parallels.
Make sure to add only the domains your organization can control.
The Parallels My Account service verifies the domain ownership by checking a specific TXT record that must be added to the DNS host of the corresponding domain. Make sure that all domains added to the list are verified before proceeding with the next steps.
Depending on the software and/or provider, a TXT record may take up to 72 hours to propagate. You can check whether it's been configured using the following command:
$ dig TXT {yourdomain}.{com}Registering the Parallels enterprise application (required for integrating with the Parallels My Account service) in the IdP Directory allows you to configure the SSO-related parameters and correctly provision the integration between your IdP and the Parallels My Account service. The description below illustrates the registration procedure for Okta. It is assumed that you have the permissions required to register and configure enterprise applications with Okta. If your organization uses a different IdP service, follow the instructions provided in the admin guide specific to your IdP of choice. To register a Parallels enterprise application with Okta:
Log into the Okta management portal using an account that has privileges for registering and configuring enterprise applications for your organization.
On the portal’s landing page, expand the Applications section and choose the Applications item from the left-hand side panel to open the page with the list of enterprise applications registered for your organization.
Click the Create App Integration button, which is located above the list of registered applications. It opens the pop-up dialog titled Create a new app integration.
In the Create a new app integration dialog, choose SAML 2.0 as your sign-in method, then click Next.
On the next page, type the name of the application (the actual name remains at your discretion) in the App name field, then select the Do not display application icon to users option. Click Next to proceed with configuring the SAML settings for the application. SAML 2.0 integration between Parallels My Account and your organization’s IdP allows your users to activate their copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition using Sign-On (SSO) and your system administrators to use it to log into your organization’s Parallels business account. To complete this step, you must copy certain parameters from Parallels My Account and save them in the settings of the Parallels enterprise application registered with Okta, then copy some data provided by Okta and save it in Parallels My Account.
Switch to the integration configurator page of Parallels My Account. Expand the Step 4 section on the integration configurator page. Note that there are two sets of parameters in the section. The first set has two values, Service Provider Entity ID and Assertion Consumer Service URL, that must be copied from Parallels My Account to Okta. The second set includes three parameters—Identity Provider Entity ID, Identity Provider SSO URL, and Public Certificate. The values for these parameters must be copied from Okta to Parallels My Account.
On Okta’s Create SAML Integration page (this page should have opened after completion of Step 5, as described above), insert the values into the Single sign-on URL and Audience URI (SP Entity ID) fields, as specified below:
The Assertion Consumer Service URL value from Parallels My Account (in the Step 4 section of the integration configurator) must be copied to the Single sign-on URL input field in Okta.
The Service Provider Entity ID value from Parallels My Account (in the section of Step 4 of the integration configurator) must be copied to the Audience URI (SP Entity ID) input field in Okta.
Keep the Use this for Recipient URL and Destination URL option enabled (it is enabled by default). Leave the parameters in the General section set to the defaults.
Scroll the page down to the section Attribute Statements (optional). Add the following attributes to the list (keep the text values and punctuation marks exactly as specified):
objectidentifier (Name format: Unspecified) > user.id
name (Name format: Unspecified) > user.login
displayName (Name format: Unspecified) > user.displayName
Scroll down the page to the section Group Attribute Statements (optional). Add the following attribute to the list (use the name of the value and punctuation mark exactly as specified):
groups (Name format: Unspecified) > (Filter: Matches regex), set the value to .*Parallels.*, making sure to follow the syntax exactly.
ATTENTION: The purpose of this filter is to avoid excessively large claims in setups with a large overall number of groups, making sure the claim only contains the groups that relate to the Parallels Desktop SSO setup. If you have named the groups differently (e.g., PD Admins/PD Users), amend the filter expression accordingly.
Scroll to the bottom of the page and click Next. It opens the section Help Okta Support understand how you configured this application. Choose the option I’m an Okta customer adding an internal app, and then, once the additional section App type opens, choose the option This is an internal app that we have created.
Finally, click Finish, and once the registration process finishes, you will end up on the application’s home page.
Switch back to the integration configurator page at Parallels My Account, expand the Step 2 section (“Register Parallels enterprise app”), and select the option Configuration in the IdP Directory is done.
Once the registration of the Parallels enterprise application with Okta is completed, you must transfer three parameters from Okta to Parallels My Account. To do so, follow these steps:
Switch back to the Okta management portal. When on the enterprise application’s home page in Okta, ensure the currently selected tab is Sign On. Locate the View SAML Setup Instructions button on the right side of the page. Clicking the link opens the page How to Configure SAML 2.0 for %1 Application, where %1 is the name of the enterprise application registered previously. The page contains the three parameters that must be transferred to Parallels My Account. The same three parameters can also be found in the Metadata Details section of the SAML 2.0 card under More details.
Transfer the values from Okta to the Step 4 section of the integration configurator page in Parallels My Account as specified below:
The value Identity Provider Issuer from Okta must be copied to the input field Identity Provider Entity ID.
The value Identity Provider Single Sign-On URL from Okta must be copied to the input field Identity Provider SSO URL.
The content of the X.509 Certificate from Okta must be copied to the input field Public Certificate.
Instead of copying and pasting these values manually, you can download the metadata in the Okta interface and then upload the resulting XML file using the Upload a metadata file link in the Parallels My Account interface.
In the SAML 2.0 card section, locate Metadata URL under the Metadata Details section.
Copy and paste the Metadata URL into a new browser tab or window.
Use Ctrl/Cmd+S to save the metadata as an XML file.
Switch to Parallels My Account interface, open the Step 4 Identity Provider Settings, click Upload a metadata file, and choose the newly created XML file.
Once you have copied the values from Okta to Parallels My Account, click the Save button in the Step 4 section on the integration configurator page at Parallels My Account and select the Configuration in the IdP Directory is done option at the bottom of the section. Then proceed to the next step.
You must create user groups associated with the Parallels enterprise application in your IdP Directory. Later, you will add users to those groups to let Parallels My Account know which users should be able to activate their copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition using SSO and which ones should have business account admin privileges in the Parallels ecosystem. At least one user group is required for adding users with admin access to your organization’s business account registered with Parallels. Once the group is created, you should add the group's names in Step 3 of the integration configurator page in Parallels My Account.
Start with creating the group in the IdP Directory. To create a user group for the Parallels enterprise application in Okta:
Log into the Okta management portal using the account with privileges for managing user groups and configuring enterprise applications.
On the portal's landing page, expand the section Directory and choose the item Groups on the left-hand side panel to open the page with the list of the groups registered for your organization. Note: You must repeat steps 3 and 4 as described below three times: first, to create the group for Parallels Administrators, then Parallels Desktop for Mac users, and finally, to create the transit group that is supposed to be assigned to the Parallels enterprise application registered with Okta. It is required to push users from the other groups to the Parallels application.
Click the Add Group button placed above the list of groups, which opens the Add group popup dialog.
Type in the name and the group description, and click Save.
Make sure you have repeated steps 3 and 4 three times and created three separate groups as specified above.
Write down the name of the group created for the Parallels Business Account Admins. You must transfer these values to Parallels My Account later.
Next, assign the Parallels enterprise application registered with Okta to the transit group that you have created before. Make sure you are on the page with the list of groups at the Okta management portal. To assign the application to the transit group, follow the instructions below:
Find the transit group in the list of groups.
Click on the group’s item in the list to open the page with the group's details.
Click the Applications tab at the top to open the list of applications assigned to the group. Since the group is new, the list is supposed to be empty.
Click the Assign Applications button to launch the popup dialog titled Assign Applications to %1, where %1 is the name of the transit group.
Locate the Parallels enterprise application that has been registered with Okta before and click Assign.
Click Done to save the assignment. You will now see the Parallels enterprise application on the list of the transit group's assigned applications.
After that, you must create a rule to push members from the groups created for the Parallels Administrators to the Parallels enterprise application through the transit group. Make sure you are on the Okta admin portal’s page with the list of groups. To create the rule, follow these steps:
When on the page with the list of groups, click Rules at the top of the list to open the list of rules created for the groups.
Click Add Rule to create a new rule. It opens the pop-up dialog titled Add Rule.
Type the name of the rule (use whatever name you find suitable).
Choose the Use basic condition option, then select Group membership from the list below.
In the input field below, type the name of the group that has been created for the Parallels Administrators.
In the THEN Assign to input field, type in the name of the transit group.
Click Save to save the rule. Now you will see the new rule in the list of rules.
Once the rule has been created, activate it by clicking on the Actions drop-down menu on the right and then Activate.
Before proceeding, make sure that the following conditions have been met:
At least one group has been created for the Parallels Business Account Admins.
You have written down the unique names of the groups you have created for the Parallels users and admins.
An additional transit group has been created, and the Parallels enterprise application has been registered with Okta and assigned to that group.
A rule has been created that enables you to push members of both the admin and user groups to the Parallels enterprise application through the transit group.
To complete this step, switch to the integration configurator page at Parallels My Account and expand Step 3 (“Configure user groups mapping”).
Click on Click to edit on the respective group and insert the Parallels Admins group name you have written down earlier into both corresponding fields (“UUID” and “Display Name”), then do the same for the Parallels Desktop Users group section. Click Save to save the changes.
The SAML 2.0 is supposed to be configured for the Parallels enterprise application registered with Okta at the time of the Parallels enterprise application registration (refer to chapter (2) Register Parallels enterprise app and configure SAML settings earlier in this document for more details).
Make sure to check the Step 4 section on the integration configurator page at Parallels My Account. All fields must be filled in, and the Configuration in the IdP Directory is done option must be enabled.
If everything is set, proceed to the next step.
SCIM 2.0 integration between Parallels My Account and your Organization’s IdP allows you to keep user identity information in Parallels My Account in constant sync with the updates made to user identities in the IdP Directory. Okta supports the SCIM 2.0 protocol, which is used for this purpose.
To configure provisioning via SCIM, you must first enable provisioning for the Parallels enterprise application registered with Okta. After that, you must copy two parameters, SCIM Base URL and Bearer Token, from Parallels My Account (the section of Step 5 of the integration configurator) to Okta. Finally, you must configure the push of the user groups from Okta to Parallels through SCIM.
The description below illustrates the procedure for Okta. It is assumed that you have appropriate permissions to configure enterprise applications in Okta. To configure the provisioning settings for the Parallels enterprise application registered with Okta:
Log into the Okta management portal using the account with privileges for configuring enterprise applications.
When on the portal's landing page, choose Applications > Applications in the left-hand side panel to open the list of enterprise applications registered for your organization.
Find the Parallels enterprise application that has been registered before (refer to chapter (2) Register Parallels enterprise app and configure SAML settings earlier in this document for details). Select the application’s item from the list to open the app’s home page.
Click on the General tab to switch to the tab that displays the app’s general settings. There, click Edit in the upper right corner of the tab to switch to edit mode.
Select the option Enable SCIM Provisioning and click Save.
A new tab called Provisioning will appear at the top of the page. Click on it to open the tab where you can configure the SCIM settings for the application.
While on the Provisioning tab, click Edit in the upper right corner to switch to edit mode.
Switch to Parallels My Account, open the integration configurator page, and expand the Step 5 section ("Configure SCIM integration”).
Copy the values from the Step 5 section Parallels My Account to Okta, as specified below:
SCIM connector base URL (Okta): insert the value of the parameter SCIM Base URL copied from Parallels My Account.
Bearer (Okta): insert the value of the parameter Bearer Token copied from Parallels My Account. The Bearer field in Okta is not displayed by default. To make it visible, switch Authentication Mode to HTTP Header.
Enable the options Push New Users, Push Profile Updates, and Push Groups on the same page in Okta.
Insert the text userName (use the text exactly as it is provided here: userName) into the input field Unique identifier field for users.
Click Save to save the changes. Okta’s interface will revert to the Provisioning tab of the Parallels enterprise application.
Make sure the section To App is selected on the left. Click Edit to switch to edit mode. Enable the following options: Create Users, Update User Attributes, Deactivate Users. Click Save to save the changes.
Click the Push Groups tab at the top to open the tab with the list of groups from which the users are supposed to be pushed to the Parallels ecosystem. The list is supposed to be empty.
Click Push Groups > Find groups by name to open the dialog, which allows you to specify the group that must be pushed. Specify the name of the group that has been created for the Parallels Admins (refer to chapter (3) Configure user groups mapping earlier in this document for more details) and select the group when it shows up in the list. The section with additional parameters will appear below. Keep the default settings. Scroll down and click Save. You will see the new group on the list.
When you complete configuring the provisioning settings for the Parallels enterprise application in Okta, switch back to Parallels My Account and select the option Configuration in the IdP Directory is done at the bottom of the Step 5 section ("Configure SCIM integration”).
Continue to the next step.
Add users to the groups created in Step 3 (described earlier in the chapter (3) Configure user groups mapping) to enable users to activate their copies of Parallels products via SSO and administrators to access your organization’s business account registered with Parallels.
To do so, switch to Okta and follow the standard procedure for adding users to groups. Please note that no user will be able to activate their Parallels product unless they have been added to the User group.
Once it is done, switch back to the integration configurator page at Parallels My Account, expand the Step 6 section ("Add users to the application groups”) and select the option Configuration in the IdP Directory is done at the bottom of the section.
The backup login can be used to access your organization’s business account registered with Parallels, bypassing Single Sign-On in case of an SSO malfunction. By default, the backup login is set to the email address of the currently logged-in user. If you want to define a different backup login, add more users first on the Users page of the Business Profile section in Parallels My Account. The new user must log into the business account at least once before being designated as a backup login.
Warning: Once you have completed the integration process and activated the SSO functionality, only users from the Administrators group in your IdP signing in via SSO will retain access to managing the Parallels business account. All previous administrative privileges based on logins and passwords will become inactive.
Your designated backup login will continue to work.
Follow the steps below one by one to integrate Parallels My Account with Ping Identity.
A domain is a part of the email addresses (after the @ symbol) used by the end users in your organization. When end users try to log in to Parallels My Account using SSO, they are prompted to enter their work email address. Parallels My Account checks the domain part of the email address and recognizes that the user belongs to your organization. Click on the title of Step 1 to expand it, and read the instructions carefully.
Add one or more domains your organization uses.
Each domain must be unique and can only be registered to one business account that your organization has registered with Parallels.
Make sure to add only the domains your organization can control.
The Parallels My Account service verifies the domain ownership by checking a specific TXT record that must be added to the DNS host of the corresponding domain. Make sure that all domains added to the list are verified before proceeding with the next steps.
Depending on the software and/or provider, a TXT record may take up to 72 hours to propagate. You can check whether it's been configured using the following command:
$ dig TXT {yourdomain}.{com}Registering the Parallels enterprise application (required for integrating with the Parallels My Account service) in the IdP Directory allows you to configure the SSO-related parameters and correctly provision the integration between your IdP and the Parallels My Account service.
The description below illustrates the registration procedure for Ping Identity. It is assumed that you have the permissions required to register and configure enterprise applications with Ping Identity. To register a Parallels enterprise application with Ping Identity:
Log into Ping Identity here using an account that has privileges for registering and configuring enterprise applications for your organization.
[OPTIONAL] If you don't yet have an environment, launch the Create Environment wizard and select the Build your own solution option using the Ping SSO service and click Next two times.
[OPTIONAL] Fill out the required parameters for the new environment, such as the name, description, type, and region. Click Finish when done.
Go back to the main page and use the drop-down menu in the top-left corner to select the right environment.
Go to the Applications section and click on the Add (+) button.
In the Add application stage, type in a name for the application you are registering (e.g., Parallels Desktop), choose SAML as your application type, and click Configure.
At the SAML Configuration step, choose the Manually Enter option and copy the respective parameter values from Step 4 (Configure SAML Integration) of the Parallels My Account IdP integration page as follows:
Assertion Consumer Service URL (My Account) -> ACS URLs (Ping Identity)
Service Provider Entity ID (My Account) -> Entity ID (Ping Identity)
The next step will require you to configure mapping attributes under the Attribute Mappings section. Use the Edit button and add the attributes as follows (note that the fields are case-sensitive):
saml_subject -> User ID
displayname -> Expression: {user.name.given + ' ' + user.name.family}
groups -> Group IDs
name -> Email Address
objectidentifier -> User ID
In case pasting values into the fields does not work, use the Advanced Expressions button and paste the expression value there.
Switch the application configuration on using the toggle:
Once the registration of the Parallels enterprise application in the IdP Directory is completed, switch back to the integration configurator page at Parallels My Account, expand the section of Step 2 and select the Configuration in the IdP Directory is done option at the bottom of the section. Then move on to the next step.
You must create user groups associated with the Parallels enterprise application in your IdP Directory. Later, you will add users to those groups to let Parallels My Account know which users should be able to activate their copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition via Single Sign-On (SSO) and which should have business account admin privileges in the Parallels ecosystem.
At least one user group is required for adding users with admin access to your organization’s business account registered with Parallels. Once the group is created, you should add the group's name and ID in Step 3 of the integration configurator page in Parallels My Account.
Start with creating the group in the IdP Directory. To do so, switch to your IdP management portal and follow the standard procedure of creating a user group and associating it with the Parallels enterprise application, as provided by your Organization’s IdP. The description below illustrates the registration procedure for Ping Identity. It is assumed that you have appropriate permissions that allow you to manage user groups in Ping Identity. If your organization uses a different IdP service, follow the instructions provided in the admin guide specific to your IdP of choice.
To create a user group for the Parallels enterprise application in Ping Identity:
Log into the Ping Identity portal using the account which has privileges for managing user groups and configuring enterprise applications.
On the Start page, choose Administrator environment (or any other environment what you could create before) to open the Ping Identity console page.
Using the left-hand side bar, navigate to the Groups menu in the Directory section.
You need to create two groups, one for the users who are supposed to be granted the admin permissions to access your organization’s business account registered with Parallels, and another for the regular Parallels Desktop users who are expected to sign into their copies of Parallels products via SSO.
Click the Add (+) icon to launch the group creation wizard, and type in the group name and description. Click Save and wait while the group is being created. Make sure to copy the Group ID parameters from both groups.
Using the left-hand side bar, navigate to the Applications page in the Applications section and select the Parallels app that you have set up in (2) Register Parallels Enterprise App and Configure SAML Settings.
In the Parallels app card, navigate to the Access tab and click on the Edit button to open the Edit Access menu.
We strongly recommend that you deselect the option to display the Parallels app on the company portal.
Under the Groups section, select the groups created in Step 4 to connect them to the application.
Copy the group's name that you have specified and its ID to Parallels My Account. To do so, switch back to the integration configuration page at Parallels My Account, expand the Step 3 section, use the click-to-edit link, paste the group's name and ID in the corresponding input fields of the section Parallels Business Account Admins, and click Save. Repeat that for the Parallels Desktop users group.
Make sure you have configured both groups: for the Parallels Desktop users and for the Parallels business account admins. If everything is set, click Save at the bottom and proceed to the next step.
SAML 2.0 integration between Parallels My Account and your organization’s IdP allows your organization's users to activate their copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition using Single Sign-On (SSO) while your admins can use it to log into the business account registered with Parallels using their main corporate login credentials.
To complete this step, you must copy some parameters from your Parallels My Account to the settings section of the Parallels enterprise application registered in the IdP Directory and then copy certain data provided in the IdP Directory to the Parallels My Account admin panel.
The following description illustrates the procedure for Ping Identity. It is assumed that you have appropriate permissions that allow you to configure enterprise applications in Ping Identity. If your organization uses a different IdP service, follow the instructions provided in the chapter specific to your IdP of choice.
Expand the section of Step 4 on the integration configurator page in Parallels My Account. Note that there are two groups of parameters in the section. The first group has two values, Service Provider Entity ID and Assertion Consumer Service URL, which must be copied from Parallels My Account to the IdP Directory. The second group includes three parameters – Identity Provider Entity ID, Identity Provider SSO URL, and Public Certificate. The values for these parameters must be copied from your IdP Directory to Parallels My Account.
Parameters can be copied between Parallels My Account and the IdP Directory either via metadata files (assuming your IdP software supports transferring those parameters via external files) or manually.
The first group of parameters, Service Provider Entity ID and Assertion Consumer Service URL (both values are pre-set automatically and cannot be changed), is already copied from Parallels My Account to the IdP Directory during the creation of Enterprise Application in Step 2.
To transfer the second set of parameters from Ping IdP to My Account:
Navigate to the Application tab and click on the application that has been created in the previous step (2) Register Parallels enterprise app. Proceed to the Overview tab and click Download Metadata under Connection Details.
Switch to the IdP integration page in My Account, scroll down, and expand Step 4 ("Configure SAML integration"). Under Identity Provider Settings, click on the Upload a metadata file link and select the downloaded XML file.
Select the Configuration in the IdP Directory is done option at the bottom of the section and click Save.
Return to the Applications tab in Ping IdP and close the Configuration tab, after which ensure that the app access switch is on.
Proceed to the next step.
SCIM 2.0 integration between Parallels My Account and your Organization’s IdP allows you to keep user identity information in Parallels My Account in constant sync with the updates made to user identities in the IdP Directory.
It is assumed that your IdP software supports SCIM. For this reason, the SCIM Support option in the Step 5 section on the integration configurator page in the Parallels My Account is enabled by default. If your IdP does not support SCIM, disable the option and move on to the next step.
The following description is based on the assumption that SCIM is supported.
To configure provisioning via SCIM, you must copy two parameters: SCIM Base URL and Bearer Token (both values are pre-set automatically and cannot be changed) from the Step 5 section of the integration configurator in Parallels My Account to the IdP Directory.
The description below illustrates the procedure for Ping Identity. It is assumed that you have appropriate permissions that allow you to configure enterprise applications in Ping Identity. If your organization uses a different IdP service, follow the instructions provided in the admin guide specific to your IdP of choice.
To configure SCIM settings at the Ping Identity management portal:
Open the navigation sidebar and go to Integrations → Provisioning.
Create a new SCIM connection by clicking the Add (+) and selecting New connection.
From the connection catalog, select SCIM Outbound and click Next.
Enter a name and description for this provisioning connection (the actual name and description remain at your discretion). The connection name will appear on the list once you have completed and saved the connection.
Click Next.
On the Configure authentication screen, enter the following:
SCIM Base URL. The fully qualified URL to use for the SCIM resources is https://account.parallels.com/scim.
Select the authentication method to use: OAuth2 Bearer Token.
Select the Auth Type Header: Bearer.
Copy the contents of the Bearer Token from Parallels My Account and paste it into the respective field.
Click Test Connection and if successful, click Next.
For the User Filter Expression parameter, the exact value should be userName eq “%s”. Make sure that the N in the userName is capitalized.
The User Identifier parameter should be workEmail.
Click Save.
Turn on SCIM by toggling the switch.
Now you need to create a provisioning rule. Follow these steps:
While remaining on the Provisioning page, click the Add (+) button in the top-left corner again, and select New Rule.
Choose the name and description for the rule.
On the next page of the wizard, click on the Target box and select your newly created SCIM connection as the target by clicking on the (+) button. Click Save.
[MANDATORY] In the next step, set up the user filter by clicking the Edit button, configuring any rule to your liking, and clicking Save. Note that this step is mandatory, and the SCIM integration will not work without a working filter.
Switch to the Attribute Mapping step by clicking the respective icon. Click on the Edit button. Here, it is essential that you do two things:
Change the userName attribute value from the default Username to email. Use the respective drop-down selector in the left column to choose Email Address.
Add another mapping rule by clicking the + Add button. Map displayName to Given Name. Click Save.
Your attribute mapping section should look like this:
Return to the Configuration tab and switch to the final icon, Group Provisioning. Click the Add Groups button and add all the groups as required, making sure the Parallels Desktop administrators and users groups, and any other groups that may need to activate Parallels Desktop for Mac, are added. Click Save.
Once the groups have been selected, enable the new rule and test synchronization by clicking Resync.
Switch back to Parallels My Account and select the Configuration in the IdP Directory is done option at the bottom of the section to confirm that you have finished the configuration procedure in the IdP Directory. Then continue to the next step.
Add users to the groups created in Step 3 (described earlier) to enable end users to activate their copies of Parallels Desktop for Mac Enterprise Edition using SSO and grant administrators permission to log into your organization’s business account registered with Parallels.
To do so, navigate to the Start page and choose Administrator environment (or any other environment that you might have created before) to open the Ping Identity console page. Navigate to Identifies, then Users, and create users by clicking the Add User button. Once it is done, or if you plan to add users later, select the Configuration in the IdP Directory is done option at the bottom of the section.
Once users have been created, you need to add them to the groups created above. To do so, navigate back to the Identifies tab and switch to the Groups tab. Click on the group name and add users to it.
The backup login can be used to access your organization’s business account registered with Parallels, bypassing Single Sign-On in the event of an SSO malfunction. By default, the backup login is set to the email address of the currently logged-in user. If you want to define a different backup login, add more users first on the Users page of the Business Profile section in Parallels My Account. The new user must log into the business account at least once before they can be designated as a backup login.
Warning: Once you have completed the integration process and activated the SSO functionality, only users from the Administrators group in your IdP signing in via SSO will retain access to managing the Parallels business account. All previous administrative privileges based on logins and passwords will become inactive.
Your designated backup login will continue to work.

































