
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Parallels® Remote Application Server (Parallels RAS) is an application delivery and virtual desktop solution. It extends Microsoft Windows Remote Desktop Services by providing centralized and simplified management, universal printing, and highly available load balanced remote access solution to Windows Terminal Services based applications and desktops from any device, anywhere.
Traditionally, application delivery and VDI solutions were challenging to set up and manage. Design and implementation could take weeks or even months to complete. In contrast, Parallels RAS can be installed in days or even hours, providing a quicker return on your investment and an easier path to realizing the benefits of remote desktop computing.
This guide is intended for system administrators responsible for installing and configuring Parallels RAS. The guide assumes that the reader is familiar with such Microsoft services as Active Directory, DNS, DHCP, Terminal Servers/Remote Desktop Session Hosts and has an intermediate networking knowledge.
Parallels RAS can be installed in both Workgroup and Active Directory (AD) environments where end users, RAS servers, and RDS servers belong to the same AD forest (domains with single root domain) or multiple forests with trust relationships. Domains and workgroups represent different methods for organizing computers in networks. The main difference among them is how the computers and other resources on the networks are managed. For better manageability and scalability, following Microsoft recommendations, Parallels recommends the use of domains where:
One or more computers are servers. Network administrators use servers to control security and permissions for all computers in the domain. This makes it easy to make changes because they are automatically made to all computers. Domain users must provide a password or other credentials each time they access the domain.
If you have a user account on the domain, you can log in to any computer in the domain without needing an account on that computer.
There can be thousands of computers in a domain.
The computers can be on different local networks.
File, folder, and user and group permissions can be assigned.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a client/server protocol that automatically provides an Internet Protocol (IP) host with its IP address and other related configuration information such as the subnet mask and default gateway.
Parallels recommends the use of static or DHCP reserved IP addressing for Parallels RAS infrastructure servers.
With regards to VDI, to create a RAS template from an existing host, the guest operating system (Windows) must be configured to obtain an IP address via the DHCP server. With regards to a Provider Agent on hypervisors it is recommended to take note of the MAC address assigned to the appliance and add a DHCP reservation. If DHCP isn't available, a static IP address needs to be configured manually.
For Wyse clients, RAS Secure Gateway can act as a Wyse broker. Please ensure that DHCP option 188 on your DHCP server is set to the IP Address of this Gateway for thin clients that are going to boot via this gateway.
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical distributed database that contains mappings of DNS domain names to various types of data, such as IP addresses. DNS allows you to use friendly names to easily locate computers and other resources on a TCP/IP network.
DNS is a key infrastructure component frequently used by various Parallels RAS components. While standard file-based storage, such as the hosts file, will provide proper DNS resolution in Proof of Concept (POC) environments, Parallels recommends implementing Active Directory integrated DNS in enterprise deployments.
Parallels recommends the use of the DNS zone integrated with Active Directory so that organizations can have the benefit of using secure dynamic updates, as well as the ability to use Access Control List (ACL) editing features to control which machines can update the DNS system.
Dynamic updates are a key feature of DNS, which allows domain computers to register their name and IP addresses with the DNS server automatically when they come online or change IP addresses through the DHCP server. The DNS Server service allows dynamic update to be enabled or disabled on a per-zone basis on each server that is configured to load either a standard primary or directory-integrated zone. By default, the DNS Client service dynamically updates host (A) resource records in DNS when the service is configured for TCP/IP. This form of update eliminates the need for manual entries of names and IP addresses into the DNS database.
There is a security concern when automatic update from a client to the DNS database could take place and thus create the possibly for a malicious entry. Therefore, secure dynamic updates will verify that the computer that is requesting the update to the DNS server also has an entry in the Active Directory database. This means that only computers that have joined the Active Directory domain can dynamically update the DNS database.
More information on how DNS works can be found at https://technet.microsoft.com/library/cc772774.aspx.
In most Domain Name System (DNS) lookups, clients typically perform a forward lookup, which is a search based on the DNS name of another computer as it is stored in a host (A) resource record. This type of query expects an IP address as the resource data for the answered response.
DNS also provides a reverse lookup process in which clients use a known IP address and look up a computer name based on its address.
Parallels recommends for consideration the usage of the following Active Directory abilities.
A particularly useful type of directory object contained within domains is an organizational unit (OU). OUs are Active Directory containers into which you can place users, groups, computers, and other organizational units. An organizational unit cannot contain objects from other domains.
An OU can be used to assign Group policy settings for centralized management and configuration of operating systems, applications, and user settings in an AD environment.
Parallels recommends the use of OUs for the following:
Terminal Servers/Remote Desktop Session Hosts (RDSH) hosting applications and desktops should be set in their own OUs. Usually TS/RDSH require various group policies applied to them. For example, in a multi-user environment, policies may be required to optimize user experience and/or add security.
Different OUs for different TS/RDSH groups identified from the Parallels RAS Console can also be used to organize different application groups.
Servers in the same Parallels RAS site should reside in the same domain or in different domains with a full trust relationship between domains.
More information on Domain trusts can be found at https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc773178(v=ws.10).aspx.
All servers that load-balance applications/desktops must be in the same domain if a domain security group is authorized to use the application.
Security Groups
Security groups are used to assign permissions to shared resources. Different resources (virtual applications, desktops, VDI machines) can be assigned to different users/groups. Parallels recommends the use of Active Directory Security groups for better manageability if filtering is done via user/groups.
Once security groups are created in Active Directory and members are added to them, group-based filtering can be carried out from the Parallels RAS Console. This will ensure that all members of that particular security group will have access to same published resources. For example, if a new user joins the company, they only need to be added to the Active Directory security group to have access to given published resources.
Examples of logical security group segregation can be based on the department user resides in or based on application/desktop that is to be delivered.
More details about Active Directory Security Groups can be found at https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn579255(v=ws.11).aspx.
Group Policy is an infrastructure that allows you to implement specific configurations for users and computers. Group Policy settings are contained in Group Policy objects (GPOs), which are linked to the following Active Directory service containers: sites, domains, organizational units (OUs). The settings within GPOs are then evaluated by the affected targets using the hierarchical nature of Active Directory. Consequently, Group Policy is one of the top reasons to deploy Active Directory because it allows you to manage user and computer objects.
Apart from the Parallels RAS policies, which allow IT administrators to manage Parallels Client policies for all users on the network who connect to a server in the farm, Parallels recommends the additional use of group policies to manage different users and computer objects accessing the infrastructure. Group policies relating to user experience and/or security are to be linked with their respective OUs mentioned in the previous sections.
Some recommended group policies include but not limited to listed below.
Logging in remotely requires users to have remote access rights to the remote server.
This can be carried out from Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), which is an administrative feature that can be installed via Server Manager or through PowerShell as described at https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc725932(v=ws.11).aspx.
Once GPMC is opened, navigate to Computer Configuration / Policies / Windows Settings / Security Settings / Restricted Groups. Right-click on Restricted Groups and click on Add User Group that should have access to log in on to the remote machine (TS/RDSH/VDI).
More information on how to add Domain Users/Group to the Remote Desktop Users group via Group policy can be found at https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc725932(v=ws.11).aspx.
You can use the Group Policy Loopback feature to apply Group Policy objects that depend only on which computer the user logs in to. This is ideal when users already reside in their respective OUs and new OUs have been created to handle Terminal Server/RDSH from where the applications and desktops are published. Essentially, we are applying user settings when they log in to those computer objects, in this case to the Terminal Servers/RDSH.
This can be carried out from Group Policy Management Console (GPMC). Navigate to Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\System\Group Policy and then enable the Loopback Policy option (Merge or Replace).
More information on loopback processing can be found at https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/231287.
Note: This section describes how to manually optimize remote desktop and terminal server performance. Beginning with RAS 18, these and other settings can be optimized automatically using the new Optimizations functionality.
The default Windows performance settings are intended for general purpose servers. In order to maximize application or desktop hosting server performance, the default Windows performance settings should be adjusted on Windows Remote Desktop/Terminal Servers.
From the Control Panel go to System and click on Advanced System Settings. Under the Advanced tab in the System Properties dialog box, click on Settings under the Performance section.
Under the Visual Effects tab from the Performance Options dialog box, change the setting to Adjust for best performance.
If a specific application has a custom setting recommendation, you should use it, but in general, the Adjust for best performance option will provide the best overall performance in a Parallels RAS environment.
Set the Windows paging file to twice the amount of RAM. For heavier workloads, a paging file of three times the amount of physical memory might be required. For more information on how to determine the exact page file size, please visit https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/2860880/how-to-determine-the-appropriate-page-file-size-for-64-bit-versions-of-windows.
By default, Microsoft Windows page file size is automatically managed for all drives and grows dynamically as necessary. However, as the system ramps up to intended capacity, dynamic page file growth can result in a fragmented page file, so it is best to set a fixed page file size upfront.
Typically, page file settings are configured when the server is first installed. However, if the server remained in production for a while, Parallels recommends optimizing and defragmenting the drive prior to setting paging options described below.
In the example below, the server has 8 GB of RAM:
Note that Microsoft sets it to 1280 but recommends 4607. Parallels recommends to double it and use a new page file on the disk. Therefore the number is 16384 (8 GB in block of 8192 x2 = 16384). Make sure you have enough free disk space to use this setting.
Please also make sure to configure antivirus exclusions for FSLogix Profile Container virtual hard drives as described in .
In order to install Parallels RAS on Windows servers, there are some required prerequisite to be installed from the Server Roles and Features.
RAS Connection Broker can be installed on any supported version of Windows. The Connection Broker does not require any specific Windows roles or features.
The Secure Gateway can be installed on any supported version of Windows. The Secure Gateway does not require any specific Windows roles or features.
RAS RD Session Host Agent requires the Terminal Server Role on Windows Server 2008.
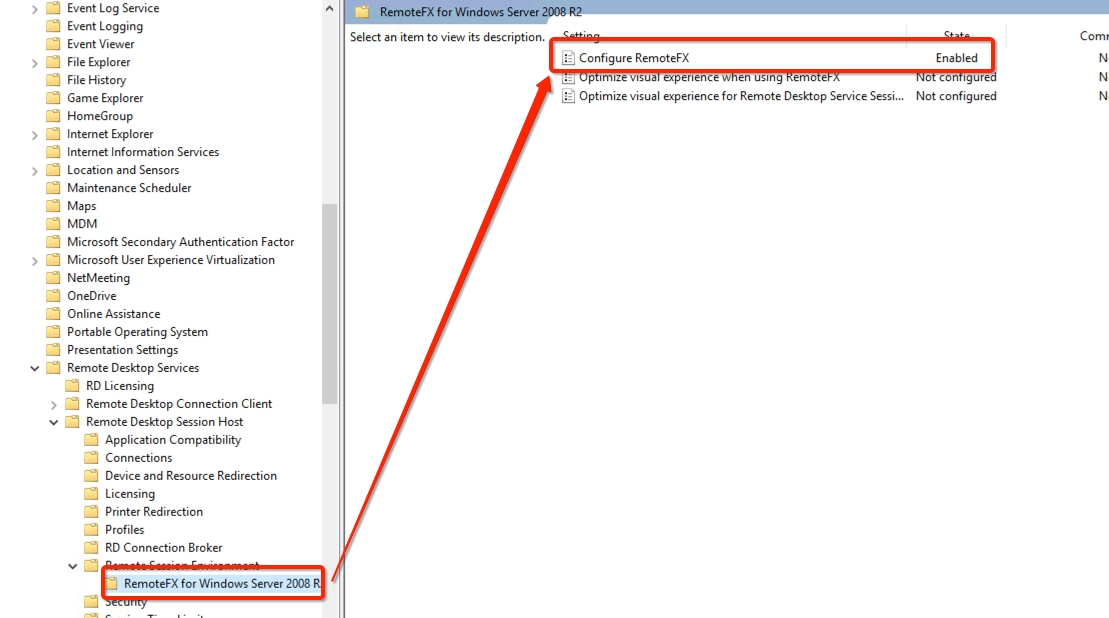
Enable the following options on all Terminal Servers in your farm. Under Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Remote Session Environment enable the following:
Configure Compression for RemoteFX Data. Set to Optimize to use less network bandwidth.
Configure image quality for RemoteFX Adaptive Graphics. Set to Medium.
Enable RemoteFX encoding for RemoteFX clients designed for Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
Configure RemoteFX Adaptive Graphics. Set to Let the system choose the experience for network conditions.
Navigate to Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Terminal Services\Terminal Server\Remote Session Environment and set compression algorithm for RDP data as follows:
Optimized to use less memory (RDP 5.2 or V1):
Bulk compressor from Windows Server 2003
Consumes more bandwidth than other compressors
Has the least memory and CPU overhead
Gives you the best server-side scalability
Balances network bandwidth and memory (RDP 6.0 or V2):
The default setting if the Group Policy setting is not configured
Balances between memory consumption and network bandwidth
Can reduce your bandwidth by 5–30 percent compared to the RDP 5.2 compressor
Optimized to use less network bandwidth (RDP 6.1 or V3):
A new compressor designed for Windows Server 2008
Tuned to give you the best network performance
Can reduce your bandwidth by 10–60 percent compared to the RDP 5.2 compressor
http://download.microsoft.com/download/4/d/9/4d9ae285-3431-4335-a86e-969e7a146d1b/RDP_Performance_WhitePaper.docx
If you have users that login from different time zones, you may want to enable this setting. This setting will redirect the local time to the app, remote PC, or VM. Time Zone Redirection is configured in the same Group Policy location as Audio Redirection: Local Computer Policy > Computer Configurations > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Remote Desktop Session Host > Device and Resource Redirection.
This policy setting allows the administrator to configure RemoteFX graphics for Remote Desktop Session Host or Remote Desktop Virtualization Host servers to be lossless. If you enable this policy setting, RemoteFX graphics will use lossless encoding. The color integrity of the graphics data will stay intact. If you disable or skip the configuration of this policy setting, RemoteFX graphics lossless encoding will be disabled.
RD Session Host host pool are recommended to be used. This ensures that published resources are configured to publish resources from host pools. If a new RD Session Host is to be added, new hosts can simply be added to the host pool created rather than changing published resources configurations to be also accessible from new servers.
RemoteFX is enabled on Windows systems using Group Policy. Parallels recommends to apply Group policies at OU (organizational unit) level in Active Directory environments. Although local Group Policies can be used, it requires to configure necessary settings on every Terminal Server/Remote PC/VDI host in the RAS Farm.
Hint: To edit domain Group Policies, from the Windows Run command, type GPMC.MSC. Once the Group Policy settings are completed, run GPUPDATE /FORCE from the Run command to apply them.
This policy setting enables system administrators to change the graphics rendering for all Remote Desktop Services sessions on a Remote Desktop Session Host (RD Session Host) server. If you enable this policy setting, all Remote Desktop Services sessions on the RD Session Host server use the hardware graphics renderer instead of the Microsoft Basic Render Driver as the default adapter. If you disable or skip the configuration of this policy setting, all Remote Desktop Services sessions on the RD Session Host server will use the Microsoft Basic Render Driver as the default adapter.
Windows Server 2008 up to Windows Server 2019
Windows Server 2016 and newer must be installed using the "Desktop Experience" installation option.
Windows Server 2012 R2 — Server Core installation option is not supported.
In Parallels RAS v15 and newer, the Remote Desktop Session Host role can be automatically installed using the "Add Terminal Server" capability in the RAS Console.
Parallels RAS does not replace the need for Microsoft Client Access Licenses (CALs). A Windows Remote Desktop/Terminal Server License server is required.
Except for very small, single-server environments, the License Server should not be installed on the production Terminal Servers or Remote Desktop Session Hosts.
More information on TS/RDS CALs can be found at https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc753650(v=ws.11).aspx.
When a user connects a Parallels RAS server, the desktop that exists on the RD Session Host server is reproduced in the remote session by default. To make the remote session look and feel more like the user's local Windows desktop, install the Desktop Experience feature on an RD Session Host server that is running Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 2012, Windows 2012 R2. Note that Windows 2016 has the Desktop Experience feature enabled by default on RDS host. This also makes the graphics look better using the Windows Aero theme.
Desktop Experience is a feature that you can install from Server Manager.
Once Desktop Experience is enabled, you will notice that applications display richer graphics and a remote desktop looks more like the client's local desktop with themes and other Windows client components.
Enable the following options on all Terminal Servers in your farm. Under Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Remote Session Environment enable the following:
Configure RemoteFX
Optimize visual experience when using RemoteFX. Set to Medium Default.
Set Compression algorithm for RDP data. Set to Optimize to use less network bandwidth.
Optimize Visual experience for Remote Desktop Services sessions. Set to Rich Multimedia.
Configure image quality for RemoteFX Adaptive Graphics (Image Quality set to Medium).
Configure RemoteFX Adaptive Graphics. Set to Let the system choose experience for network conditions.
Generally, device redirection increases how much network bandwidth RD Session Host server connections use because data is exchanged between devices on the client computers and processes that are running in the server session. The extent of the increase is a function of the frequency of operations that are performed by the applications that are running on the server against the redirected devices. Printer redirection and Plug and Play device redirection also increases CPU usage at sign-in.
Parallels recommends to not allow device redirection if not being used since this will result in inefficient bandwidth usage. Local device redirection can be configured from Parallels RAS policies, registry, or Microsoft group policies.
Parallels RAS supports the following hypervisors:
Microsoft Hyper-V, including Windows Server 2019
Microsoft Hyper-V Failover Cluster
VMware vCenter
Reboot clears up old sessions and releases resources in use (CPU, RAM, file handles, etc.). It is recommended to configure scheduled reboots for your RD Session Hosts (applicable for frequent logoffs and logons). To do so, in the RAS Console, navigate to Farm > RD Session Hosts > Scheduler and click Tasks > Add > Reboot server. Reboot frequency depends on how heavily the RD Session Hosts are utilized.
Hint: Make sure that server rebooting does not cause any downtime. This can be carried out by offloading users onto other servers prior to reboot by enabling the drain mode.
Parallels Remote Application server comes preconfigured with a self-signed certificate to enable SSL access to the Farm during the testing phase. Self-signed certificates will generate a warning that the connection is not secure/private. For production purposes, certificates should be purchased from a Certificate Authority.
During the testing phase you may wish to suppress the self-signed certificate error which can be done using RAS Policy settings. Note that this policy only works with Parallels Client for Windows, Mac, and Linux.
To remove the certificate error simply follow the steps below:
Navigate to Policies from within the RAS Console.
Click to add a Local/Domain group which will be affected by this policy.
When configuring Filtering for published resources and selecting User as the filtering type, select Secure Identifier as the Browse Mode. This is the fastest method that supports group nesting and renaming.
Remote FX Settings for Windows 7 SP1. Under Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Remote Session Environment enable the following options for virtual PC or VDI host which has guest agent installed:
Enable RemoteFX.
Set Compression algorithm for RDP data. Set to Optimize to use less network bandwidth.
Optimize Visual experience for Remote Desktop Services sessions. Set to Rich Multimedia.
By default, the Resource Based load balancing is enabled. It is recommended that this setting is remained as is for better resource utilization and load balancing to RD Session Hosts mitigating users experience degradation due to limited RD Session Host resources.
RemoteFX is a set of Microsoft Windows technologies that greatly enhances the end-user visual and performance experience over the RDP protocol. It is available in Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 and later. Windows 7 was the first client side operating system to support RemoteFX. Both the client and the server versions must be able to support RemoteFX in order for these enhancements to work.
Although RAS supports earlier versions of Windows Server, certain performance capabilities will not be available when those versions are used. RemoteFX has been improved with subsequent releases of Windows. The best performance will always occur when running the latest version of Microsoft Windows Server being accessed from the latest workstation version.
Parallels RAS supports RemoteFX on the following clients:
Parallels Windows Client for Windows installed on Windows 7 SP1 and higher.
Parallels Client for Mac
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 and later include bulk compressors that compress all data sent from the server to the client. These compressors can be enforced by the computer-wide Set compression algorithm for RDP data Group Policy setting.
The choice of compression algorithm impacts the memory and CPU consumption on the server and thus affects server scalability. RDP optimization can be configured to:
Use the least amount of memory
Use the least amount of network bandwidth
To save system resources on RD Session Hosts, it is possible to disable application monitoring if it is not required.
Keep your gateway private on your local LAN:
In the Parallels RAS console under Farm, select Gateways.
Open the gateway properties for each Gateway server in your farm.
Under the Network tab, uncheck "Broadcast RAS Secure Gateway Address"
Scale Computing HC3
Nutanix Acropolis
Configure RemoteFX (Windows 7 and later) using the RemoteFX Settings for Windows Workstations Runnings Remote PC agents and Provider Agents in the RemoteFX section of this guide.
Parallels Client for Linux
Parallels Client for iOS
Parallels Client for Android
Parallels Client for ChromeApp running on ChromeBooks
Click OK and then Apply Settings.
Whether you are using graphics intensive applications or streaming media across RDP, some configurations can be applied to provide performance benefits in your environment:
Display driver optimization – this is probably the most important component, particularly on the Windows CE platforms that tend to have a lot less CPU power than their desktop counterparts. The display "device driver interface" we provide in Windows CE uses only the basic graphics engine functions; where software acceleration is provided through emulation libraries, and hardware acceleration is limited to two-dimensional graphics operations. If at all possible, hardware acceleration should be used.
Ensure that your video and network card drivers are up to date based on the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Enable bitmap caching in your RDP session. This can result in some significant bandwidth savings and can also improve the refresh speed. However, this does not mean that graphics intensive applications will run at the same performance level as they would in a non-RDP session.
Understanding how font exchange works can also lead to some opportunities for performance improvements. Font exchanges occur between the client and server to determine which common system fonts are installed. The client notifies the Terminal Server of all installed system fonts to enable faster text rendering during an RDP session. When the Terminal Server knows what fonts the client has available, passing compressed fonts and Unicode character strings rather than larger bitmaps to the client can save network bandwidth
If network bandwidth is not as much of a concern, you can increase the frame rate on the client side via a registry modification.
https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/askperf/2009/04/17/terminal-services-and-graphically-intensive-applications/.
To learn how to increase the frame rate on the server side, see https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/2885213/frame-rate-is-limited-to-30-fps-in-windows-8-and-windows-server-2012-remote-sessions.
RemoteFX supports two Group Policy settings that give administrators the flexibility to manually choose the best configuration for their scenario. Both policies are under this path: Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Remote Session Environment.
The first policy setting is Configure image quality for RemoteFX Adaptive Graphics. This policy setting specifies the graphics quality for a remote session. Administrators can use this option to balance network bandwidth usage with graphics quality delivered.
The options are Medium (default), High, and Lossless. The Medium setting consumes the lowest amount of bandwidth, The High setting increases the image quality with a moderate increase in bandwidth consumption, while the Lossless setting uses lossless encoding, which preserves full color and resolution integrity but requires significant increase in bandwidth.
The second policy setting is Configure RemoteFX Adaptive Graphics. This policy setting allows the administrator to choose the encoding configuration to be optimized for server scalability or bandwidth usage. If you enable this policy setting, the RemoteFX experience could be set to one of the following options:
Let the system choose the experience for the network condition
Optimize for experience (balanced)
Optimize to use minimum network bandwidth
By default, the system will choose the best experience based on available network bandwidth.
It is recommended to use the CPU optimization feature to optimize CPU load balancing according to your requirements. When configured, the CPU load balancer will lower the priority of a process when its CPU usage exceeds a specified value for a specified number of seconds. The load balancer will revert the priority to its original level when the process has been running below a certain percentage for a certain number of seconds.
To configure CPU optimization, select the Enable CPU Optimization option and then specify the values as described below.
Specifies when the CPU optimization should be activated. The Total CPU usage exceeds field specifies the system wide CPU usage in percent.
Specifies thresholds per process when a specific process exceeds or falls below the specified CPU percentage. Here you can specify Critical and Idle values. The CPU load balancer will adjust other priorities with respect to these values.
Please note that CPU usage values are attenuated and calculated based on the agent refresh time configured on the Load Balancing tab.
Use the Exclusions list to specify processes that should be excluded from CPU optimization. Click Tasks > Add to select a process. To remove a process from the list, select it and click Tasks > Delete.
Irregular values for critical/idle may cause issues (processes set to idle due to incorrect configuration). If there are issues with getting the CPU usage counter, optimizations cannot be applied.
Log files can be found in %ProgramData%\Parallels\RASLogs\cpuloadbalancer.log. Use the log to confirm thresholds. You can check the CPU usage performance counter on Windows.
Absolute CPU usage equals to total CPU usage. For example, if there are 2 processes taking 30% each, the total CPU usage is 60%. The usage threshold when CPU load balancer kicks in is 25% (default).
The highest process CPU usage is the CPU usage of the process taking the most CPU. For example, if you have three processes, two taking 10% and the third taking 40%, the highest CPU usage is 40%.
Limit audio playback quality
Select Options under Policy.
Then click on the Advanced Settings tab.
Check the option Do not warn if server certificate is not valid.
Click OK and then Apply Settings.
Configure compression for RemoteFX data. Set to Optimize to use less network bandwidth.
Configure image quality for RemoteFX Adaptive Graphics. Set to Medium.
Configure RemoteFX Adaptive Graphics. Set to Let the system choose the experience for the network condition.
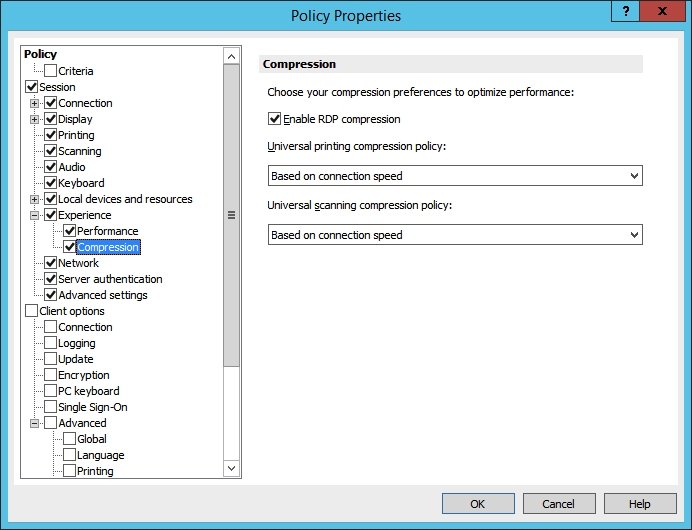
For Windows desktop clients (full and basic), Parallels RAS v15.5 and higher includes Universal printing compression policy and Universal scanning compression policy options. These options allow system administrator to adjust printing and scanning compression levels via client policy settings in the RAS Console.
To set printing and scanning compression policies:
In the RAS Console, select the Policies category.
Right-click an existing policy and choose Properties.
In the Policy Properties dialog, navigate to Session > Experience > Compression.
Select one of the following options from the Universal printing compression policy or Universal scanning compression policy drop-down lists:
Compression disabled
Best speed (uses less CPU)
Best size (uses less network traffic)
If the type of printed or scanned documents is predictable — for instance, your documents are always very small or always very large — you can benefit by selecting an appropriate compression policy. However, compression brings the most benefit to network connections with limited bandwidth or latency when printing or scanning often slows down thus negatively affecting user experience.
Parallels recommends using the Best size compression policy to make printing/scanning jobs smaller and transfer them faster if the client devices are powerful enough from the CPU and memory perspective. If the client devices are not powerful enough, the Best speed option policy should be used.
For more info, please also see the Parallels RAS Universal Printing Best Practices Guide, which can be downloaded from http://www.parallels.com/products/ras/resources/.
Physical PCs can be accessed remotely using the RAS infrastructure:
Parallels RAS Remote PC Agent is used to publish both applications and desktops.
Desktop operating systems can only support one remote user at a time.
Supported operating systems:
Windows 7 and newer
Windows Server 2008 R2 and newer
Configure RemoteFX (Windows 7 and later) using the in the RemoteFX section of this guide.
For a consistent visual display of personal data associated with a specific user and/or a customized desktop environment irrespective to which TS/RDSH or VDI machine user is connecting, Parallels recommends the use of FSLogix Profile Container as a complete profile management solution with Parallels RAS.
To administer FSLogix Profile Container, you must be signed in as a member of the Domain Administrators security group, the Enterprise Administrators security group, or the Group Policy Creator Owners security group.
Client computers must be running Windows 7 and newer, or Windows Server 2008 R2 and newer.
Client computers must be joined to the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) that you are managing.
A file server must be available to host roaming user profiles or User Profile Disks.
If the file share uses DFS Namespaces, the DFS folders (links) must have a single target to prevent users from making conflicting edits on different servers.
If the file share uses DFS Replication to replicate the contents with another server, users must be able to access only the source server to prevent users from making conflicting edits on different servers.
If the file share is clustered, disable continuous availability on the file share to avoid performance issues.
For more information about deploying FSLogix Profile Container, visit .
For the information about migrating to FSLogix Profile Container, visit .
To reach high availability for FSLogix Profile Container on-premises, Parallels recommends using multiple SMB locations with a single VHD path and Distributed File System Namespace in front of one or many SMB locations (note that only one SMB location can be active at one time) as active-passive HA. DFSR is applicable to NTFS based SMB locations but for ReFS, a third party synchronization tool is required, such as .
For FSLogix Profile Container on Microsoft Azure, multiple storage solutions are available with the recommended ones being Azure Files or Azure NetApp Files. Additional best practices apply such as setting up the storage solution in the same datacenter location and excluding the VHD(X) files for Profile Container from antivirus scanning. For more information about FSLogix Profile Container and Azure deployment options, visit
More information on DFS and DFSR can be found at .
In order to get Point of Sale / USB Scanning devices to work properly with Windows Server 2008 R2 and higher, you must enable RemoteFX USB redirection on the user Windows devices using GPO. Please note that this policy setting allows you to permit RDP redirection of other supported RemoteFX USB devices from this computer. Make sure that you set RemoteFX USB Redirection Access Rights to Administrators and Users. This is configured by navigating to Computer Configurations > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Remote Desktop Connection Client:
Parallels recommends setting up recurrent backups of Parallels RAS farm settings. This can be accomplished using Parallels RAS PowerShell, which is a part of Parallels RAS beginning with version 15.5.2. Parallels RAS PowerShell is installed by default when you install Parallels RAS. If you chose not to install it, please run the Parallels RAS installer again and install the Parallels RAS PowerShell component.
The following sample PowerShell script shows how to export Parallels RAS farm settings to a file.
Save the above sample script to a file with the ".ps1" extension. To test the script, you can execute it in the PowerShell console. To execute the script on a schedule, do the following:
Open Windows Scheduler and click Create Task.
On the General tab page of the
User Portal enables clientless remote access to Parallels RAS from most modern web browsers that support HTML5. The User Portal can be accessed using the following URL:
HTTPS://<Hostname/IP>/userportal
Access is delivered through a web access site hosted on the Secure Gateway Server. Multiple Gateway servers can be load-balanced by the High Availability Load Balancer (HALB).
The HML5 Gateway is enabled by default and requires SSL. A self-signed certificate can be used and is pre-installed with the product. For production, Parallels recommends that an approved SSL certificate from a Certificate Authority is used.
Due to the clientless nature of the solution, Local drive access from clients is not available. However, files can be saved on File Shares and on Cloud Drives (Drop Box, Google Drive, OneDrive, etc.) if those applications are published by the administrator.
Universal printing is supported when using User Portal.
Navigate to Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates \Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services \ Remote Desktop Session Host\ Remote Session Environment and configure compression for RemoteFX data as follows:
Optimized to use less memory. Consumes the least amount of memory per session but has the lowest compression ratio and therefore the highest bandwidth consumption.
Balances memory and network bandwidth. Reduced bandwidth consumption while marginally increasing memory consumption (approximately 200 KB per session).
Installing antivirus software on an RD Session Host server greatly affects overall system performance, especially the CPU usage. We highly recommend that you exclude all folders that hold temporary files from the active monitoring list, especially folders generated by services and other system components.
The Parallels RAS folder to be excluded from real-time scanning is %programfiles(x86)%\Parallels\ApplicationServer.
For Parallels RAS port reference, please refer to Parallels Remote Application Server Administrator's Guide, which can be downloaded from http://www.parallels.com/products/ras/resources. For additional information, please also see http://kb.parallels.com/124003.
The Parallels Client for Windows folder to be excluded from real-time scanning is as follows:
32-bit: %programfiles(x86)%\Parallels\Client
When configuring RAS Secure Gateway to use SSL encryption, you should pay attention to how the SSL server is configured to avoid possible traps and security issues. Specifically, the following SSL components should be rated to determine how good the configuration is:
The certificate, which should be valid and trusted.
The protocol, key exchange, and cipher should be supported.
The assessment may not be easy to perform without specific knowledge about SSL. That's why we suggest that you use the SSL Server Test available from Qualys SSL Labs. This is a free online service that performs an analysis of the configuration of an SSL web server on the public Internet. To perform the test on a RAS Secure Gateway, you may need to temporarily move it to the public Internet.
The test is available at the following URL: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/.
You can read a paper from Qualys SSL Labs describing the methodology used in the assessment at the following URL: https://github.com/ssllabs/research/wiki/SSL-Server-Rating-Guide.
You can also choose not to engage a RemoteFX compression algorithm. This will use more network bandwidth and it is only recommended if you are using a hardware device that is designed to optimize network traffic. Even if you choose not to use a RemoteFX compression algorithm, some graphics data will still be compressed.
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/hardware/dn567648(v=vs.85).aspx.
The following policy setting specifies whether the Remote Desktop Protocol will try to detect the network quality (bandwidth and latency): Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Connections\Select network detection on the server.
If you enable the above policy setting, you must select one of the following:
Connect Time Network Detect
Continuous Network Detect
Connect Time Detect
Continuous Network Detect
If you select Connect Time Network Detect, Remote Desktop Protocol will not try to determine the network quality at the connect time, and it will assume all traffic to this server originates from a low-speed connection.
If you select Continuous Network Detect, Remote Desktop Protocol will not try to adopt to changing network quality.
If you select Connect Time Detect and Continuous Network Detect, Remote Desktop Protocol will not try to determine the network quality at the connect time, it will assume all traffic to this server originates from a low speed connection and it will not try to adopt to changing network quality.
If you disable or do not configure this policy setting, Remote Desktop Protocol will spend a few seconds trying to determine the network quality prior to the connection and it will continuously try to adopt to the network quality.
The following policy setting specifies whether the UDP protocol will be used for Remote Desktop Protocol access to this server: “Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates \Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services \ Remote Desktop Session Host\ Connections\Select RDP transport protocols".
If you enable the above policy setting, Remote Desktop Protocol traffic to this server will only use the TCP protocol. If you disable or do not configure this policy setting, Remote Desktop Protocol traffic to this server will use both the TCP and UDP protocols.
64-bit: %programfiles%\Parallels\Client
Parallels recommends to exclude the above Parallels RAS and Parallels Client for Windows folders from real-time or on-access scanning and scan them on a regular basis using scheduled scans. You should also monitor the creation of new files in the excluded folders.
For FSLogix Profile Container to work properly, configure your antivirus to exclude the following objects, as per Microsoft’s recommendations:
Files:
%TEMP%\*\*.VHD
%TEMP%\*\*.VHDX
%Windir%\TEMP\*\*.VHD
%Windir%\TEMP\*\*.VHDX
\\server-name\share-name\*\*.VHD
\\server-name\share-name\*\*.VHD.lock
\\server-name\share-name\*\*.VHD.meta
\\server-name\share-name\*\*.VHD.metadata
\\server-name\share-name\*\*.VHDX
\\server-name\share-name\*\*.VHDX.lock
\\server-name\share-name\*\*.VHDX.meta
\\server-name\share-name\*\*.VHDX.metadata
Cloud Cache specific exclusions:
%ProgramData%\FSLogix\Cache\ (folder and files)
%ProgramData%\FSLogix\Proxy\* (folder and files)

Select the Actions tab page and then click the New button.
In the New Action dialog, make sure Start a program is selected in the Action drop-down list, then click Browse and select your .ps1 script file.
Click OK in the New Action dialog.
Select the Triggers tab page and click New.
In the New Trigger dialog, specify the desired schedule settings.
Click OK to close all dialogs.
To import the settings from a saved file into a Parallels RAS farm:
In the Parallels RAS Console, navigate to Administration \ Backup and click Import. Specify the ".dat2" file to import the farm settings from.
Using Parallels RAS PowerShell, execute the Invoke-RASImportSettings cmdlet passing the path and filename of the backup file.
The complete Parallels RAS PowerShell documentation can be viewed and downloaded from http://www.parallels.com/products/ras/resources/
#Get the current datetime to be used as a name for the backup file.
#You can use any other unique name format that you like.
$Date = Get-Date -Format yyyy.MM.dd.mm.ss
#Import the Parallels RAS PowerShell module.
Import-Module RASAdmin
#Create a Parallels RAS session.
#Since the password must be passed as SecureString, we need to convert it first.
#In your own script, replace "secret" with your Parallels RAS password.
$Pass = "secret" | ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText -Force
#We can now create a Parallels RAS session.
#Replace "user" and "server.company.dom" with your RAS user and server names.
#If executing the script locally, you can omit the -Server parameter.
New-RASSession -Username "user" -Password $Pass -Server "server.company.dom"
#Export farm settings to a file.
#You can specify a different folder for saving the file if you wish.
#.dat2 is the default extension Parallels RAS uses for backup files.
Invoke-RASExportSettings $env:userprofile\$Date.dat2
#Close the current RAS session.
Remove-RASSessionBased on connection speed (default)
Disable Server Manager Pop up for users logging in. This can be done from the Group Policy Microsoft Management Console (MMC):
User Configuration \ Polices \ Administrative Templates \ Start Menu and Taskbar
Some administrative group polices might not be available in the Group Policy Manager Console (GPMC). These can be imported from https://www.microsoft.com/en-au/download/details.aspx?id=41193.
You must perform these modifications on the RD Session Host servers. You can use the Registry to make these changes directly or using group policy preferences (GPP).
For Favorites, the key is:
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOTCLSID{323CA680-C24D-4099-B94D-446DD2D7249E}ShellFolder] "Attributes"=dword:a0900100 Changing a0900100 to a9400100 will hide Favorites from the navigation pane.
For Libraries, the key is:
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOTCLSID{031E4825-7B94-4dc3-B131-E946B44C8DD5}ShellFolder] "Attributes"=dword:b080010d Changing b080010d to b090010d will hide Libraries from the navigation pane.
You can use Group Policy settings to hide and restrict access to drives on the RD Session Host server. By enabling these settings you can ensure that users do not inadvertently access data stored on other drives, or delete or damage programs or other critical system files on drive C.
This can be carried out from the Group Policy Microsoft Management Console (MMC) as follows:
For Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2: User Configuration\Policies\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Windows Explorer.
For Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2: User Configuration/ Administrative Templates/ Windows Components/ File Explorer.
Additional policies can be set to:
Hide the Manage item on the Windows Explorer context menu
Remove Hardware tab
Remove "Map Network Drive" and "Disconnect Network Drive"
Remove Search button from Windows Explorer
.
You can use this policy setting to specify the maximum amount of time that an active, disconnected, or idle session remains in its current state.
Set the time limit for disconnected sessions. When a session is disconnected, running programs are kept active even though the user is no longer actively connected. By default, these disconnected sessions are maintained for an unlimited time on the server.
Set the time limit for logoff of published resources sessions. You can specify how long a user session will remain in a disconnected state after closing all programs but before the session is logged off from the RD Session Host server. By default, if a user closes a published resource, the session is disconnected from the RD Session Host server but it is not logged off.
This option can also be changed in the Parallels RAS Console by navigating to Farm \ Terminal Servers \ Properties \ Publishing Session.
Set time limit for logoff of published resources sessions. When a user closes the last running published resource associated with a session, Remote Application Server will keep the session in a disconnected state until the specified time limit is reached. When it is, the session will be logged off from the RD Session Host server. If the user starts another published resource before the time limit is reached, the user will reconnect to the disconnected session on the RD Session Host server.
In some cases bandwidth and other factors can cause a memory error when transferring large files between remote applications and local drives.
For large file transfer optimization, the following settings should be made on both the server and client side.
Referencing the Remote Desktop/Terminal Server Performance Settings section at the beginning of this document:
Set Visual Effects to "Best Performance".
Set the Windows Paging file to three times the physical RAM.
Disable Desktop Composition under Group Policy (on Windows Server 2008 R2 only).
Under Local Computer Policy > Computer Configurations > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Remote Session Environment, set Desktop Composition to "Not Configured."
Client settings can be changed on a per client basis using Connection Properties or centrally from the Parallels RAS management console using Policies.
For an individual client, under Connection Properties, go the Experience tab and set the Connection Optimization to WAN (10 Mbps or higher with high latency):
To change this setting centrally for multiple clients, in the Parallels RAS Console, select the Policies category. Add a policy for a group of users and under Session > Experience, set the connection speed to WAN.

Various control panels, administrative tools, and server settings should be disabled for standard user access if otherwise not required by organization. To disable control panel items, the following policies can be carried out from the Group Policy Microsoft Management Console (MMC): User Configuration\Administrative Templates\Control Panel
For added security, users should be restricted to not make any registry modifications: User Configuration\Policies\Administrative Templates\System
These policy setting prevents users from using Windows Installer to install patches and disables Windows update and shutdown notifications. This can be carried out from the Group Policy Microsoft Management Console (MMC):
Computer Configuration\Policies\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Windows Installer
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Windows Update
The following Control Panel items may be removed from the list of items available for standard user access:
Microsoft.AdministrativeTools
Microsoft.AutoPlay
Microsoft.ActionCenter
Microsoft.ColorManagement
Microsoft.DefaultPrograms
Microsoft.DeviceManager
Microsoft.EaseOfAccessCenter
Microsoft.FolderOptions
Microsoft.iSCSIInitiator
Microsoft.NetworkAndSharingCenter
Microsoft.NotificationAreaIcons
Microsoft.PhoneAndModem
Microsoft.PowerOptions
Microsoft.ProgramsAndFeatures
Microsoft.System
Microsoft.TextToSpeech
Microsoft.UserAccounts
Microsoft.WindowsFirewall
Microsoft.WindowsUpdate
Microsoft.DateAndTime
Microsoft.RegionAndLanguage
Microsoft.RemoteAppAndDesktopConnections
Install Application On Remote Desktop Server
Java
Flash Player
Navigate to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings.
Right click on File System, choose Add File.
In the Add a file or folder window, put %AllUsersProfile%\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Administrative Tools in the Folder field and click OK.
On the next window Database Security for%AllUsersProfile%\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Administrative Tools\Server Manager.lnk remove Users and check that Administrators have Full Access
On the Add Object window choose Configure this file or folder then Propagate inheritable permissions to all subfolders and files. Click OK.
Do the same for PowerShell shortcut (+ delete Creator Owner in database security): %AllUsersProfile%\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\System Tools\Windows PowerShell.lnk
Do the same for Server Manager shortcut: %AllUsersProfile%\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Administrative Tools\Server Manager.lnk
Disable Windows Explorer’s default context menu
Remove Run menu from Start Menu


When publishing applications, sometimes the applications will open faster than GPO’s, logon scripts, profiles or printer mapping can complete. To resolve this, Parallels RAS has the capability to introduce a delay which allows these processes to complete before launching the application.
Beginning with RAS v15 the default setting is 20 second delay. The default can be changed and the delay can be adjusted on a per application basis.
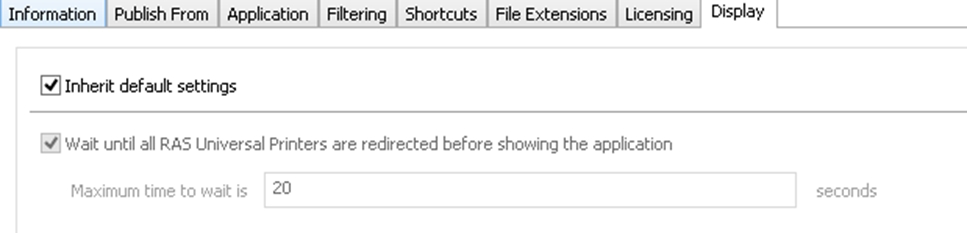
You can see from the example below that the Inherit default setting option is set for all applications to wait until RAS Universal Printers are redirected.
This option only works on Published applications from RDS/TS servers, Remote PC published applications and VDI published applications. It does not affect full desktop publishing as this type of remote access utilizes the standard Windows logon process.
To configure the Application Delay Settings:
In the RAS console, navigate to Publishing.
Click on a desired published application.
Click on the Display tab.
For individual applications, select the Wait until all RAS Universal Printers are redirected before showing the application option.
This option will also force drive mapping with an application.
If you have an application that must utilize a mapped network drive, this option will insure that the drive is mapped prior to running the application.
When the printers are properly mapped, they will appear on the client side as "%PRINTERNAME% for %USERNAME% by Parallels".

Set the Configure image quality for RemoteFX Adaptive Graphics option to Medium:
Audio and video playback allows users to redirect the remote computer audio in a remote session. It provides an improved experience for video playback in remote sessions. By default, audio and video playback is not allowed when connecting to a computer running Windows Server 2008 R2.
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd759165.aspx.
Audio and video playback redirection is allowed by default when connecting to a computer running Windows 7 or newer, or Windows Server 2012 R2 or newer.
Beginning with version 18, Parallels RAS includes built-in automated optimization capabilities for RD Session Hosts, VDI, and Azure Virtual Desktop workloads. Different preconfigured optimizations for multi-session (such as RD Session Hosts) or single-session (such as VDI) hosts are available for administrators to choose from manually or automatically to ensure a more efficient, streamlined and improved delivery of virtual apps and desktops.
Preconfigured optimizations were designed to be easily updated to support future releases of Microsoft Windows. Moreover, custom scripts may also be used within the tool to make use of already available optimizations to be deployed on Parallels RAS workload machines.
Over 130 image optimizations are available out-of-the-box and divided into the following main categories:
UWP application packages (removal; available for VDI only)
Windows Defender ATP (turn ON or OFF, disable real-time scan, exclude files, folder, processes, and extensions)
Windows components (removal)
Windows services (disable)
Windows scheduled tasks (disable)
Windows advanced options (Cortana, system restore, telemetry, custom layout)
Network performance (disable task offload, ipv6, etc.)
Registry (service startup timeout, disk I/O timeout, custom, etc.)
Visual effects (best appearance, best performance, custom)
Disk cleanup (delete user profiles, image cleanup, etc.)
Custom scripts (.ps1, .exe, .cmd, and other extensions/formats)
For the complete list of optimization categories and components, please see https://kb.parallels.com/125222.
Optimizations are applicable to RD Session Hosts, VDI, Azure Virtual Desktop, and Remote PC host pools (through VDI) based on:
Windows Server 2012 R2 and later
Windows 7 SP1
Windows 10
Optimization can be configured for the following:
RD Session Hosts
VDI
Azure Virtual Desktop
Optimization settings are configured for the above on the Site level (Site defaults) and can also be configured for individual components if the RAS administrator decides to use custom settings for a given component.
To configure optimizations on the Site level, navigate to Farm > Site, click the Tasks > Site defaults menu and choose one of the following:
RD Session Host
VDI
AVD multi-session hosts
AVD single-session hosts
In a Site defaults dialog that opens, select the Optimization tab. The user interface for configuring optimization is the same for all of the above.
To configure optimization:
If you are in the host Properties dialog or in a wizard, clear the Inherit default settings options if you want to modify them for this host.
Select the Enable optimization option.
Choose optimization type from the following:
Automatic
The Custom script optimization category is used to execute an optimization script on a target host. Before configuring this category, make sure that the script exists on target hosts and that the path and file name are the same on each host.
To configure the Custom script optimization:
Enable the Custom script category in the list (select the checkbox), then highlight it and click Tasks > Properties.
In the dialog that opens, specify the command to execute, arguments (if required), the initial directory, and credentials that will be used to execute the script.
Click OK.
When you apply the optimization to a host, the script will be executed as part of applying other optimization parameters.
After you enable optimization for a host and then click Apply in the RAS Console, the following will happen the next time the host communicates with Parallels RAS:
The host status changes to Optimization pending and the host enters the drain mode. At this stage, you can stop optimization by selecting a host in the list and clicking Tasks > Stop optimization.
Once all users are logged off, the host status changes to Optimization in progress.
After all optimization settings are applied, the host will reboot.
Optimization results are logged on a host at the following location: %ProgramData%\Parallels\RASLogs\ImageOptimizer.log. Open the file and search for entires similar to the following:
[I 78/00000009/T10C4/P0FD4] 11-30-20 10:09:19 - Image Optimization completed with 98 successful and 0 unsuccessful optimizations.
When Parallels RAS is upgraded from an older version:
The optimization feature is disabled.
The inheritance is off.
To use optimization after the upgrade, the administrator needs to enable it manually either in Site defaults or in the host pool settings.
Please note the following:
Some optimizations may fail and generate warnings if they had been already applied.
Some optimizations may fail and generate warnings depending on OS specifics. For example, removal of UWP apps may fail because apps are already absent.
Manual: Gives you full control over which optimization options to use and allows you to configure each one. This option also gives you an option to use a custom optimization script that will be executed on the host.
If you selected Manual in the previous step, configure optimization categories and components according to your requirements. See Configure optimization below.
Force optimization on all enabled categories: This is a special option that should only be used in situations when some parts of optimization failed to apply to a host for some unforeseen reason (e.g. the host went offline unexpectedly). When you select this option, then click OK and then Apply in the RAS Console, the entire optimization configuration will be applied to the host. This way you can make sure that changes that you made to optimization components last time, and that were not applied to the host, will be applied again. The state of the Force optimization on all enabled categories option (selected or cleared) is not saved because this is a one-time action, so the next time you open the dialog, the option will be cleared again. Note that in a standard scenario, when you make changes and then apply them to a host, you don't need to select this option, because normally you want to apply just the changes that you made, not the entire optimization configuration.
The Category list contains optimization categories that can be configured. To include a category in optimization, select the corresponding checkbox. Some categories contain multiple components, which can be configured individually, some have settings that can be customized. To configure category settings or components, highlight the category and click the gear icon (or click Tasks > Properties, or simply double-click a category). Depending on the category selected, you can do the following:
Configure category settings (choose from available options, select or clear individual settings, specify values, add or remove entries).
Add or remove underlying components to include or exclude them from optimization (use the plus- and minus-sign icons). When adding a component (where available), you can select from a predefined list or you can specify a custom component.
In some cases (specifically registry entries) you can double-click an entry and specify multiple values for it.
If you remove a predefined component, you can always get it back in the list by clicking Tasks > Reset to default. You can also use this menu to reset category settings to default values if they were modified.
The last optimization category in the list is Custom script. You can use it to execute an optimization script that you may have available. Read the Using custom script subsection below for details.
When done, click OK to close the dialog.
RDSH template
Yes
RDSH Site defaults
RDSH from template
No
None
VDI Site defaults
Yes
None
VDI host standalone
Yes
VDI Site defaults
VDI host template
Yes
VDI Site defaults
VDI host from template
No
None
Azure Virtual Desktop Site defaults
Yes
None
Azure Virtual Desktop host pool - hosts from a template
No
None
Azure Virtual Desktop host pool - standalone hosts
Yes
AVD multi-session hosts Site defaults or AVD single-session hosts Site defaults.
Azure Virtual Desktop template
Yes
AVD multi-session hosts Site defaults or AVD single-session hosts Site defaults.
Azure Virtual Desktop hosts from template
No
None
RDSH Site defaults
Yes
None
RDSH host pool
No
None
RDSH standalone
Yes
RDSH Site defaults



















All Parallels RAS server components are Windows Server based, with the exception of Parallels HALB appliance and VDI virtual appliances.
RAS Connection Broker and RAS Secure Gateway are supported on the following operating systems:
Windows Server 2016 up to Windows Server 2022
On Windows Server 2016, 2019, and 2022 both Server Core and Desktop Experience installations are supported
Same OS requirements as for RAS Connection Broker (see above). Note that for larger environments (2000 or more concurrent connections), it is recommended to install the component on a dedicated server. For details, please see https://kb.parallels.com/en/124988.
RAS RD Session Host Agent is supported on the following operating systems:
Windows Server 2012 R2 up to Windows Server 2022
Windows Server 2016 and newer must be installed using the "Desktop Experience" installation option.
Windows Server 2012 R2 — Server Core installation option is not supported.
Windows Server 2016 up to Windows Server 2022
For the list of supported VDI providers, see RAS Provider Agent Installation Options.
Windows Server 2008 R2 up to Windows Server 2022
Windows 10 up to Windows 11
Windows Server 2012 R2 up to Windows Server 2022
Windows 10 up to Windows 11
Windows Server 2016 up to Windows Server 2022
Windows 10 up to Windows 11
Windows Management Framework 3.0 and .NET Framework 4.5.2 must be installed
Windows Server 2016 up to Windows Server 2022
Windows 16 up to Windows 11
Windows Server 2012 R2 up to Windows Server 2022
Windows Server 2016 up to Windows Server 2022
For complete software requirements, please see the Parallels RAS Administrator's Guide (the Software Requirements section). To view and download the guide, please visit https://www.parallels.com/products/ras/resources/.
Parallels RAS can be installed using Active Directory or Local Windows Security.
VDI for RAS requires Active Directory.
Installation of any RAS component on an Active Directory Domain Controller is not supported.
If using Active Directory, Windows Servers must be joined to a Domain and the right hostname configured before installing RAS.
Do not change the server hostname after installing Parallels RAS or reconfiguration of Parallels RAS would be required.
Use a static or permanently reserved DHCP address.
SSL on the Gateway servers requires name resolution. For Gateways to function properly, one of the two following conditions must be met:
DNS resolution must be available.
HOSTS files can be configured for DNS resolution.
See the chapter.
RAS v15 and higher can automatically configure Windows Firewall settings during installation or deployment of additional RAS farm components to allow communication between different RAS servers in a farm.
For manual configuration of the Windows Firewall, do not check the "Add Firewall Rules" when deploying RAS components.
A comprehensive list of required Firewall ports can be found in the Port Reference section of the Parallels RAS Administrator’s Guide, which can be download from http://www.parallels.com/products/ras/resources/.
When pushing RAS components to another server from the RAS console, one of the following conditions must be met on the remote server:
Open Windows Firewall ports TCP 135, 445, 49179, then push the RAS components and have the Windows Firewall ports automatically configured.
Temporarily disable Windows Firewall, push the RAS components and have RAS automatically configure the firewall settings, and then re-enable the Windows Firewall.
Manually configure Windows Firewall settings as described in the Port Reference section of the Parallels RAS Administrator's Guide, and then install the RAS component(s).
The below highlights the prerequisites required to use HALB:
Firewall or router in front of a HALB configured to preserve the source IPs of client devices