
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Regardless of the size of a Parallels RAS installation, redundancy among core components of your setup is recommended to ensure the greatest possible uptime. For small deployments, all roles can be installed on a single server, whereas role segregation is recommended for large setups.
The physical location of a Parallels RAS farm, including RD Session Hosts and VDI hosts, must be selected based on the location of back-end resources, such as databases and file servers. This means that if a front-end application connects to a database or works with files on a file server, the RD Session Host on which it will be installed should be located close to the database (or the file server) on the intranet with fast, reliable, low latency LAN connections. For example, let's say you have a client-server application that you want to make available to your users. To do so, you will install the client part on an RD Session Host and publish it for your users. The database will continue to run on a dedicated server. To guarantee fast and reliable database access, the RD Session Hosts server and the database server must be close to each other on the local network.
This guide is intended for system administrators deploying and managing Parallels® Remote Application Server (RAS) in their organizations. It begins with the introduction to Parallels RAS and its key components and then outlines the basic principles of how these components operate. The main topics of this guide describe various Parallels RAS deployment scenarios, complete with diagrams and other information. The guide concludes with the information about communication ports used by Parallels RAS and the information about using SSL certificates.
This scenario can be implemented by an organization that needs to use single image management for RD Session Hosts and dynamic resource allocation for published applications and desktops.
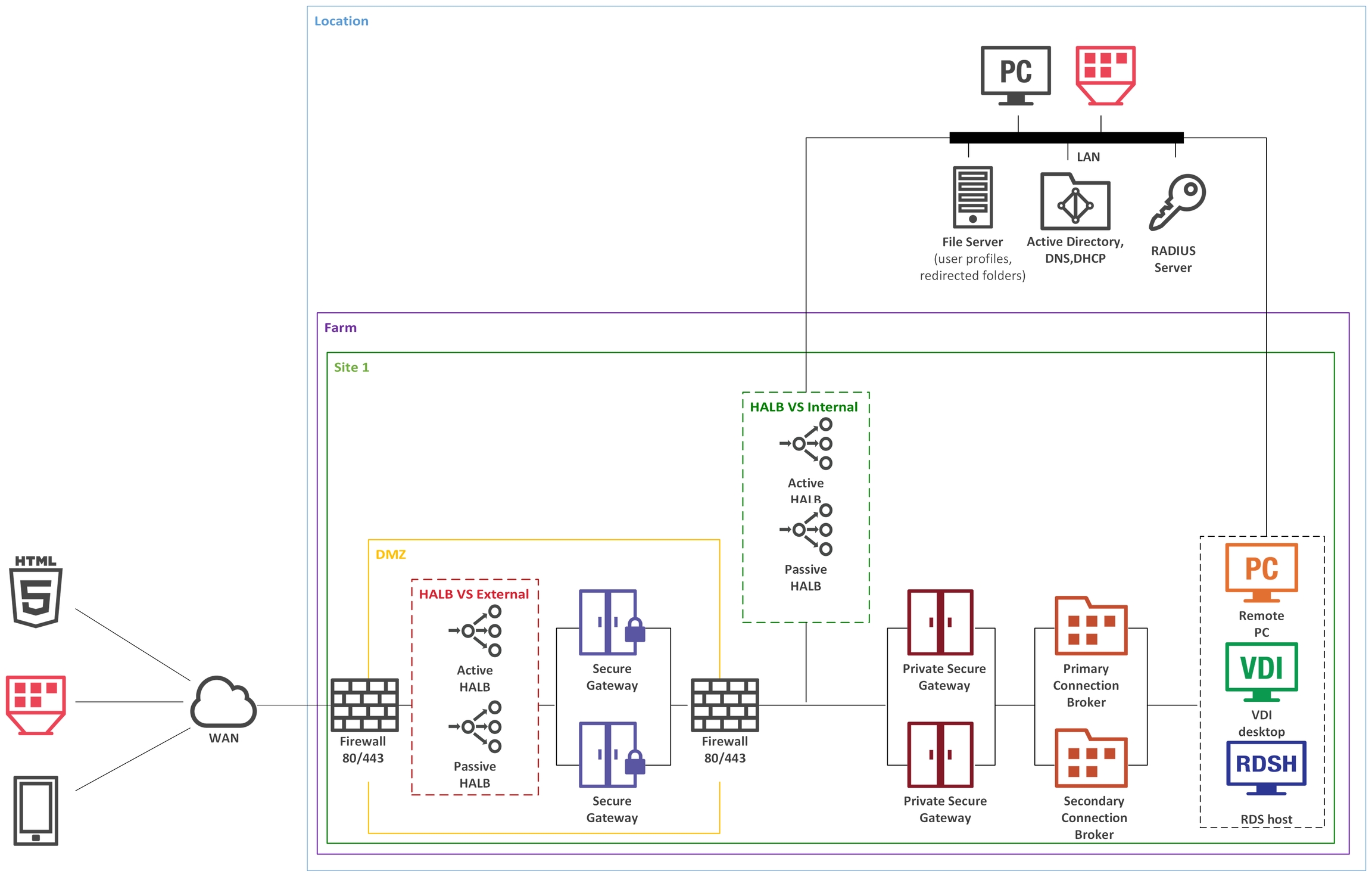
For high availability, HALB Virtual Server (VS) should have a secondary HALB appliance, additional RAS Connection Broker and RAS Secure Gateway should be deployed. HALB Virtual Server (VS) is a virtual representation of the HALB appliances.
The components on the primary RAS Connection Broker are installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
A new type of RAS Template adds support for an RD Session Host running in a guest VM where both the RAS Guest Agent and RD Session Host Agent are push-installed in the VM from the RAS Console.
An RD Session Host pool is assigned a RAS Template and is then used for publishing of applications and desktops.
RD Session Host creation, maintenance and deletion is done via the RAS Template.
An RD Session Host pool assigns RD Session Hosts on demand providing more resources on the workload increase and unassigns RD Session Hosts on the workload decrease.
HALB Virtual Server (VS) is configured with two HALB appliances.
A Parallels RAS farm placement depends on the location of a back-end resource. Therefore, it is possible to continue operations by adding an additional remote location where the back-end resources are replicated (the appropriate software and hardware solutions are out of the scope of this document) and placing one more Parallels RAS site in this location.
Setting up a disaster recovery site, and then configuring the Parallels Client to use the closest site as the primary connection and the disaster recovery site as the secondary connection, allows users to always be connected to the primary site and to continue working using the disaster recovery site in case of failure.
WAN users can be invited to use all sites and setup HALB VS IP address of the first site as Server Address and HALB VS IP address of the second and third sites as Secondary Server IP in the RAS connection settings on the Parallels Client side. The RAS connection settings can be configured either centrally (via Client Policy in the Parallels RAS Console) or manually.
By using this scenario you can publish applications and desktops from virtual machines, RD Session Hosts, and Windows desktop computers located in your office.
RAS Secure Gateway and primary RAS Connection Broker are installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
All other components are push-installed from the RAS console.
Primary RAS Connection Broker is installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation). Secondary RAS Connection Broker is push-installed from the RAS Console.
HALB is installed as a ready-to-use virtual appliance and configured in HALB VS properties.
All other components are push-installed from the RAS console.


A Remote PC is a physical desktop running Windows that can be used for remote application and desktop publishing. In addition to individual Remote PCs, where every PC is published for a single user and must be specified for publishing, we've added Remote PC host pools to Parallels RAS.
Remote PC host pools are targeted for application and desktop publishing from Remote PCs which are located in a single data center. Remote PC host pools provide the most effective hardware utilization for companies that use shift work (e.g. companies that provide 24/7 service) or when users are located in different time zones. A user is assigned a Remote PC on the first use. After a shift ends, the PC is either released back to the host pool to be re-used by a user from the next shift or, depending on the admin settings, the persistence is kept (3 days by default).
The RAS Guest Agent is used with Remote PC host pools instead of the Remote PC Agent. Host pool membership is built from either a PC list (manually adding individual PCs or importing the list from a CSV file) or based on an Active Directory OU location (the list is refreshed by the RAS Connection Broker every 5 minutes).
RAS Connection Broker is installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
RAS Secure Gateway, RAS Guest Agent are push-installed from the RAS console.
Many companies use the perimeter network (DMZ) to separate the public network with servers that handle exposed services and the internal network with servers that handle internal services. There are two types of DMZ: single-hop and double-hop, with the latter using three firewalls and therefore being more expensive, but more secure (with three firewalls, using different firewall technologies, you can avoid one weakness or one type of attack breaking all firewalls). A firewall between RAS Secure Gateways and the intranet must allow gateways and systems to connect to a RAS Connection Broker using the standard port.
This scenario enables high availability for client connections using RAS connection settings on either the Parallels Client side or round-robin DNS.
To enable high availability for client connections using RAS connection settings, the Parallels Client should be configured to connect to primary and secondary Secure Gateways using the primary and secondary connection settings in the RAS connection properties. In this case primary and secondary RAS Secure Gateways must be configured to connect to the same RAS Connection Brokers (using Advanced Client Gateway Settings). When the Primary RAS Secure Gateway is not available, Parallels Clients can connect to the farm using the Secondary RAS Secure Gateway. The client settings can be applied either centrally (via Client Policy in the RAS Console) or manually.
To enable high availability for client connections using round-robin DNS, two new host records must be created in the DNS forward lookup zone with the same name (e.g. myhost.example.com) but with two different IP addresses of primary and secondary RAS Secure Gateways.
RAS Connection Broker is installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
All other components are push-installed from the RAS console.
Farm is a collection of Parallels RAS components maintained as a logical entity with a unique database and licensing.
Site is a managing entity usually based on a physical location. Each site consists of at least a RAS Connection Broker, RAS Secure Gateway, and agents installed on RD Session Hosts, virtualization servers, and Windows PCs. There can be multiple sites in a given farm.
Parallels RAS Console is a desktop application for administrators who manage Parallels RAS.
Parallels RAS Management Portal is a modern web-based configuration and administration portal. The Management Portal is designed for administrators using a desktop or laptop computer or a mobile device to carry out configurations and day-to-day activities.
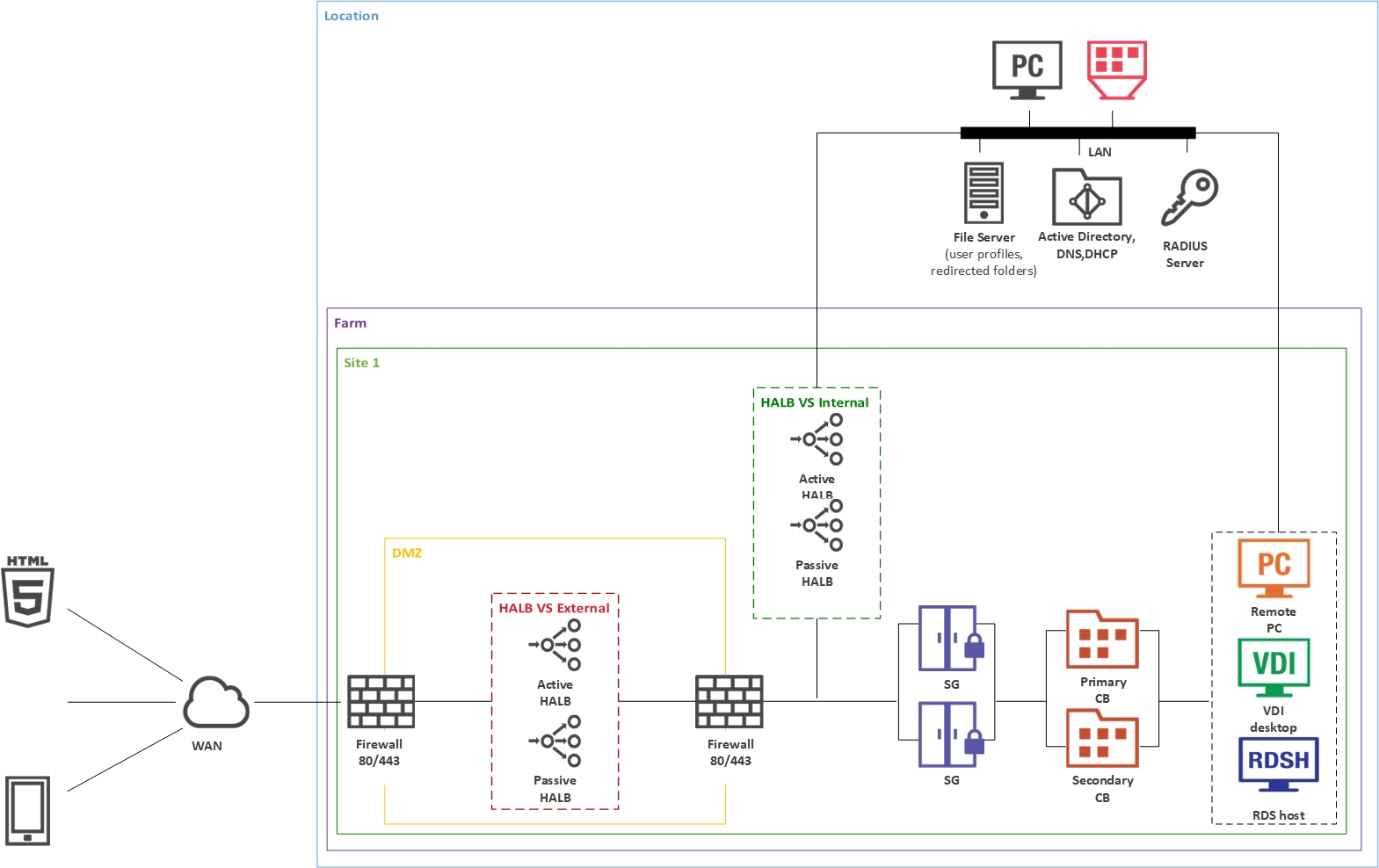
RAS Connection Broker provides access to published applications and desktops and load balances application traffic. High availability can be achieved by adding a secondary RAS Connection Broker to a site.
RAS RD Session Host Agent is installed on an RD Session Host and enables publishing of server resources (applications and desktop). RAS RD Session Host Agent also collects the necessary information from the server on which it's running and sends it to the RAS Connection Broker, which uses it for load balancing and some other purposes.
This scenario can be implemented by an organization that needs to load-balance published applications and desktops between two RD Session Hosts. For high availability, a secondary RAS Connection Broker and RAS Secure Gateway should be installed on the second server.
The components on the primary RD Session Host (where the primary RAS Connection Broker is installed) are installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
The components on the secondary RD Session Host are push-installed from the RAS console.
This scenario is suited for environments where it is necessary to keep published resources of distinct clients (departments, groups, teams, etc.) isolated. Parallels RAS Multi-Tenant architecture enables organizations to share the RAS infrastructure components among different tenants while keeping client data segregated and reducing costs.
The RAS Multi-Tenant architecture offers the following advantages to Service Providers and organizations:
Cost savings due to reduction of number of RAS Secure Gateways and High Availability Load Balancers (HALBs) while maximizing resource usage and consolidation.
Faster onboarding of new tenants/customers.
In a single-hop DMZ scenario, the firewall system must be capable of routing connections properly from RAS Secure Gateways to RAS Connection Brokers. The firewall system is also responsible for connections from the Internet to the virtual IP address of a HALB Virtual Server (HALB VS) representing HALB virtual appliance(s) or other generic protocol load balancing scenarios. Note that in this case two HALB Virtual Servers are used for internal and external traffic load balancing to internal Secure Gateways.
To differentiate traffic between internal and external network, you can use public and private Secure Gateways (both are equal from the RAS perspective):
In a configuration of this type, HALB appliances installed in front of RAS Secure Gateways in the internal perimeter network (DMZ). The WAN users connect to the IP address of external HALBS VS, while LAN users use IP address of the internal HALB VS, which use HALB appliances installed in front of the Secure Gateways located in internal network. The Parallels Client settings can be configured either centrally (via Client Policy in the Parallels RAS console) or locally on a device where Parallels Client is running. To add high availability for HALB VS, the second appliance can be deployed for external internal and HALB VS.
SAML authentication allows Service providers and enterprises with multiple subsidiaries to reduce costs by offload the Identity Management burden to the identity providers. Integrating with third party Identity Providers allows customers and partners to provide end users with a true SSO experience.
Comparing to previously described scenarios, the new server role needs to be added the Farm. As part of the SAML SSO process, the new host with RAS Enrollment Server component communicates with Microsoft Certificate Authority (CA) to request, enroll, and manage digital certificates on behalf of the user to complete authentication without requiring the users to put in their Active Directory credentials.
Parallels RAS supports the following delivery options:
Web Client
Web Client portal initiated SAML for Windows
The following diagram illustrates communication ports used in Parallels RAS.
The above diagram include SAML SSO components such as RAS Enrollment Server, however it does not include Tenant Broker.
Tip: If you are reading the PDF version of this guide, click the following link to view the full-sized diagram in a web browser:
This scenario uses a single RD Session Host for publishing applications and desktops. SSL and User Portal are enabled by default with a self-signed server certificate. The server certificate should be trusted by client devices. Enterprise certificate or third-party trusted Certificate Authority can be used for external access (for details, please see the section).
All server Parallels RAS components are installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
Single server deployment is not recommended for production environments, as it does not provide high availability of service. Such deployment should be used for test or developer environments.
For Active Directory and Active Directory Domain Services port requirements, please see the following article: .
RAS Guest Agent is installed in the guest operating system of a virtual machine. RAS Guest Agent enables resource publishing from VDI hosts and VDI RD Session Hosts and collects information required by RAS Connection Broker.
RAS Provider Agent collects information from the Parallels RAS Infrastructure and is responsible for controlling a Provider through its native API. RAS Provider Agent comes in two varieties. One is built into the RAS Connection Broker and is available by default. It can be used to control multiple Providers in a Parallels RAS Farm. The other is a separate component that can be installed manually on a Provider host, in which case it will work with that host only. The built-in RAS Provider Agent can be used with any Provider supported by Parallels RAS except QEmu KVM with libvirt and Nutanix Acropolis. With these two hypervisors, a dedicated RAS Connection Broker must be manually installed on a Provider host. See RAS Provider Agent dedicated below for more info.
RAS Provider Agent dedicated is a separate component that can be installed from the Parallels RAS installer. It serves the same purpose as the built-in RAS Provider Agent described above. The difference is, you can only use a dedicated RAS Provider Agent to control the Provider on which it is installed.
RAS Secure Gateway is a service that acts as a proxy between the Parallels Client software running on client devices and Parallels RAS. A Secure Gateway encrypts the communications using SSL. Multiple RAS Secure Gateways can work in high availability mode with Parallels HALB.
High Availability Load Balancing (HALB) is an appliance that provides load balancing for RAS Secure Gateways. Parallels HALB virtual appliance is available for Hyper-V and VMware. Multiple HALB Virtual Servers can be configured, each assigned with different virtual (and floating) IPs to load balance traffic to Secure Gateways in the same RAS Site. This enables administrators to configure Virtual Servers for segregated access, for example when using different Secure Gateways for internal and external access or different office branches. Multiple HALB deployments can run simultaneously, one acting as the primary and others as secondary. The more HALB deployments a site has, the lower the probability that end users will experience downtime. Primary and secondary HALB deployments share a common or virtual IP address (VIP). Should the primary HALB deployment fail, a secondary is promoted to primary and takes its place. Because HALB virtual appliances use source IP for load balancing, a firewall or router in front of them should be configured to preserve the source IPs of the client devices.
Parallels Device Manager is a Parallels RAS feature that allows the administrator to manage Windows computers. Windows 7 and new are supported.
Parallels Desktop Replacement is a sub-feature of Parallels Device Manager (see above). It allows the administrator to convert a standard desktop into a limited device similar to a thin client without replacing the operating system on it.
RAS Enrollment Server is an essential component of the SAML SSO Authentication functionality. It communicates with Microsoft Certificate Authority (CA) to request, enroll, and manage digital certificates on behalf of the user for SSO authentication in the Parallels RAS environment.
Azure Virtual Desktop is a desktop and app virtualization service running on Microsoft Azure, providing access to RD Session Hosts and VDI, including the new offering of Windows 10 and Windows 11 Enterprise multi-session hosts. Parallels RAS 18 provides the ability to integrate, configure, maintain, support and access Azure Virtual Desktop workloads on top of the existing technical capabilities of Parallels RAS.
Microsoft FSLogix Profile Container is the preferred Profile Management solution as the successor of Roaming Profiles and User Profile Disks (UPDs). It is set to maintain user context in non-persistent environments, minimize sign-in times and provide native profile experience eliminating compatibility issues.
SSRS
Microsoft SQL Server
TCP
1433
RAS Console is connected to RAS Reporting


Use IIS to receive a certificate from the Enterprise CA and export the certificate in the PFX format. To install the PFX certificate in Parallels RAS, import it as described in the Import the certificate subsection above.
This section explains how to use SSL certificates in Parallels Application Server deployments. You should read this section if you are setting up a RAS environment to test one or more of the deployment scenarios described earlier in this guide.
By default, a self-signed certificate is installed on a RAS Secure Gateway. Each RAS Secure Gateway has its own certificate, which should be added to Trusted Root Authorities on the client side to avoid security warnings.
To simplify the Parallels Client configuration, using a certificate issued either by a third-party Trusted Certificate Authority or Enterprise Certificate Authority (CA) is recommended.
If an Enterprise CA certificate is used, Windows clients receive a Root or Intermediate Enterprise CA certificate from Active Directory. Client devices on other platforms require manual configuration.
If a third-party certificate issued by a well-known Trusted Certificate Authority (e.g. Verisign) is used, the client device trusts using Trusted Certificate Authority updates for the platform.
For internal commands - memshell, printer redirector)
RAS Performance Monitor
TCP
8086
Agent (Telegraf service) sends collected performance data to InfluxDB
RAS Enrollment Server
TCP
30030
RAS Guest Agent (PrlsSCDriver) connects to get logon credentials
FSlogix
TCP
443
Download FSlogix installer
RAS Guest Agent (used by Azure Virtual Desktop)
Provider Agent
TCP, UDP
30006
Communication with Provider Agent
Subnet broadcast is sent to find Provider Agent
Regular UDP heartbeats
Localhost
TCP
30005
Extended market reach through reduction of operational costs for organizations of any size by allowing cost scaling through shared infrastructure.
Tenants are deployed as separate individual RAS Farms or Sites.
A Tenant Farm doesn't need its own RAS Secure Gateways and HALB. However, deployments with Secure Gateways and HALB are possible if a Tenant needs them for internal connections.
All external users connect to a Tenant Farm through the Tenant Broker infrastructure.
The network configuration of a Tenant requires the Tenant Connection Broker to Tenant Broker Connection Broker connectivity. Additionally, shared RAS Secure Gateways need to communicate with servers hosting published resources and the Tenant Connection Broker. These communications require only a limited number of open ports, which are listed below:
Tenant Connection Broker > Tenant Broker Connection Broker: port 20003
Tenant Broker Gateway > Tenant Broker Connection Broker: port 20002
Tenant Broker Gateway > Tenant Connection Broker: port 20002
Tenant Broker Gateway > Servers hosting published resources: port 3389
Communications with a Tenant domain are always performed from a local Tenant Connection Broker and never from the Tenant Broker infrastructure.
Every Tenant must have a unique public domain address. Multiple unique domain addresses, however, can resolve to the same IP address.
RAS Connection Broker on the Tenant Broker is installed from the Parallels RAS installer using the Tenant Broker installation option.
RAS Connection Broker on a Tenant is installed from the Parallels RAS installer using standard installation.
HALB is installed as a ready-to-use virtual appliance and configured in HALB VS properties.
All other components are installed remotely from the RAS console:
Tenant Broker components are installed from the Tenant Broker console.
Tenant components are installed from the Tenant console.
RAS Connection Broker is installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
HALB is installed as a ready-to-use virtual appliance and configured in HALB VS properties.
All other components are push-installed from the RAS console.
Web Client initiated SAML for Mac and Linux
Web Client initiated SAML for Android and iOS
Parallels Client for Windows initiated SAML Authentication
Parallels Client for Mac initiated SAML Authentication
The below high-level logical diagram depicts SAML authentication and login process within a Parallels RAS environment:
The SAML authentication and login steps on the diagram above are:
RAS Secure Gateway redirects the Parallels Client login request to the IdP site.
The user authenticates with IdP.
IdP redirects the user to the RAS Secure Gateway with the SAML Assertion.
The user is authenticated using the SAML Assertion and the user is logged in.
The list of the available RAS published resources is retrieved.
The user chooses a published resource and launches it from Parallels Client.
The launch request from the user is sent to the server side and the resource is started on the available server.
A Parallels RAS session is established.
User certificate is processed:
Certificate is requested.
Certificate is created.
Encryption is preformed using the certificate.
Smartcard logon.
This scenario is suited for environments where published resources are distributed between two or more physical locations. Different administrators can administer a Parallels RAS farm containing multiple sites.
Each site consists of at least a RAS Connection Broker, RAS Secure Gateway (or multiple Secure Gateways), and agents installed on RD Session Host or VDI servers, or Windows PCs.
If the resource set is similar, end users can use both sites via a single RAS connection. The following settings should be used as RAS connection properties in Parallels Client:
Primary connection: local Primary Secure Gateway.
Secondary connections:
Local Secondary Secure Gateway.
HALB VS IP address of Site2.
Primary connection – local Primary Secure Gateway
Secondary connections:
Local Secondary Secure Gateway
HALB VS IP address of Site1
Primary connection - HALB VS IP address of Site1
Secondary connections - HALB VS IP address of Site2
RAS connection settings can be configured either centrally (via Client Policy in the Parallels RAS Console) or manually.
RAS Connection Broker is installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
HALB is installed as a ready-to-use virtual appliance and configured in HALB VS properties.
All other components are push-installed from the RAS console.
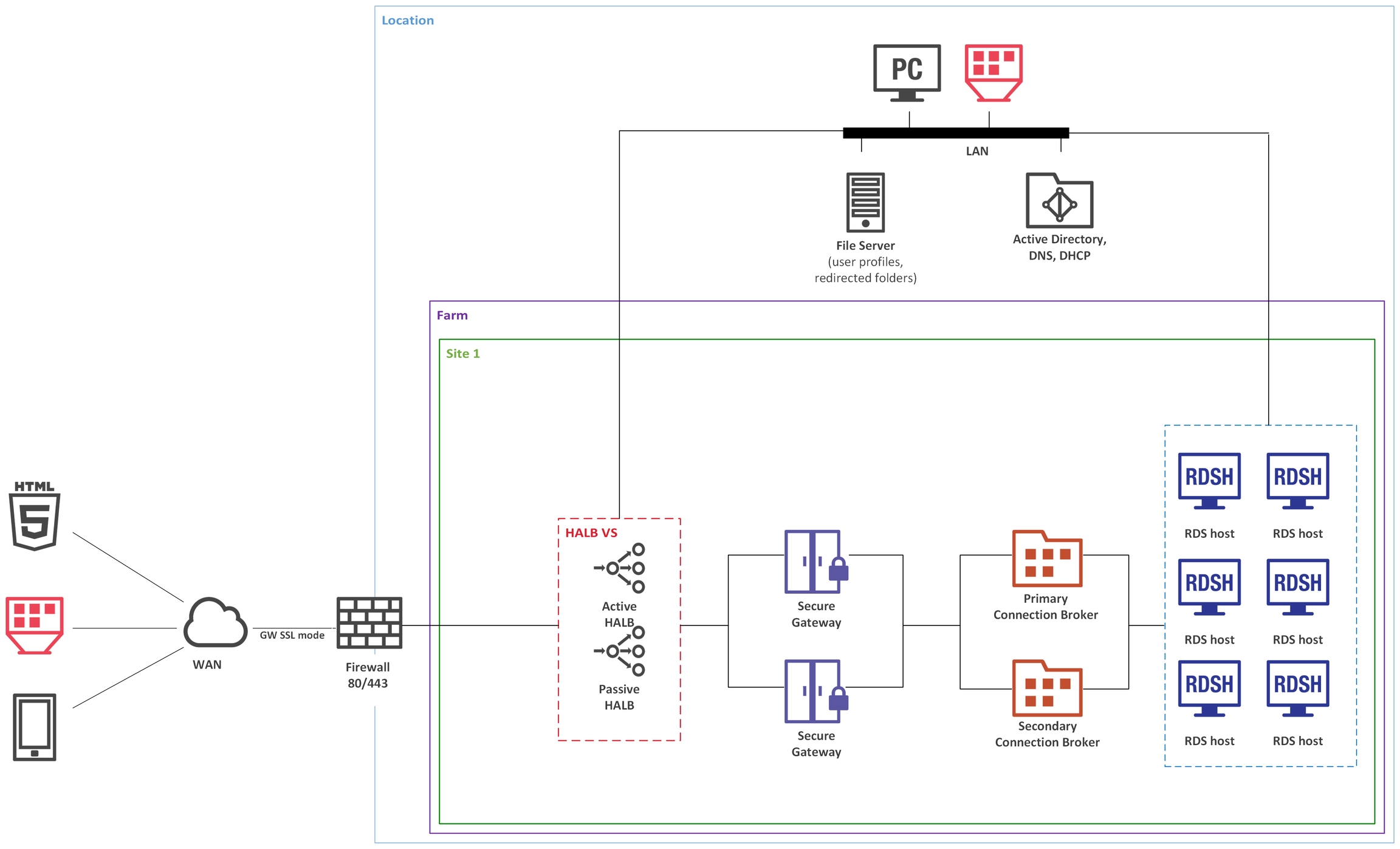
To handle more connections on Secure Gateways, using a designated RAS Secure Gateway is recommended for intranet users (private) with direct client connection mode.
To apply stricter security settings to servers with Internet access, using a designated Secure Gateway is recommended for Internet users (public) with Gateway SSL client connection mode.
The appropriate RAS connection settings can be applied either centrally via Client Policy in the Parallels RAS Console or manually in the Parallels Client.
Public RAS Secure Gateway and primary RAS Connection Broker are installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
All other components are push-installed from the RAS console.
Web browser (HTML5) and Let's Encrypt service
RAS Web Admin Service [RAS Management Portal]
TCP
20443
Admin access to HTML5 based Management Portal of RAS environment
HALB
TCP
HALB
HALB
VRRP
112
HALB to HALB communication used for automatic assignment of VIP to active HALB.
RAS Secure Gateway in Forwarding Mode
TCP, UDP
RAS RD Session Host Agent
RAS Connection Broker
TCP, UDP
20003
Used for communications with RAS Connection Brokers.
Localhost
TCP
The Client Manager feature allows the administrator to convert Windows devices running Windows 7 and newer into a thin-client-like OS. After the Windows Device Enrollment has been performed, features like Desktop Replacement, Kiosk Mode, Power Off, Reboot, and Shadow become available.
Shadowing provides access to the full Windows client device desktop and allows controlling applications running locally on the system, as well as any remote applications published from Parallels RAS. Shadowing requires a direct connection between the machine on which the Parallels RAS console is running and the device itself.
The Replace Desktop option limits users from changing system settings or installing new applications. Replacing the Windows Desktop with Parallels Client transforms the Windows operating system into a thin-client-like OS without replacing the operating system itself. This way, users can only deploy applications from the client, thus providing the administrator with a higher level of control over connected devices.
Additionally, Kiosk mode prevents users from shutting down or rebooting their computers.
RAS Connection Broker is installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
All other server-side components are push-installed from the RAS console.
Parallels Client is installed on client desktop computers and converted Windows PCs using the Parallels Client installer.
RAS Enrollment Server
AD DS controllers
TCP
TCP
TCP,UDP
UDP
389, 3268
636, 3269
88
53
LDAP
LDAPS
Kerberos
DNS
RAS Connection Broker
TCP
UDP
Parallels RAS Management Portal is a modern web-based configuration and administration console designed for Parallels RAS administrators using a desktop or a mobile device to carry out configurations and day-to-day activities. To use RAS Management Portal in a RAS Farm, you need to install the RAS Web Administration Service component. You can install this component on the machine with a Connection Broker or on a dedicated machine.
In this scenario, all components, including RAS Web Administration Service, are installed on a single RD Session Host. This configuration is only recommended for proof-of-concept and small environments.
The components on the primary RAS Connection Broker are installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
For larger environments with multiple administrative activities, it is recommended to use a dedicated server for hosting RAS Web Administration Service in order to decrease load on the Connection Broker.
The components on the primary RAS Connection Broker are installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
RAS Web Administration Service is installed using Windows Installer (custom installation).
This scenario is ideal for high availability environments with more than 300 concurrent users connected in SSL mode. Each client gateway should optimally handle 300 to 500 concurrent user connections* (see the note below). This can be scaled horizontally accordingly.
Both LAN and WAN users connect to IP address of the HALB VS which represents the HALB virtual appliances in the internal network.
Please note that the diagram above includes an optional secondary RADIUS server which can be used as active/active or active/passive to provide high availability.
See also Capacity Considerations.
All RAS Secure Gateways must be configured to connect to the same RAS Connection Brokers (using the Advanced Client Gateway Settings—see above).
Installation Notes
RAS Connection Broker is installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
HALB is installed as a ready-to-use virtual appliance and configured in HALB VS properties.
All other components are push-installed from the RAS console.
RAS Reporting Service
MS SQL
TCP
1433
Store RAS activity information
SSRS
TCP
Azure Virtual Desktop is a desktop and app virtualization service running on Microsoft Azure, providing access to RD Session Hosts and VDI, including the new offering of Windows 10 and Windows 11 Enterprise multi-session hosts. Parallels RAS provides the ability to integrate, configure, maintain, support and access Azure Virtual Desktop workloads on top of the existing technical capabilities of Parallels RAS.
The diagram below illustrates a hybrid deployment of Parallels RAS and Azure Virtual Desktop with the following characteristics:
Workload hosts are available both on-premises through standard Parallels RAS deployment and on Microsoft Azure through the service.
Azure Virtual Desktop objects such as workspaces, host pools, desktop and RemoteApp groups are created and configured from the Parallels RAS Console.
RAS Reporting relies on Microsoft SQL Server and SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS). In small environments, a SQL Server database instance, SSRS and RAS Reporting can be installed on the same server where primary RAS Connection Broker is running.
Primary RAS Connection Broker is installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
Secondary RAS Connection Broker is push-installed from the RAS console.
RAS Reporting is installed using Parallels RAS installer.
VDI host pools are targeted for application and desktop publishing from hosts (full or linked clones) which are located in a single data center.
VDI hosts have the following advantages:
Rapid deployment of a common supported desktop environment across the company's network using a single Windows 7, 8, or 10 desktop image for creating virtual machines (VMs) on a hypervisor.
Centralized deployment of updates and changes to Windows VDI desktops — all you need to do is update a single image.
In case of failure, the VDI desktops can be easily restored using a single image backup.
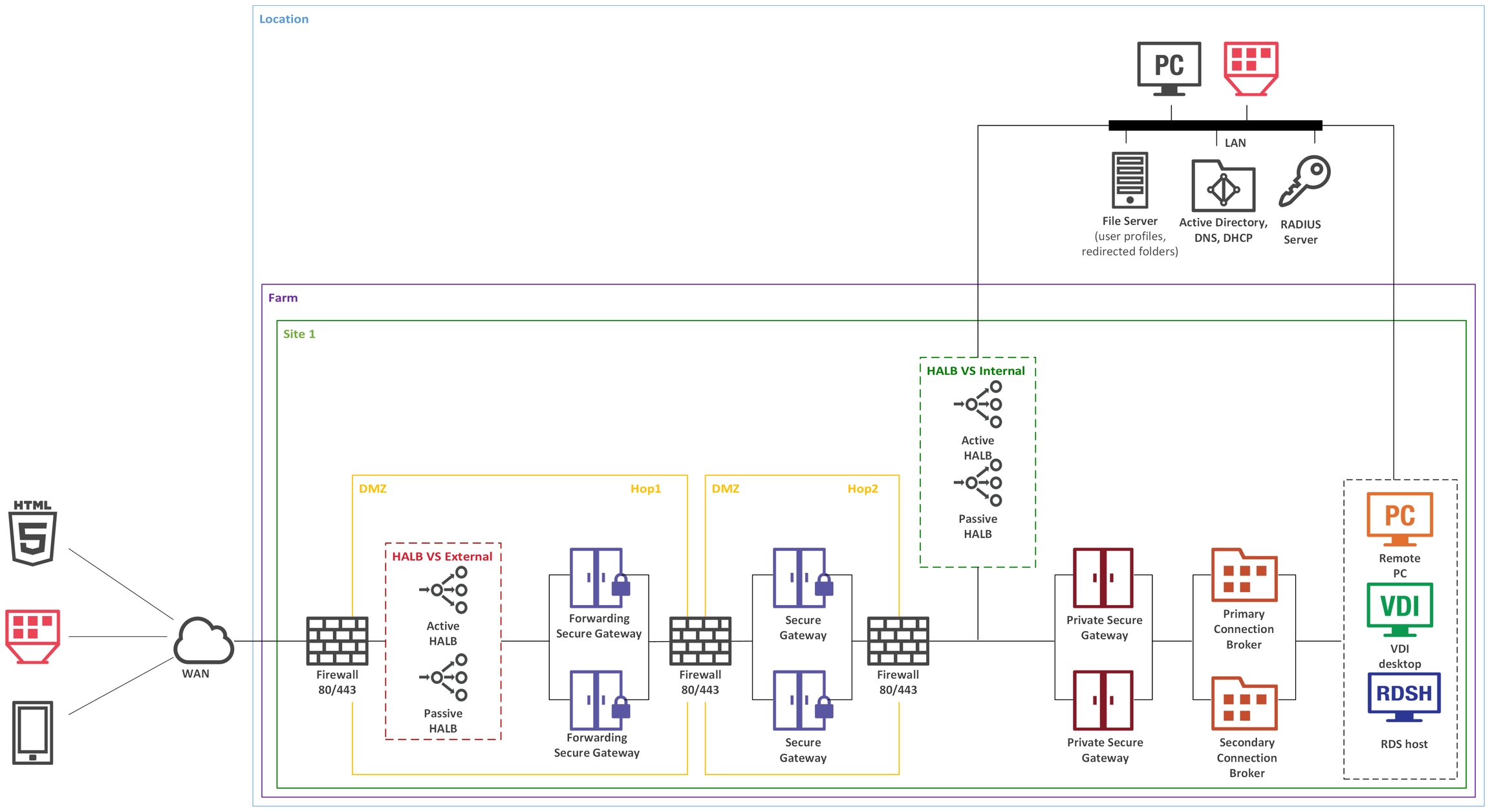
In a double-hop DMZ scenario, settings are simpler and the protection from external malicious agents is higher. Double-hop DMZ requires Forwarding RAS Secure Gateways installed in the perimeter network to pass client connections to RAS Secure Gateways residing in the internal second perimeter network (the second hop).
In such configuration, the HALB VS with a HALB pair (primary and secondary) is installed in front of Forwarding RAS Secure Gateways in DMZ. WAN users connect to Parallels RAS using the IP address of the HALB VS, while LAN users use IP address of the internal HALB VS, which use HALB appliance installed in front of the gateways located in internal network. Parallels RAS connection properties can be configured either centrally (using Client Policy in the RAS Console) or manually in Parallels Client.
Forwarding RAS Secure Gateways forward network traffic using the Forward requests to next RAS Secure Gateway in chain option in the Advanced tab of the Forwarding RAS Secure Gateway properties.
Parallels recommends using Forwarding RAS Secure Gateways in double hop DMZ deployments only.
To differentiate traffic between internal and external network, you can use public and private gateways (both are equal from the RAS perspective):
80, 443
End-user access to Parallels RAS Web Client (on Secure Gateway in Normal mode) through the HALB Note: Ports 80 and 443 must be open for incoming requests when using Let's Encrypt.
RAS Secure Gateway
TCP
80, 443
End-user access to Parallels RAS Web Client (on Secure Gateway in Normal mode) Note: Ports 80 and 443 must be open for incoming requests when using Let's Encrypt.
80, 443
Management and user session connections.
RAS Secure Gateway in Normal Mode
TCP, UDP
TCP, UDP
80, 443
20009
Management and user session connections.
Device Manager shadowing via Firewall (indirect network connection).
30005
For internal commands (memshell, printer redirector).
FSlogix
TCP
443
Download FSlogix installer
RAS Performance Monitor
TCP
8086
Agent (Telegraf service) sends collected performance data to InfluxDB.
RAS Enrollment Server
TCP
30030
RAS RD Session Host Agent (PrlsSCDriver) connects to get logon credentials.
20003
20003
Settings synchronization and performance counters.
Deny Connection Request
Certificate Authority (CA)
TCP
TCP
135
dynamic range
49152 - 65535
DCOM/RPC ports
8085, 443
Enumeration of reports (incl. custom reports)
Tenant - RAS Connection Broker
Tenant Broker - RAS Connection Broker
TCP
20003
Tenant's RAS Connection Broker communicates with Tenant Broker to join Tenant Broker, synchronize configuration and statuses

Log retrieval
RAS Provider Agent
TCP
30006
Log retrieval
RAS Connection Broker
TCP
20002, 20001 30020
Communication with GA and Redundancy
Used during publishing to browse for installed applications or single file/folder browsing.
30020 - remote agent pushing (pre-RAS 18).
RAS RD Session Host Agent
RAS Guest Agent
RAS Remote PC Agent
RAS Connection Broker
RAS Secure Gateway
RAS Enrollment Server
TCP
135, 445
Remote Install Push/Takeover of Software (pre-RAS 18).
RAS Reporting Service
TCP
3000
Integration of RAS Reporting in Management Portal iFrame
RAS Web Administration Service
RAS RD Session Host Agent
TCP
30004
Log retrieval
RAS Guest Agent
TCP
30010
For internal commands - memshell, printer redirector)
RAS Performance Monitor
TCP
8086
Agent (Telegraf service) sends collected performance data to InfluxDB
RAS Enrollment Server
TCP, UDP
30030
RAS Remote PC (PrlsSCDriver) connects to get logon credentials
FSlogix
TCP
443
Download FSlogix installer
RAS Remote PC Agent
RAS Connection Broker
TCP, UDP
20003
Used for communications with RAS Connection Brokers
Localhost
TCP
30005
RDSH, RDS host
RDSH Agent
RD Session Host (formerly Terminal Server)
RAS RD Session Host Agent installed on an RD Session Host.
Remote PC
A remote Windows computer with RAS Remote PC Agent installed
VDI
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (a VDI host with a hypervisor running virtual machines). Each virtual machine must have RAS Guest Agent installed.
HALB
High Availability Load Balancing. An appliance that provides load balancing for RAS Secure Gateways.
Converted PC
A PC with Windows converted to a thin-client-like OS.
Enrollment Server
RAS Enrollment Server (an essential part of SAML SSO Authentication functionality).
The following table describes the icons used in deployment scenario diagrams.
Parallels RAS Server Components
A server hosting RAS Connection Broker. May also host other Parallels RAS components depending on a deployment.
RAS Secure Gateway (including User Portal) used for secure (SSL) client connections.
Private RAS Secure Gateway, used for direct client connections.
RD Session Host with RAS RD Session Host Agent installed.
A remote Windows computer with RAS Remote PC Agent installed. Not to be confused with Converted PC described below (a similar icon in red color).
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (a VDI host with a hypervisor running virtual machines). Each virtual machine must have RAS Guest Agent installed.
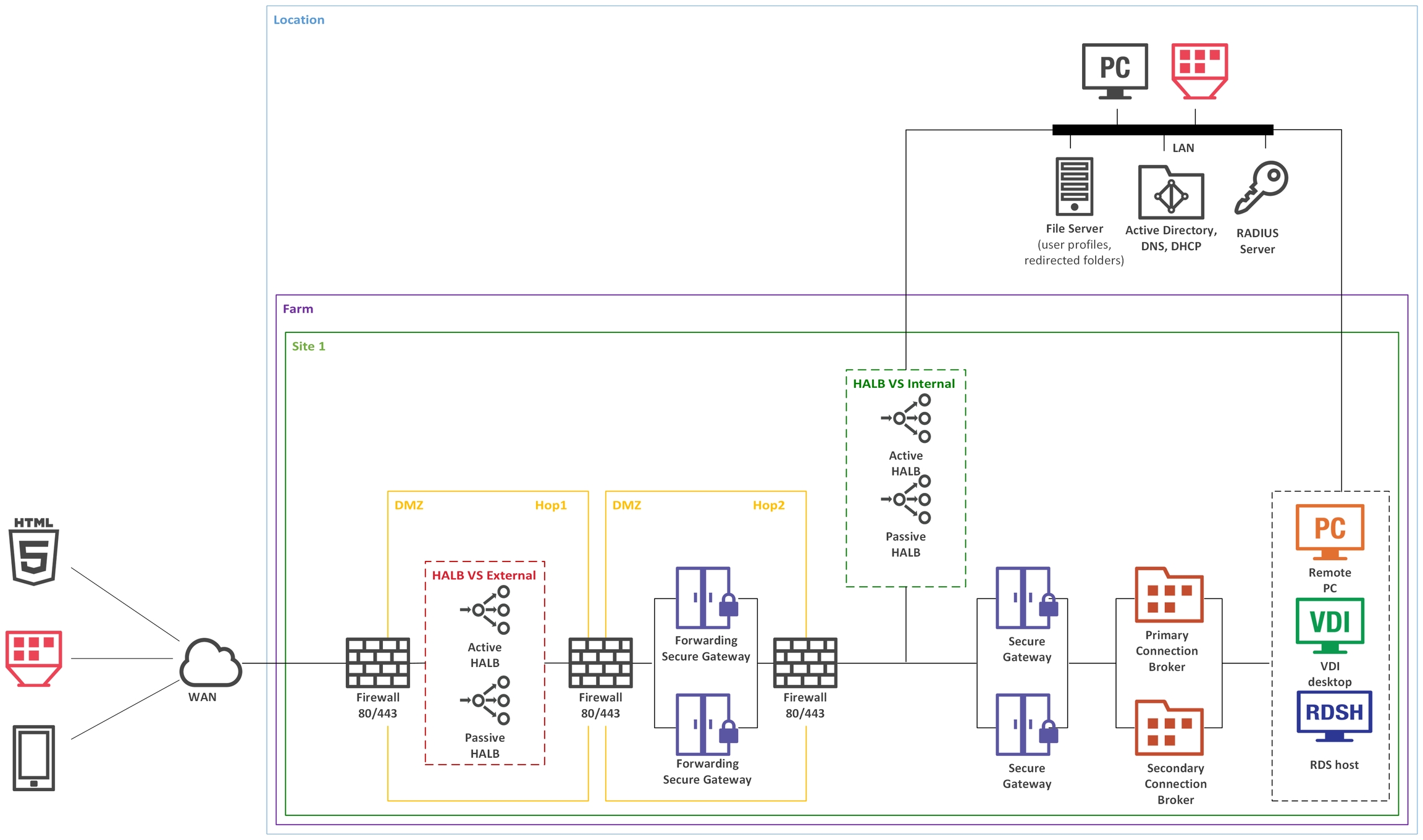
To understand the diagram layout, consider the following sample diagram:
The left side of the diagram displays client devices that can connect to Parallels RAS. In the example above, the clients are (from top to bottom):
HTML5 enabled web browser
A converted Windows PC running in Kiosk mode
A mobile device (iOS, Android)
The Location rectangle denotes a physical location, such as an office.
Firewall, represented by a brick wall, is responsible for network protection. Please note that if the scenario description doesn't include any specifics about DMZ or firewall(s), it is up to the administrator or network security officer to decide how network protection should be implemented.
The Farm rectangle represents a Parallels RAS farm, which is comprised of one or more sites.
The Site 1 rectangle represents a site with individual servers and components. In the example above, the site has a single server with RAS Connection Broker (CB), RAS Secure Gateway (SG), and RAS RD Session Host Agent installed.
The LAN bar represents a local area network with the following computers and servers connected to it:
Desktop computer
Converted Windows PC running in Kiosk mode.
File server
Active Directory, DNS, and DHCP server(s)
RADIUS server
The lines between icons denote the communication channels between individual components.
The Installation Notes section describes how a component (or components) must be installed on a corresponding server. The following installation methods are used to install Parallels RAS server components:
Parallels RAS Installer (standard installation). This is a standard MSI installer package that you run in Windows to install an application.
Windows Installer (custom installation). This is the same type of installer as described above, but you must choose the Custom installation type, which allows you to select which component(s) you want to install.
Push Installation. A component is installed remotely from the RAS console by pushing the MSI installer packages to a remote server and then performing an unattended installation on it.
Virtual appliance. A preconfigured virtual appliance for VMware or XenServer. You can download a virtual appliance for the hypervisor you are using from the Parallels website by visiting the following URL: http://www.parallels.com/products/ras/download/server/links/
CB
RAS Connection Broker
SG
RAS Secure Gateway (including User Portal)
Private SG
Private RAS Secure Gateway (used for direct client connections)
Azure Virtual Desktop hosts (multi-session or single-session) contain both Azure Virtual Desktop Agent and RAS Agent for management and configuration purposes.
Parallels Client for Windows is connecting to both Parallels RAS Secure Gateway and Azure Virtual Desktop service providing resource availability to end-users from a single interface.
As highlighted earlier, the complete Parallels RAS environment can also reside on Microsoft Azure for a full cloud deployment with Azure Virtual Desktop.
Simplify and enhance Azure Virtual Desktop deployment and management.
Unify administration and UX – single pane of glass – Parallels Clients and Parallels RAS Console.
Extend reach with flexibility to use hybrid and multi-cloud deployments.
Automate and streamline administrative routines, provisioning, and management of Azure Virtual Desktop workloads.
Built in Auto-scale capability on Microsoft Azure and/or on-premises.
Management of users, sessions, and processes.
Utilize RAS Universal Printing and Scanning.
Utilize AI based session prelaunch for ultra-fast logons.
Accelerated file redirection with the use of the Enable drive cache redirection option.
Integrated automatic image optimizations and FSLogix Profile Containers.
Client management.
Security policies for clients.
Leverage RAS Reporting and Monitoring from the RAS Console.
Increased data security provides organizations with an extra layer of protection with dynamic security permissions. This is a security feature which prevents access to VDI without using Parallels RAS Client. After the session is established, Parallels RAS dynamically adds the user to the "Remote Desktop Users" group, granting permissions on logon and removing permissions on logoff. Even if a VDI virtual machine (VM) hostname or IP address is noted, users will not be able to connect to the VDI VM unless connection is setup from the Parallels Client.
RAS Connection Broker is installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
RAS Secure Gateway, RAS Guest Agent are push-installed from the RAS console.
RAS Connection Broker is installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation).
HALB is installed as a ready-to-use virtual appliance and configured in HALB VS properties.
All other components are push-installed from the RAS console.
If the Forwarding RAS Secure Gateway cannot be push-installed for any reason, you can run the Parallels RAS installer on the target server. When doing so, select Custom installation type and then choose the RAS Secure Gateway component.
Please plan your deployment using the following information:
Azure regions — An Azure region is a set of data centers deployed within a latency-defined perimeter and connected through a dedicated regional low-latency network. Azure gives customers the flexibility to deploy applications where they need to: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/global-infrastructure/regions/.
Availability Zones — Availability Zones are physically separate locations within an Azure region. Each Availability Zone is made up of one or more data centers equipped with independent power, cooling and networking. Availability Zones allow customers to run mission-critical applications with high availability and low-latency replication. To ensure resiliency, there’s a minimum of three separate zones in all enabled regions: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/availability-zones/az-overview .
Availability Sets — An Availability Set is a logical grouping capability for isolating VM resources from each other when they're deployed. Azure makes sure that the VMs you place within an Availability Set run across multiple physical servers, compute racks, storage units, and network switches. If a hardware or software failure happens, only a subset of your VMs are impacted and your overall solution stays operational. Availability Sets are essential for building reliable cloud solutions: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/windows/tutorial-availability-sets .
Please note that Microsoft Azure design is out of scope of this guide.
Parallels RAS provides the two most common scenarios for delivering applications and desktops on Azure. These scenarios are described below.
Parallels RAS infrastructure servers, including RAS Connection Brokers, RAS Secure Gateways, RAS Enrollment Servers etc. are located on Azure. Each component of a RAS deployment should be in its own Availability Set to maximize overall availability. For example, a separate Availability Set should be used for Connection Brokers, Secure Gateways, Enrollment Servers etc.
You can also use Azure as a SAML IdP provider and as cloud computing platform for VDI/RDS resource hosts to deliver applications and desktops.
Parallels RAS infrastructure servers, including RAS Connection Brokers, RAS Secure Gateways, RAS Enrollment Servers etc. are located on premises, whereas VDI/RDSH resource hosts are deployed on Azure in Availability Sets. This can be practical when you need to support burst growth of the usage or business continuity.
RAS PowerShell
RAS RD Session Host Agent
TCP
30004
Log retrieval
RAS Guest Agent
TCP
30010
Log retrieval
RAS Remote PC Agent
TCP
30004
Log retrieval
RAS Provider Agent
TCP
30006
Log retrieval
RAS Connection Broker
TCP
20002, 20001
Communication with GA and Redundancy
Used during publishing to browse for installed applications or single file/folder browsing.



High Availability Load Balancing. An appliance that provides load balancing for RAS Secure Gateways.
Parallels RAS Client Devices
A desktop computer (Windows, Linux, Mac) with Parallels Client installed.
A PC with Windows converted to a thin-client-like OS. Not to be confused with a remote PC described above (a similar icon in orange color).
A converted PC (same as above) with Kiosk mode enabled.
HTML5 enabled web browser.
Mobile device (iOS, Android).
Other Components
Active Directory, DNS, and DHCP server(s).
Microsoft SQL Server database.
RAS Reporting and SQL Server Reporting Services (installed on the same server).
RADIUS server (used for second-level authentication).
File server for storing user profiles and redirected folders.
Firewall (ports 80 and 443 are open).
On-premises VPN gateway.
RAS Enrollment Server.
Azure Load Balancer and/or Azure VPN Gateway.
Parallels Client
HALB
TCP, UDP
TCP, UDP
80, 443
20009
Management and user session connections.
Device Manager shadowing via Firewall (indirect network connection).
RAS Secure Gateway Forwarding mode
TCP, UDP
TCP, UDP
UDP
RAS Connection Broker
AD DS controllers
TCP
TCP
TCP,UDP
UDP
389, 3268
636, 3269
88
53
LDAP
LDAPS
Kerberos
DNS
RAS Connection Broker
TCP
20001
20030
Redundancy service.
Communication between RAS Connection Brokers ruAgent (Telegraf service) sends collected performance data to InfluxDB.nning in the same site.
Parallels Licensing Server
TCP
443
RAS Provider Agent
RAS Connection Broker
TCP
20003
Connection Broker communication port.
RAS Guest Agent
TCP
UDP
Parallels conducted in-house Parallels RAS scalability testing using a total of two HP DL360 consisting of the following hardware components:
The following Parallels RAS lab environment was used:
For Parallels RAS installations running in a multi-server environment, it is recommended to install RAS Reporting and SSRS on a dedicated server. SQL Server database engine should also be installed on a dedicated server but can be installed together with SSRS and RAS Reporting.
Primary RAS Connection Broker is installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation). Secondary RAS Connection Broker is push-installed from the RAS Console.
HALB is installed as a ready-to-use virtual appliance and configured in HALB VS properties.
RAS Reporting is installed using Windows installer.
80, 443
3389
20000
Management and user session connections.
Optional - Used for user session if RDP load balancing is enabled (Standard RDP).
Secure Gateway lookup broadcast.
RAS Secure Gateway Normal mode
TCP, UDP
TCP, UDP
TCP, UDP
UDP
80, 443,
3389
20009
20000
Management and user session connections.
Optional - Used for user session if RDP load balancing is enabled (Standard RDP).
Device Manager shadowing via Firewall (indirect network connection)
Secure Gateway Lookup Broadcast
Session host (VDI, RDS, RemotePC)
TCP, UDP
3389
Used for user session connections in Direct Mode only. RDP connection is always encrypted
Azure Virtual Desktop Services
TCP
UDP
443
3390
Azure Virtual Desktop Gateway connection
Used for user session connections in ShortPath mode only.
Microsoft site
TCP
443
Download Microsoft Remote Desktop (MSRDC) client
Parallels site
TCP
80, 443
Check for updates and download Parallels Client
RAS Connection Broker (primary Connection Broker in Licensing Site) communicates with Parallels Licensing Server (https://ras.parallels.com).
Note: Not required for Tenant Broker RAS Connection Broker (see the Tenant Broker section).
RAS Performance Monitor
TCP
8086
Agent (Telegraf service) sends collected performance data to InfluxDB.
RAS RD Session Host Agent
TCP, UDP
30004
Server for Connection Broker requests.
RAS Provider Agent
TCP, UDP
30006
Provider Agent communication port.
RAS Remote PC Agent
TCP, UDP
30004
Remote PC Agent Communication Port (agent state, counters and session information)
2FA Server(s)
TCP, UDP
8080, 80
1812, 1813
Deepnet/ Safenet
Radius
RAS Enrollment Server
TCP
30030
RAS Connection Broker Sends RAS Enrollment Server connection Request
RAS Reporting
TCP
30008
Master RAS Connection Broker communicates with RAS Reporting (installed on the same host as SSRS).
RAS Remote Installer Service
TCP
30020
Remote agent pushing
RAS RD Session Host Agent
RAS Guest Agent
RAS Remote PC Agent
RAS Connection Broker
RAS Secure Gateway
RAS Enrollment Server
TCP
135, 445, 49179
Remote Install Push/Takeover of Software
SMTP
TCP
587
Notifdispatcher is the service which sends the emails using port specified in the Mailbox settings (+SSL/TLS)
Let's Encrypt Service
TCP
80, 443
Communication between the Let's Encrypt client (available in the primary Connection Broker) and a Let's Encrypt server.
30010
30009
TCP is used to send the commands.
UDP is used during the initial handshake.
RAS Performance Monitor
TCP
8086
Agent (Telegraf service) sends collected performance data to InfluxDB - applicable to Hyper-V only.
Hyper-V
TCP
135, 49152-65535
Used to check if the host is powered on and send export, import, delete, shutdown, restart or suspend commands.
Nutanix AHV (AOS)
TCP
9440
Used to check if the host is powered on and sends clone, delete, shutdown, restart commands (RestAPI calls, PoSH, remote ncli).
VMWare
TCP
443
Used to check if the host is powered on and sends clone, delete, shutdown, restart and suspend commands.
Microsoft Azure
TCP
443
Used to check if the guest is powered on and sends clone, shutdown, restart commands (via REST).
Azure Virtual Desktop
TCP
443
Used to check if the host is powered on and sends clone, shutdown, restart commands (via REST).
AWS
TCP
443
Used to check if the host is powered on and sends clone, shutdown, restart commands (via REST).
Scale
TCP
443
Used to check if the host is powered on and sends clone, shutdown, restart commands (via REST).
Remote PC over VDI
TCP
135, 49152-65535
Used to check if the host is powered on and sends shutdown, restart or suspend commands.

Parallels RAS is a market leader for Windows application publishing on any device, anywhere. It works with major hypervisors and Microsoft Remote Desktop Services, providing PC, Mac, and mobile users with a seamless experience while increasing security and reducing IT costs. In addition, Parallels RAS supports Azure Virtual Desktop. It’s simple and empowers users with the freedom and flexibility to work how they want.
With Parallels RAS, remote desktops and applications can be accessed from any device running virtually any operating system, including Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS, Android, Chrome. Access via browser-based Web Client is also available.
For an in-depth information about the rich Parallels RAS features, please read the Parallels RAS Administrator's Guide, which can be downloaded from the Parallels website.
Reports retrieval.
HALB
TCP, UDP
31006
Used for configuration.
Parallels Client
TCP
50005
Shadowing from the RAS Console in case of direct network connection.
RAS RD Session Host Agent
UDP, TCP
30004
Used for the "Check Agent" task.
Used to manage components.
TCP
UDP
TCP
UDP
30010
30009
Used for the "Check Agent" task.
Used to manage components.
RAS Remote PC Agent
UDP, TCP
30004
Used for the "Check Agent" task.
Used to manage components.
RAS Provider Agent
UDP, TCP
30006
Used for the "Check Agent" task.
Used to manage component.
MFA Server(s)
TCP, UDP
8080, 80, 1812, 1813
Deepnet / Safenet / Radius
Microsoft site
TCP
80, 443
Check for updates and download Parallels Client
Parallels site
TCP
80
Check for updates and download Parallels Client
RAS Performance Monitor
TCP
3000
RAS browser plugin connection to Grafana.
RAS Connection Broker
TCP
20002, 20001
Communication with Connection Broker and redundancy.
RAS Enrollment Server
TCP, UDP
30030
Used for the "Check Agent" task.
Used to manage components and for troubleshooting.
Wyse Broker
UDP
1234 (outbound only)
68 (inbound only)
Wyse broker discovery request broadcast packet (V_WYSEBCAST).
Wyse broker discovery reply packet (V_WYSETEST).
SMTP
TCP
587
RAS Console can send test emails using port specified in the Mailbox settings (+SSL/TLS)
RAS Console
RAS Reporting
TCP
30008
RAS Console is connected to primary RAS Connection Broker which communicates with RAS Reporting (installed on the same host as SSRS). SSRS talks to SQL via TCP 1433 (or dynamic if 1433 is not established in the settings).
SSRS
TCP
443

A farm consists of 1 site.
Single hop DMZ.
Each Secure Gateway can host 1200 sessions in Gateway SSL mode (enumeration and proxying RDP session in SSL + User Portal).
Each Secure Gateway has User Portal enabled and balanced by HALB using the same port 443 (When using URL https://HALB-VIP/userportal/ the incoming connections will be distributed appropriately because SSL session persistence is in a place).
Parallels RAS was deployed on VMware vSphere 6.5 on Windows 2016 Server as follows:
RAS Connection Broker
2
2
4 GB
RAS Secure Gateway
2
2
4 GB
High Availability Load Balancing
2
All components doubled for redundancy.
RDSH N+1 for redundancy.
The above configuration has been tested with both our internal tools and Login VSI. For more details, you could read the Parallels RAS Scalability Testing with Login VSI paper, which is available at the following URL: https://download.parallels.com/ras/v18/docs/en_US/Parallels-RAS-Scalability-Testing-Login-VSI.pdf
Parallels RAS was deployed on VMware vSphere 6.5 on Windows 2016 Server as follows:
RAS Connection Broker
2
2
4 GB
RAS Secure Gateway
2
2
4 GB
High Availability Load Balancing
2
All components doubled for redundancy.
RDSH N+2 for redundancy.
1000 users
RAS Connection Broker
2
2
4 GB
RAS Secure Gateway
2
2
4 GB
High Availability Load Balancing
2
All components doubled for redundancy.
RDSH N+4 for redundancy.
CPU
2x Xeon E5-2670 v1, 2.6GHz, 20 MB L3, 115W TDP
RAM
128 GB, 16x 8 GB Micron DDR-4-2100 at 1600MHz
HDD
Western Digital Blue 1 TB SSD





1
2 GB
RD Session Host
6
6
24 GB
1
2 GB
RD Session Host
12
6
24 GB
1
2 GB
RD Session Host
24
6
24 GB
When a user connects to Parallels RAS from Parallels Client, they are presented with published resources (applications, desktops, documents, etc). The user selects a resource and launches it. The system load-balances user requests automatically and launches the resource from a least-loaded host. The user is then presented with the resource seamlessly via RDP protocol
The Parallels RAS building blocks are (see the previous section for a detailed explanation):
Farm
Site
Agents
The first server added to a farm creates a new site and becomes the primary RAS Connection Broker in that site. The server also becomes the farm’s Licensing Server handling device connection licenses. Every Connection Broker in the farm (when more than one exists) keeps a synchronized copy of the Parallels RAS configuration database. When the administrator makes any changes to the Parallels RAS configuration in the Parallels RAS console, the changes are replicated to all other Connection Brokers.
The following diagram illustrates a Parallels RAS installation with two sites (Site 1 and Site 2), each consisting of a primary Connection Broker (Primary CB), RAS Secure Gateway (SG), RD Session Host (RDS host 1), a second RD Session Host (RDS host 2), VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) server, and a Windows PC.
Adding more RAS Connection Brokers and RAS Secure Gateways adds redundancy to the system. HALB Virtual Server (VS) is a virtual representation of the HALB appliances (optional component), which can be added to load balance application traffic.

All data is kept on a server side with centralized security and backup management. Only mouse clicks, keyboard keystrokes, and desktop/application screenshots are transmitted to and from the client device, thus preventing data leakages, viruses, Trojans, and other vulnerabilities on clients.
Support for virtually all platforms on client devices, including Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS, Android, Chrome, and HTML5, all with minimum hardware requirements.
Parallels RAS Multi-Tenant architecture with Parallels RAS Tenant Broker allow for sharing of the access layer such as Parallels Secure Gateways and front-end High Availability Load Balancers (HALBs) among Tenants, which may be represented as isolated Parallels RAS Farms and/or sites. Tenant Broker is a separate RAS installation that hosts shared RAS Secure Gateways and HALB. Tenant farms are deployed just like traditional RAS environments and are joined to the Tenant Broker. Each Tenant farm has its own RAS Connection Brokers and servers hosting published resources (RD Session hosts, VDI, Azure Virtual Desktop, Remote PCs). No local RAS Secure Gateways or Load Balancers are needed.
Parallels RAS offers flexible cloud deployment model support, whether using on-premises, cloud or multi-cloud environments, allowing businesses to leverage different technologies while reducing total cost of ownership.
Employees, customers, and partners telecommute/roam more easily with follow-me apps and desktops on any device from anywhere.
Achieve cost savings in hardware replacement by converting Windows PCs into pseudo thin clients. Continue using Windows legacy operating systems to securely run virtual applications while also restricting access to native OS features. What’s more, the administrator can choose which applications a user runs locally and remotely on a PC.
Parallels RAS Reporting helps IT administrators to proactively tackle any potential issue before it occurs, providing reports and statistics on resources and services shown under one roof in the Parallels RAS console.
Windows Client Management enables client device shadowing (user session control) and power management for help desks, making routine end user assistance easier.



RAS Secure Gateway in Forwarding mode
RAS Secure Gateway in Normal mode
TCP, UDP
TCP, UDP
80, 443
3389
Management and user session connections.
Optional - Used for user session if RDP Load Balancing is enabled.
RAS Performance Monitor
TCP
Second-level authentication provides a high level of protection via different types of security tokens for two-factor authentication. Users have to authenticate through two successive stages to get the remote application list. In addition to a standard user name and password, or a smart card authentication, second-level authentication uses a one-time password generated by a token. The second level of authentication can be provided by DualShield, Safenet, RADIUS, or Google authenticator.
A RADIUS server is recommended to be placed in the Intranet together with the RAS Connection Broker and Active Directory domain controller to speed up application enumeration.
It is recommended to specify Access Control Lists to only allow the IP addresses and protocols/ports necessary for the Wireless Access Points and other devices to communicate with the RADIUS server. No other devices should have a pathway to the RADIUS server.
In a configuration of this type, the second-level authentication via a RADIUS server is performed first. If the authentication procedure is successful, the next authentication takes place at the Active Directory level using either the username and password or a smart card.
8086
Agent (Telegraf service) sends collected performance data to InfluxDB.
RAS Secure Gateway in Normal mode
Remote Desktop Services
TCP, UDP
3389
RDP Connections.
RAS Connection Broker
TCP
TCP, UDP
20002
20009
RAS Connection Broker service port - communications with RAS Secure Gateways and the RAS Console (in Normal mode only).
Device Manager shadowing via Firewall (indirect network connection) if RAS Console runs on RAS Connection Broker
RAS Performance Monitor
TCP
8086
Agent (Telegraf service) sends collected performance data to InfluxDB.
Localhost
TCP
20020
Communication with User Portal web server (NodeJS).
Primary RAS Connection Broker is installed using the Parallels RAS installer (standard installation). Secondary RAS Connection Broker is push-installed from the RAS Console.
HALB is installed as a ready-to-use virtual appliance and configured in HALB VS properties.
All other components are push-installed from the RAS console.
After you add a certificate to a Site, you can assign it to a RAS Secure Gateway, HALB, or both depending on the usage type that you specified when you created the certificate (described in the beginning of this chapter). More on the certificate Usage option below.
Certificate Usage is an option that you specify when you create a certificate. It specifies whether the certificate should be available for RAS Secure Gateways, HALB, or both. When setting this option, you can choose from the following:
Gateway: If selected, makes the certificate available for RAS Secure Gateways.
HALB: If selected, makes the certificate available for HALB.
You can select one of the options above or both, in which case the certificate becomes available for both, Secure Gateways and HALB.
When you configure SSL for a RAS Secure Gateway or HALB later, you need to specify an SSL certificate. When you select a certificate, the following options will be available depending on how the Usage option is configured for a particular certificate:
<All matching usage>: This is the default option, which is always available. It means that any certificate on which the Usage selection matches the object type (Secure Gateway or HALB) will be used. For example, if you are configuring a Secure Gateway and have a certificate that has Usage set to "Gateway", it will be used. If a certificate has both, Gateway and HALB usage options selected, it can also be used with the given Secure Gateway. This works the same way for HALB when you configure the LB SSL Payload. Please note that if you select this option for a Secure Gateway or HALB, but not a single matching certificate exists, you will see a warning and will have to create a certificate first.
Other items in the Certificates drop-down list are individual certificates, which will or will not be present depending on the certificate's Usage settings. For example, if you configure LB SSL Payload for HALB and have a certificate with the Usage option set to "HALB", the certificate will appear in the drop-down list. On the other hand, certificates with Usage set to "Gateway" will not be listed.
As another example, if you need just one certificate, which you would like to use for all of your Secure Gateways, you need to create a certificate and set the Usage option to "Gateways". You can then configure each Secure Gateway to use this specific certificate or you can keep the default <All matching usage> selection, in which case the certificate will be picked up by a Secure Gateway automatically. Same exact scenario also works for HALB.
To assign a certificate to a RAS Secure Gateway:
Navigate to Farm > Site > Gateways.
Right-click a Secure Gateway and choose Properties.
Select the SSL/TLS tab.
In the Certificates drop-down list, select the certificate that you created.
Please note that you can also select the <All matching usage> option, which will use any certificate that either has the usage set to Secure Gateway or both Secure Gateway and HALB.
Click OK.
In case the certificate is self-signed, or the certificate is issued by an Enterprise CA, Parallels Clients should be configured as follows:
Export the certificate in Base-64 encoded X.509 (.CER) format.
Open the exported certificate with a text editor and copy the contents to the clipboard.
To add the certificate with the list of trusted authorities on the client side and enable Parallels Client to connect over SSL with a certificate issued from an organization’s Certificate Authority.
On the client side in the directory "C:\Program Files\Parallels\Remote Application Server Client\" there should be a file called trusted.pem. This file contains certificates of common trusted authorities.
Paste the content of the exported certificate (attached to the list of the other certificates).






To obtain a certificate from a third-party CA, you need to generate a certificate signing request (CSR) as described below.
In the RAS Console, navigate to Farm / Site / Certificates. Click Tasks > Generate a certificate request. In the dialog that opens, specify the following options:
Name: Type a name for this certificate. This field is mandatory.
Description: An optional description.
Usage: Specify whether the certificate should be used for RAS Secure Gateways or HALB, or both. This selection is mandatory.
Key size: The certificate key size, in bits. Here you can select from the predefine values. The default is 2048 bit, which is the minimum required length according to current industry standards.
Country code: Select your country.
Expire in: The certificate expiration date.
Full state or province: Your state or province info.
City: City name.
Organization: The name of your organization.
Organization unit: Organizational unit.
E-mail: Your email address. This field is mandatory.
Common name: The Common Name (CN), also known as the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). This field is mandatory.
After entering the information, click Generate. Another dialog will open displaying the request. Copy and paste the request into a text editor and save the file for your records. The dialog also allows you to import a public key at this time. You can submit the request to a certificate authority now, obtain the public key, and import it without closing the dialog, or you can do it later. If you close the dialog, the certificate will appear in the RAS Console with the Status column indicating Requested.
To submit the request to a certificate authority and import a public key:
If the certificate request Properties dialog is closed, open it by right-clicking a certificate and choosing Properties. In the dialog, select the Request tab.
Copy the request and paste it into the certificate authority web page (or email it, in which case you will need to come back to this dialog later).
Obtain the certificate file from the certificate authority.
Click the Import public key
You know need to import the certificate into Parallels RAS. To do so, on the Certificates tab, click Tasks > Import certificate. In the dialog that opens, specify the following:
Name: Type a name for the certificate.
Description: An optional description.
Private key file: Specify a file containing the private key. Click the [...] button to browse for the file.
Certificate file: When you specify a private key file (above) and have a matching certificate file, it will be inserted in this field automatically. Otherwise, specify a certificate file.
Click OK when done. The certificate will appear in the list in the RAS Console with the Status column indicating Imported.
To view the certificate info, right-click it and choose Properties. In the dialog that opens, examine the properties and then click the View certificate info button to view the certificate trust information, details, certification path and the certificate status. You can also view the certificate info by right-clicking it and choosing View certificate info.
For imported certificates, the Properties dialog has an additional tab Intermediate. If the original certificate included an intermediate certificate (in addition to the root certificate), it will be displayed here. You can paste a different intermediate certificate here if you wish.
Usage: Specify whether the certificate will be used for RAS Secure Gateways or HALB, or both.