Parallels Desktop allows you to use three types of networking with Windows:
Shared Networking: Windows applications share a network connection with macOS. This is the default setting.
Bridged Ethernet: Windows can use one of your Mac's network adapters. This makes Windows appear as a separate computer on the network.
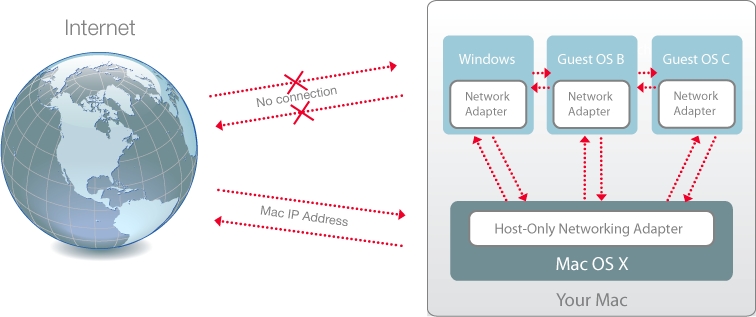
Host-only networking: Windows can access only your Mac.
In most cases, you don't need to adjust network settings. If your Mac is set to connect to a network or to the Internet, Windows applications have access to the same network and the Internet.
The Bridged Ethernet networking mode is more complex and you may need to contact your system administrator to set it up properly.
Read on for detailed information on these types of networking and how to configure them.
If your Mac is a VLAN (virtual local area network) member, Parallels Desktop allows you to bridge Windows to this VLAN.
To bridge Windows to the VLAN, do one of the following:
Click the Parallels Desktop icon in the menu bar and choose Configure.
If the Parallels Desktop menu bar is visible at the top of the screen, choose Actions > Configure.
After that:
Click Hardware and then click Network.
Select Bridged Network > VLAN from the Source list.
Windows is bridged to the selected VLAN.
When operating in the Bridged Ethernet mode, Windows appears on the network as a stand-alone computer with its own IP address and network name.
Note: The Bridged Ethernet networking mode is more complex than the Shared Networking mode, and you may need to contact your system administrator to configure it properly.
To configure Windows to work in the Bridged Ethernet mode:
Do one of the following:
Click the Parallels Desktop icon in the menu bar and choose Configure.
If the Parallels Desktop menu bar is visible at the top of the screen, choose Actions > Configure.
Click Hardware and then click Network.
In the Network pane, select the appropriate network adapter from the list. To connect the virtual machine's adapter to the active network adapter of your Mac, choose Default Adapter.
Note: In the MAC address field, you can change the MAC address currently assigned to Windows. MAC addresses are automatically generated when you first set up Windows. However, you can modify the default MAC address by typing another value in the MAC address field or clicking the Generate button. When entering a new MAC address, make sure that it is unique within your network.
If you can't configure Windows to function in the Bridged Ethernet mode, consider using Shared Networking.
For information on troubleshooting networking problems, refer to the Parallels knowledge base available on the Parallels website.
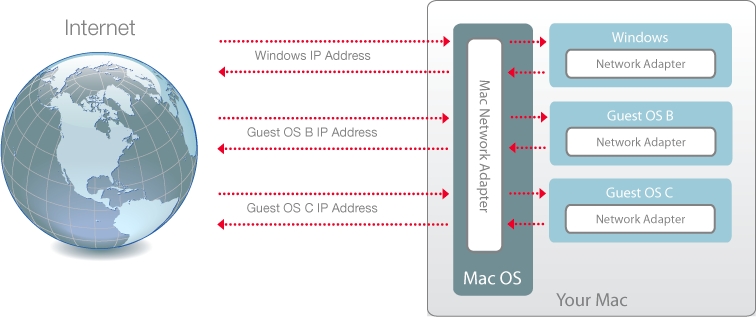
By default, Windows is set to access the network via macOS. Windows applications can access other computers on your local network and the Internet by using the IP address of your Mac. Windows does not have its own IP address on the network.
In most cases, you don't need to adjust network settings. If your Mac is set to connect to a network or to the Internet, Windows applications have access to the same networks and the Internet.
You may wish to use Shared Network mode in the following cases:
Your Mac accesses the Internet via a modem or another non-Ethernet device.
You need to access the Internet from inside Windows but are concerned about security.
You are having problems working in Bridged Ethernet mode.
To configure Windows to use Shared Networking:
Do one of the following:
Click the Parallels Desktop icon in the menu bar and choose Configure.
If the Parallels Desktop menu bar is visible at the top of the screen, choose Actions > Configure.
Click Hardware and then click Network.
In the Network pane, make sure that the Shared Network option is selected.
For the information about troubleshooting networking problems, refer to the Parallels knowledge base available at the Parallels website.
If your Mac is already connected to the Internet wirelessly, by default Windows is also set to access the Internet wirelessly, with no setup required.
You can also bridge your virtual machine to Wi-Fi. When operating in this mode, Windows appears on the network as a stand-alone computer with its own IP address and network name.
To bridge the virtual machine to Wi-Fi:
Do one of the following:
Click the Parallels Desktop icon in the menu bar and choose Configure.
If the Parallels Desktop menu bar is visible at the top of the screen, choose Actions > Configure.
Click Hardware and then click Network.
In the Network pane, choose Wi-Fi from the list.
After you perform these steps, Windows is able to connect to the Internet through the Wi-Fi adapter of your Mac.
If you can't configure your virtual machine to function in the Bridged Ethernet mode, consider using Shared Networking.
For information about troubleshooting networking problems, refer to the Parallels knowledge base available on the Parallels website.
Parallels Desktop provides a closed network that is accessible only to macOS and Windows. macOS is connected to this network via the Parallels Host-Only Networking adapter automatically created on your Mac during the Parallels Desktop installation. The addresses for Windows are provided by the Parallels DHCP server.
To configure Windows to use Host-Only Networking:
Do one of the following:
Click the Parallels Desktop icon in the menu bar and choose Configure.
If the Parallels Desktop menu bar is visible at the top of the screen, choose Actions > Configure.
Click Hardware and then click Network.
In the Network pane, make sure that the Host-Only option is selected.
For information about troubleshooting networking problems, refer to the Parallels knowledge base available on the Parallels website.